 |
Sample Accounts of a Company |
| << Sample Transactions of a Company |
| THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION >> |
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-11
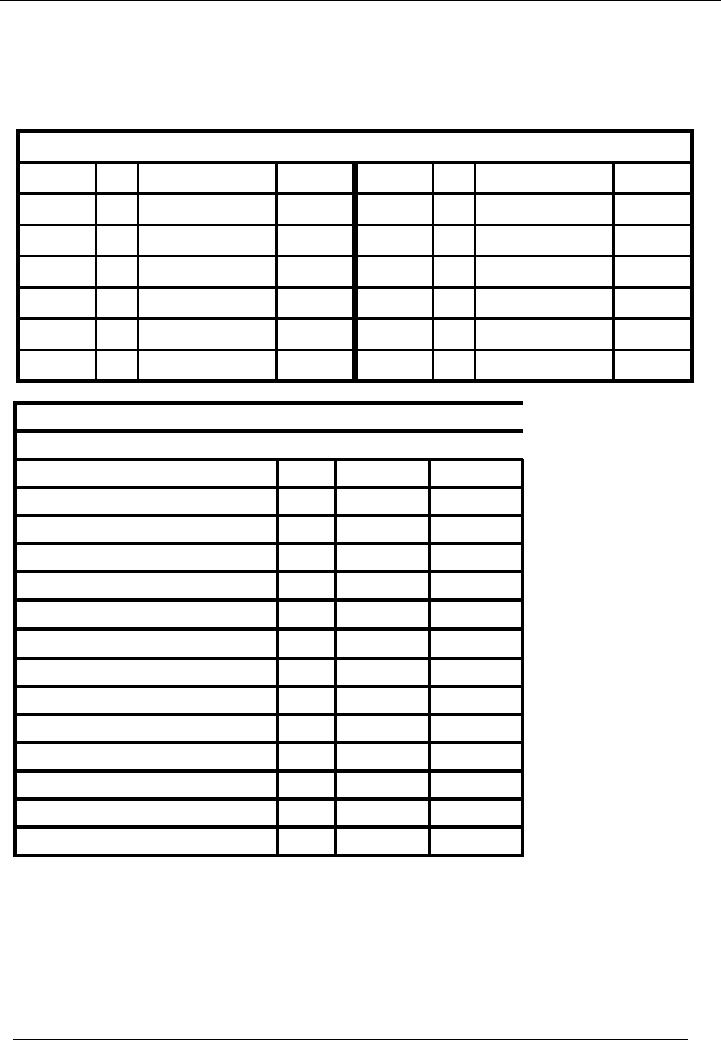
Cash
Account
Cash
Account Code 01
Date
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
195,000
200,000
01-01--- 02 Cash
deposited
01-01---
01 Capital
Introd.
60,000
08-01---
06-01---
06 Goods
sold
07 Goods
purch.
20,000
31-01---
15 Cash
deposited
10,000
260,000
225,000
Balance
35,000
260,000
260,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Total
50
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
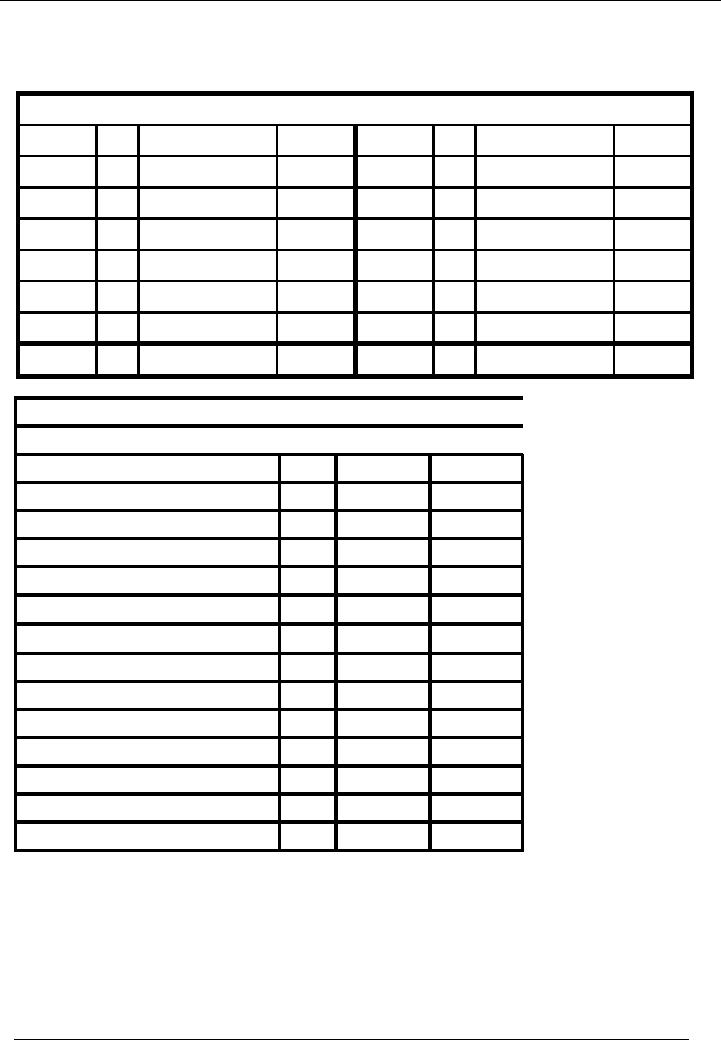
Bank
Account
Bank
Account Code 02
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
195,000
02-01---
03 Furniture
purch.
15,000
01-01---
02 Cash
deposited
20,000
03-01---
25-01---
12 Received
from B
50,000
04 Vehicle
purch.
10,000
21-01---
31-01---
15 Cash
deposited
11 Paid to
Mr. A
25,000
5,000
31-01---
13 Salaries
paid
225,000
95,000
Balance
130,000
225,000
225,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Bank
Account
02
130,000
Total
51
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
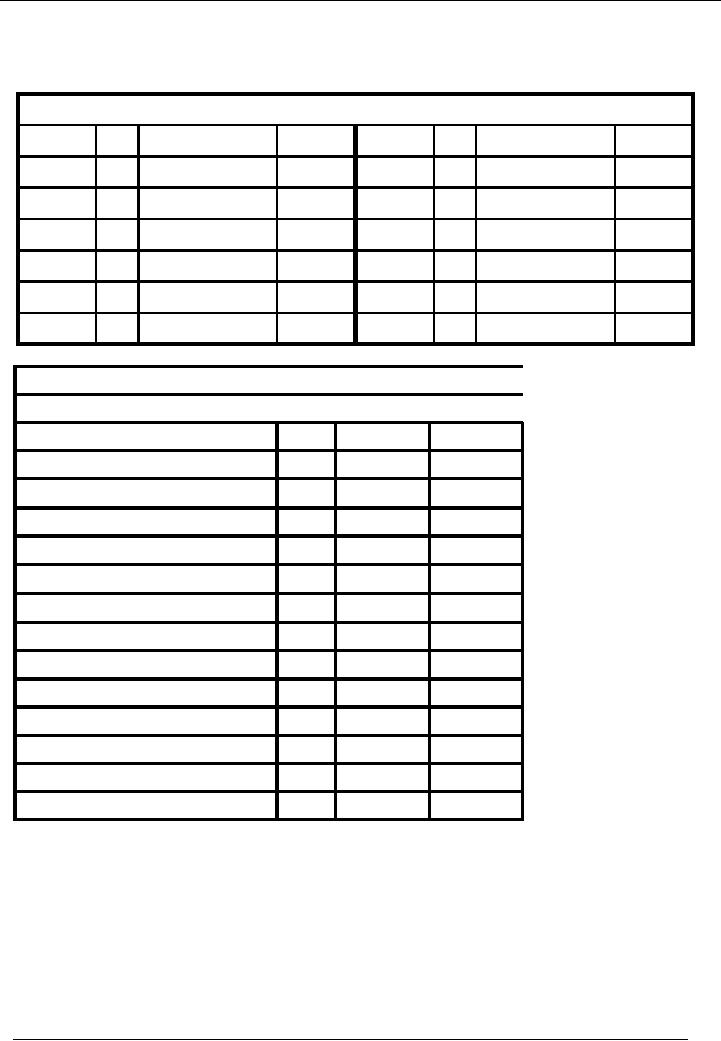
Capital
Account
Capital
Account Code 03
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
01-01---
01 Capital
Introd.
200,000
0
200,000
200,000
Balance
200,000
200,000
200,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Bank
Account
02
130,000
Capital
Account
03
200,000
Total
52
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
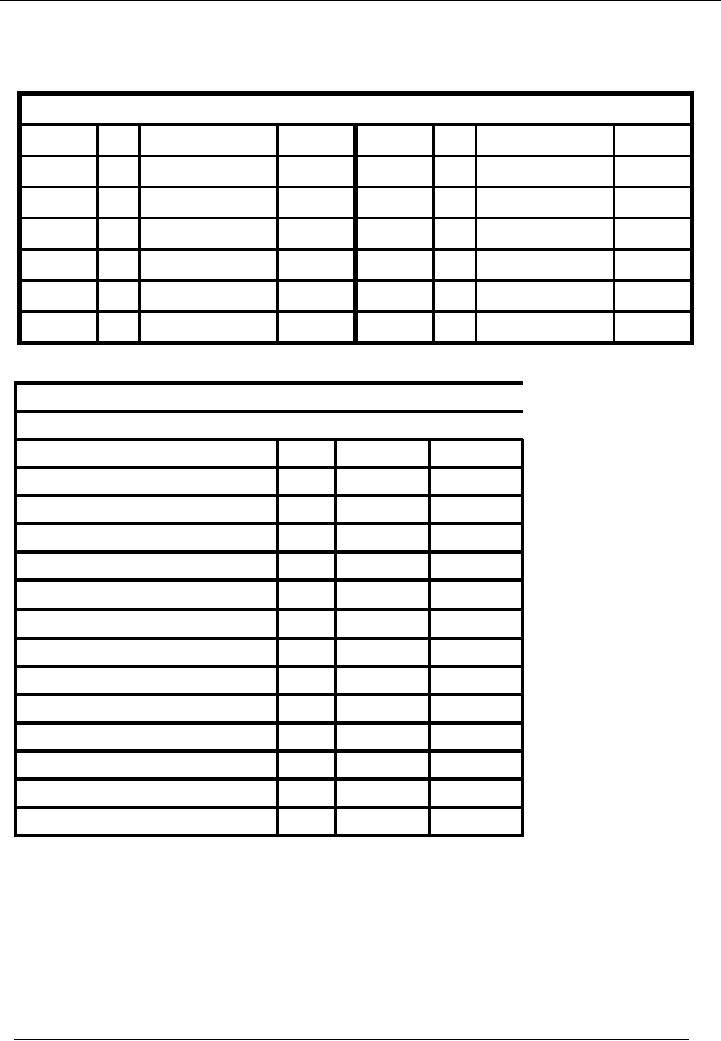
Furniture
Account
Furniture
Account
Code 04
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
02-01---
03 Furniture
purch.
15,000
15,000
0
Balance
15,000
15,000
15,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Bank
Account
02
130,000
Capital
Account
03
200,000
Furniture
Account
04
15,000
Total
53
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
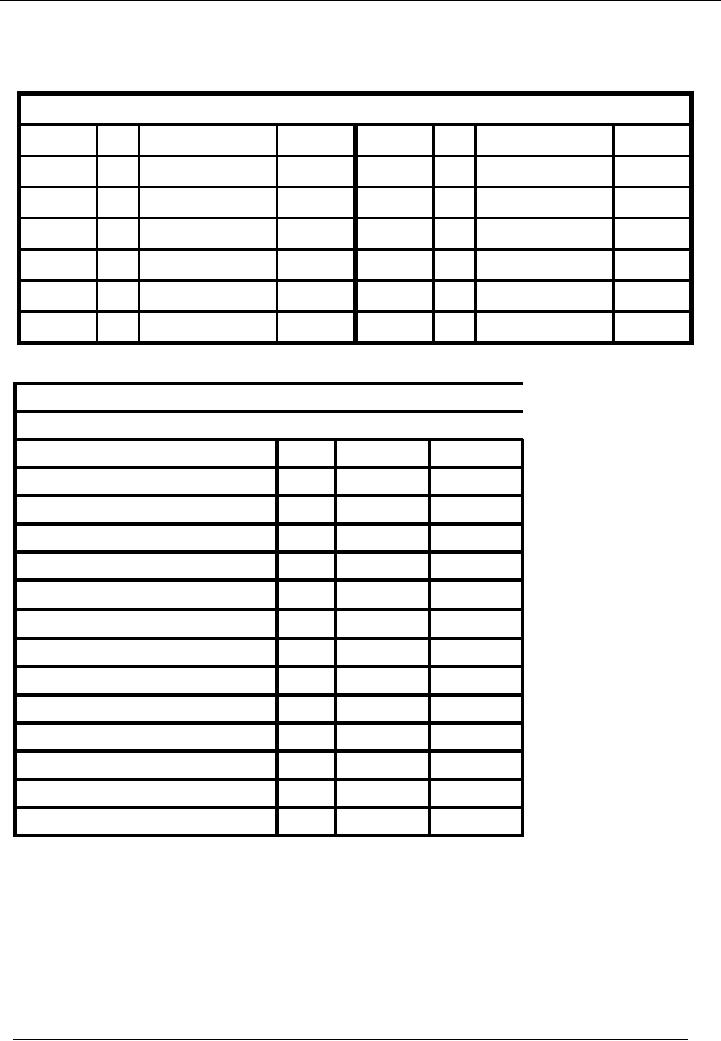
Vehicle
Account
Vehicle
Account
Code 05
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
03-01---
04 Furniture
purch.
50,000
0
50,000
Balance
50,000
50,000
50,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Bank
Account
02
130,000
Capital
Account
03
200,000
Furniture
Account
04
15,000
Vehicle
Account
05
50,000
Total
54
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
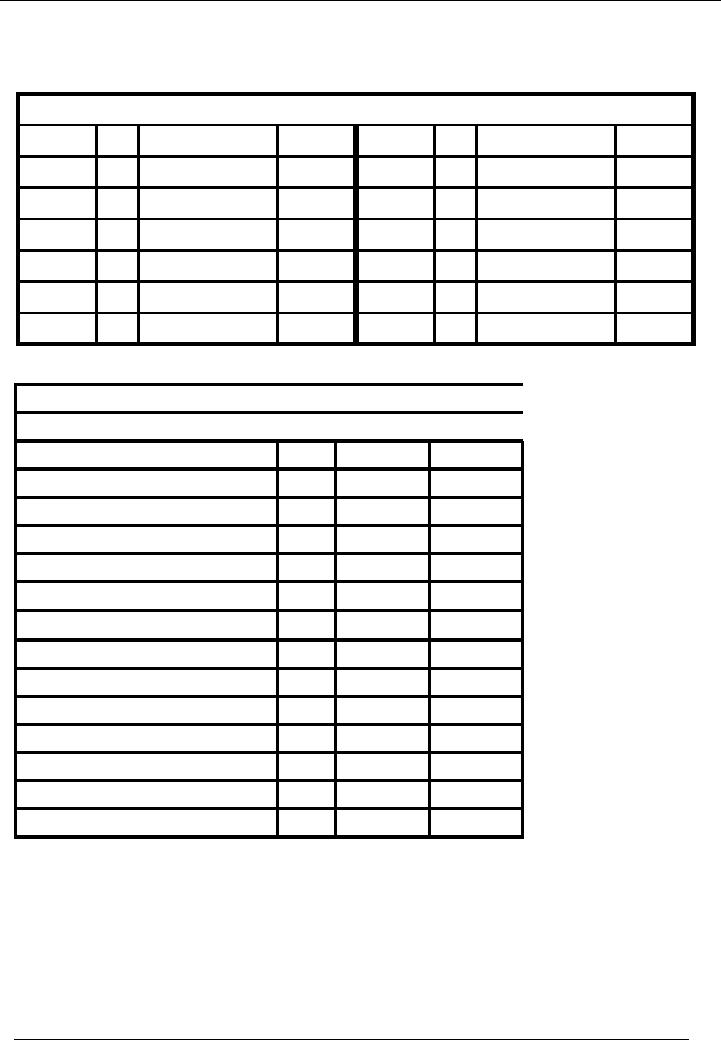
Purchases
Account
Purchases
Account
Code 06
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
05-01--- 05
Goods purch.
50,000
10-01---
10,000
08 Purchase
return
20,000
08-01---
07 Goods
purch.
70,000
10,000
Balance
60,000
70,000
70,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Bank
Account
02
130,000
Capital
Account
03
200,000
Furniture
Account
04
15,000
Vehicle
Account
05
50,000
Purchases
Account
06
60,000
Total
55
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
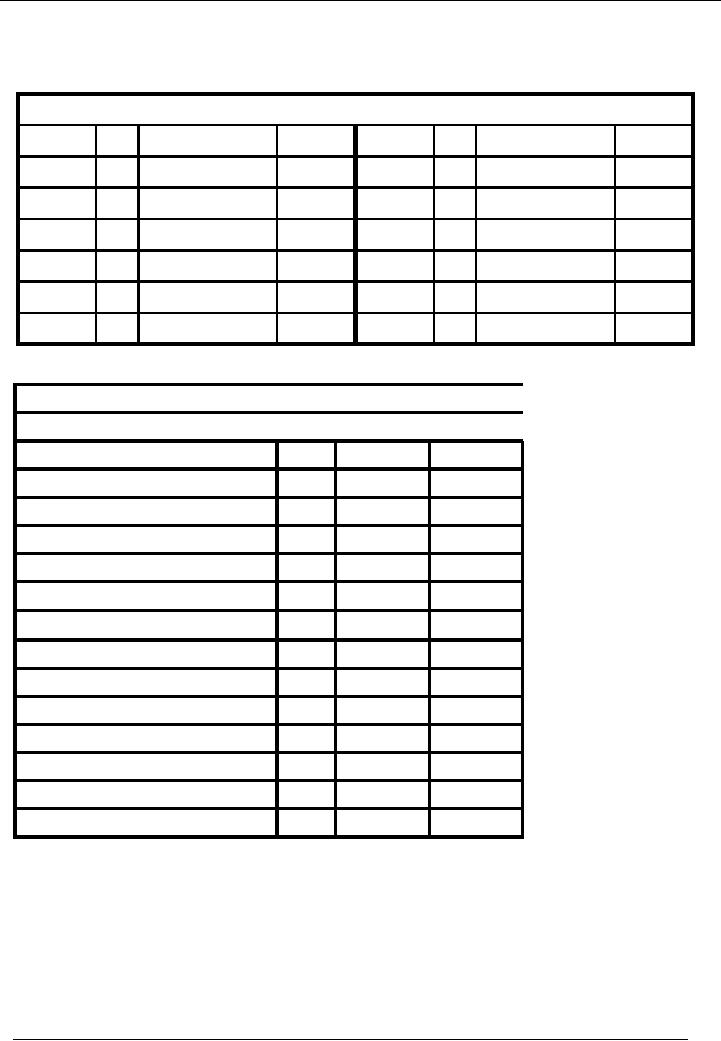
Mr. A
(Supplier)
Mr. A
(Creditor)
Account
Code 07
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
10,000
05-01---
05 Goods
purch.
50,000
10-01---
08 Purchase
return
25,000
21-01---
11 Paid to
Mr. A
35,000
50,000
Balance
15,000
50,000
50,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Bank
Account
02
130,000
Capital
Account
03
200,000
Furniture
Account
04
15,000
Vehicle
Account
05
50,000
Purchases
Account
06
60,000
Mr.
A (Creditor)
07
15,000
Total
56
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
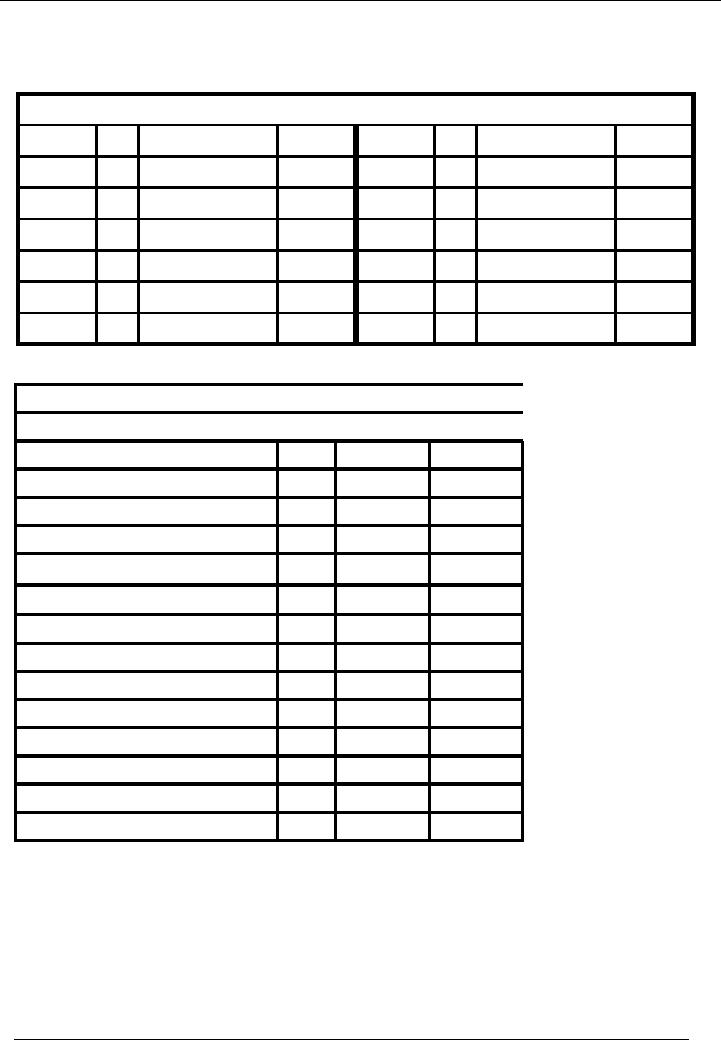
Sales
Sales
Account Code 08
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
18-01---
10 Sales
return
5,000
06-01---
06 Goods
sold
60,000
40,000
12-01---
09 Goods
sold
5,000
100,000
Balance
95,000
100,000
100,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Bank
Account
02
130,000
Capital
Account
03
200,000
Furniture
Account
04
15,000
Vehicle
Account
05
50,000
Purchases
Account
06
60,000
Mr.
A (Creditor)
07
15,000
Sales
08
95,000
Total
57
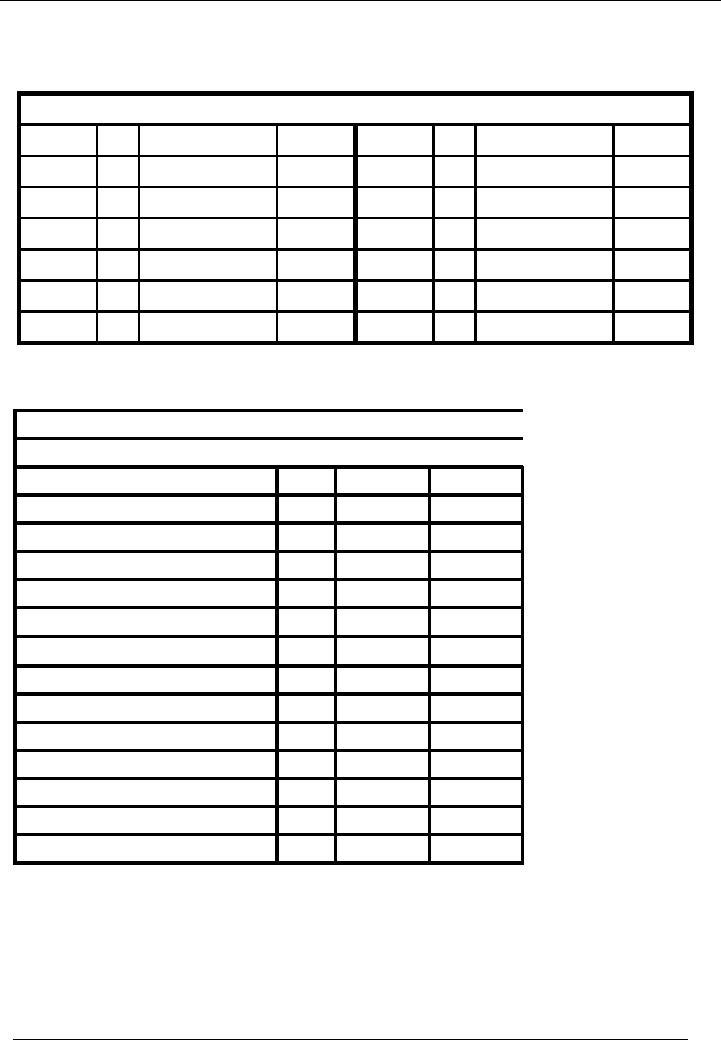
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Mr. B
(Customer)
Mr. B
(Debtor) Account Code
09
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
12-01---
09 Goods
sold
40,000
18-01---
10 Sales
return
5,000
20,000
25-01---
12 Received
from B
40,000
25,000
Balance
15,000
40,000
40,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Bank
Account
02
130,000
Capital
Account
03
200,000
Furniture
Account
04
15,000
Vehicle
Account
05
50,000
Purchases
Account
06
60,000
Mr.
A (Creditor)
07
15,000
Sales
08
95,000
Mr.
B (Debtor)
09
15,000
Total
58
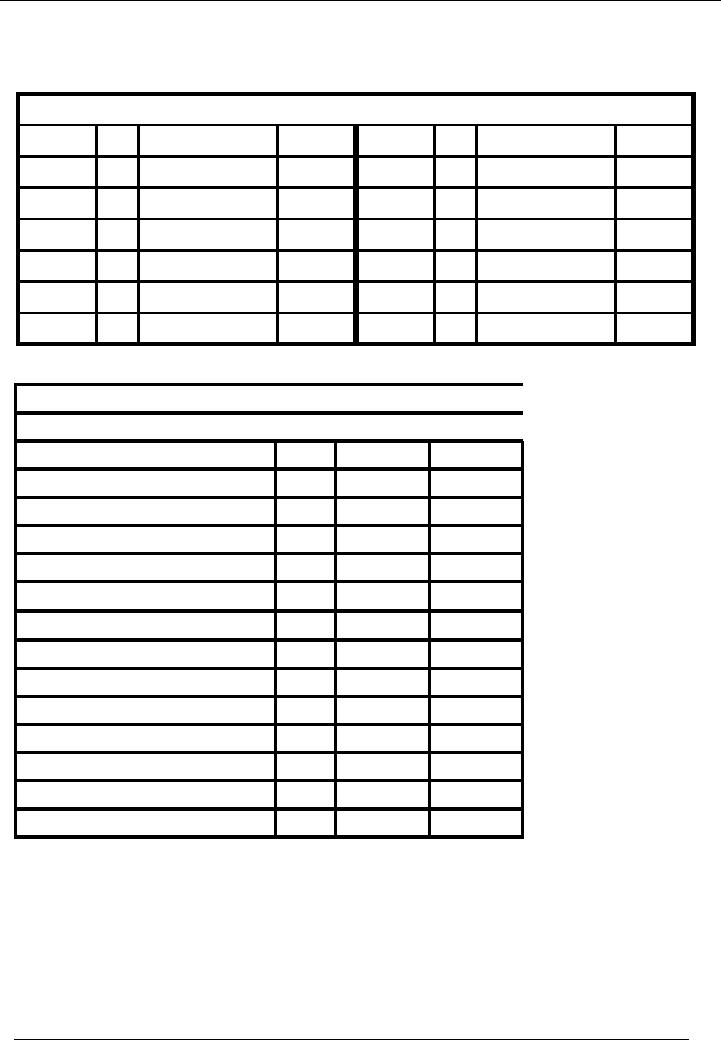
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Salaries
Salaries
Account
Code 10
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
31-01---
13 Salaries
paid
5,000
0
5,000
Balance
5,000
5,000
5,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Bank
Account
02
130,000
Capital
Account
03
200,000
Furniture
Account
04
15,000
Vehicle
Account
05
50,000
Purchases
Account
06
60,000
Mr.
A (Creditor)
07
15,000
Sales
08
95,000
Mr.
B (Debtor)
09
15,000
Salaries
10
5,000
Total
59
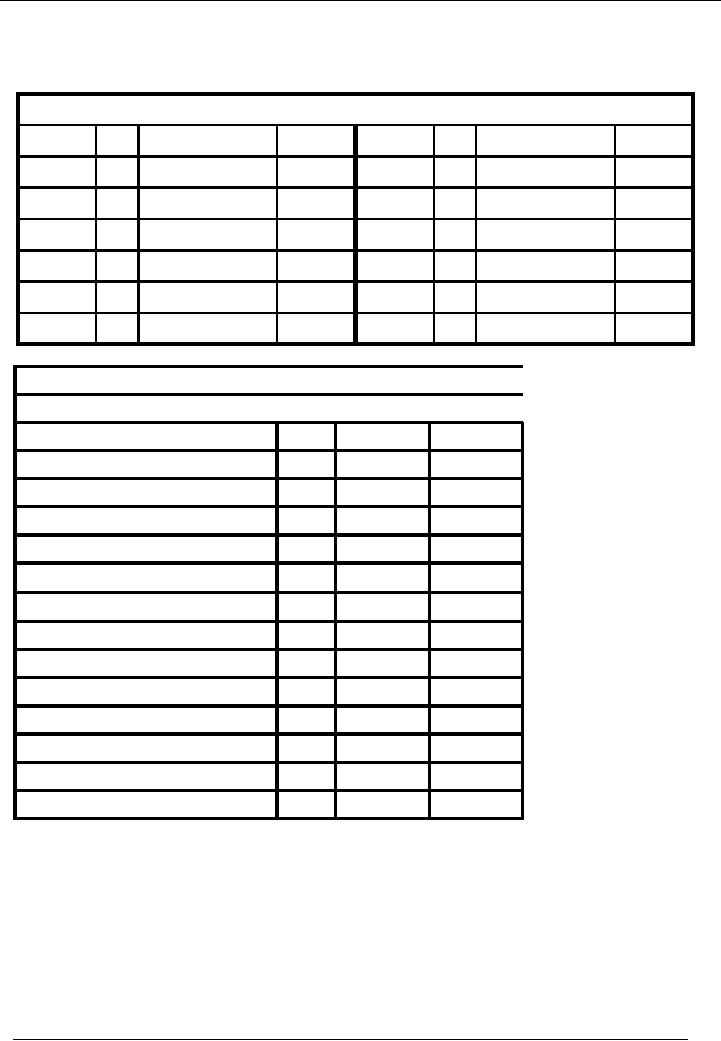
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Expenses
Expenses
Account
Code 11
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
31-01---
14 Exp.
accrued
20,000
20,000
0
Balance
20,000
20,000
20,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Bank
Account
02
130,000
Capital
Account
03
200,000
Furniture
Account
04
15,000
Vehicle
Account
05
50,000
Purchases
Account
06
60,000
Mr.
A (Creditor)
07
15,000
Sales
08
95,000
Mr.
B (Debtor)
09
15,000
Salaries
10
5,000
Expenses
11
20,000
Total
60
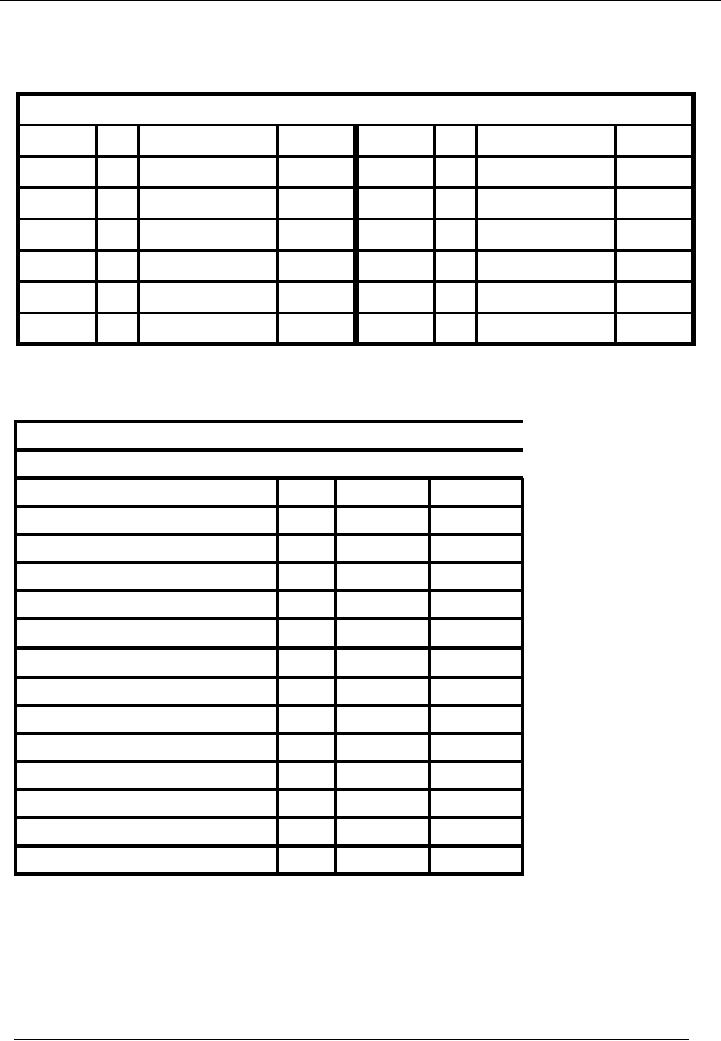
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Expenses
Payable
Expenses
Payable
Account
Code 12
No.
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
Date
No.
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
31-01---
14 Exp.
accrued
20,000
0
20,000
Balance
20,000
20,000
20,000
Name
Of The Organization (Ali
Traders)
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
20--)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
35,000
Bank
Account
02
130,000
Capital
Account
03
200,000
Furniture
Account
04
15,000
Vehicle
Account
05
50,000
Purchases
Account
06
60,000
Mr.
A (Creditor)
07
15,000
Sales
08
95,000
Mr.
B (Debtor)
09
15,000
Salaries
10
5,000
Expenses
11
20,000
Expenses
Payable
12
20,000
Total
330,000
330,000
61
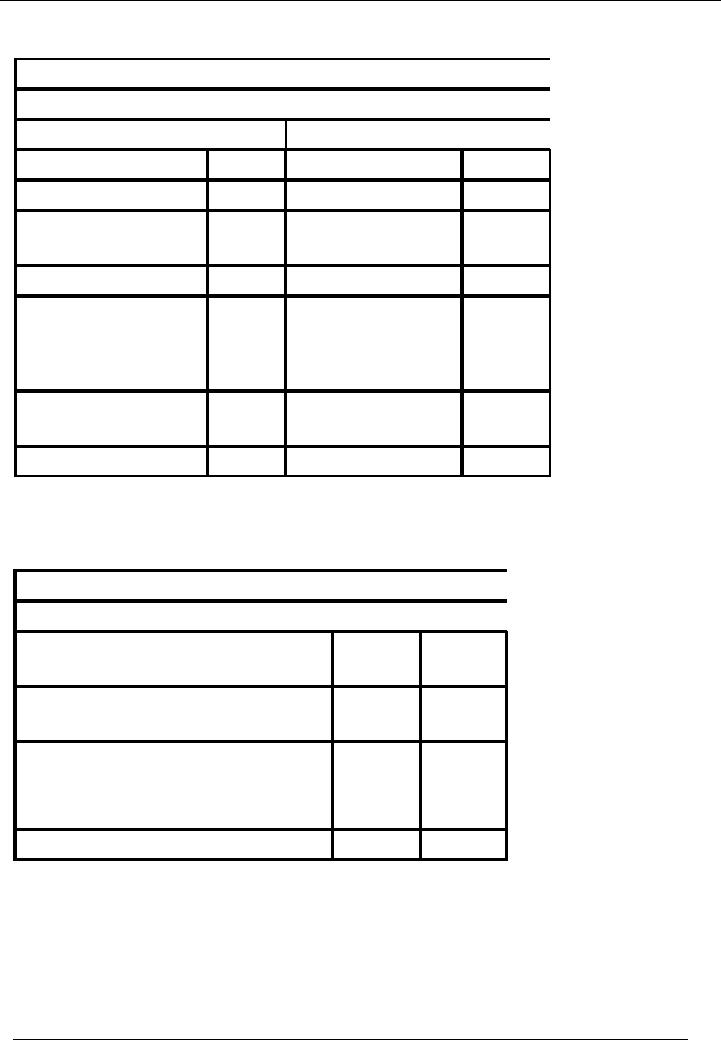
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
PROFIT
AND LOSS ACCOUNT (ACCOUNT
FORM)
Name
of the Entity (Ali
Traders)
Profit and
Loss Account for the
Month Ending January 31,
20--
Debit
Credit
Particulars
Rs.
Particulars
Rs.
Cost
of Sale (Purchases)
60,000
Income
95,000
Gross
Profit
35,000
(income
Cost of Sale)
Total
95,000
Total
95,000
Admin
Expenses
25,000
Gross
Profit
35,000
Salaries
5,000
Expenses
20,000
Net
Profit
10,000
(gross
Profit expenses)
Total
35,000
Total
35,000
PROFIT
AND LOSS ACCOUNT (EPORT
FORM)
Name
of the Entity (Ali
Traders)
Profit and
Loss Account for the
Month Ending January 31,
20--
Particulars
Amount
Amount
Rs.
Rs.
Income
/ Sales / Revenue
95,000
Less:
Cost of Goods
Sold
(60,000)
Gross
Profit
35,000
Less:
Administrative Expenses
(25,000)
(25,000)
Net
Profit
10,000
Rules
of debit & credit
·
Any
account that obtains a benefit is
Debit and
·
Anything
that will provide benefit to
the business is Credit.
·
Both
these statements may look
different but in fact if we consider
that whenever an
account
benefits as a
result of a transaction it will
have to return that benefit
to the business then both
the
statements
will look like different
sides of the same picture.
Rules
of debit & credits can
also be explained like:
62
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
·
EXPENDITURE
o Increase
in Expenditure is Debit
o Decrease
in Expenditure is Credit
·
INCOME
o Increase
in Income is Credit
o Decrease
in Income is Debit
·
ASSETS
o Increase
in Asset is Debit
o Decrease
in Asset is Credit
·
LIABILITY
o Increase
in Liability is Credit
o Decrease
in Liability is Debit
Now we
will explain these rules
with the help of the following
illustration:
No.
Date
Particulars
01
Jan
01
Mr.
Rizwan invests Rs. 100,000
to commence his
business.
02
Jan
03
He
opened an account with bank &
deposited Rs. 30,000.
03
Jan
05
He borrows
Rs. 50,000 from Mr.
Saleem at 12% per
annum.
04
Jan
07
He
purchased furniture worth
Rs. 20,000 for
cash.
05
Jan
09
He
purchased goods (for resale)
worth of Rs. 10,000 from
Mr. Afzal
on
credit.
06
Jan
10
He
sold goods for cash
Rs. 5,000
07
Jan
12
He
sold goods for Rs.
5,000 to Mr. Naeem on credit
basis.
08
Jan
15
Cash
deposited in bank Rs.
5,000
09
Jan
16
He
purchased stationery fore Rs.
3,000.
10
Jan
18
He
purchased office equipment for
Rs. 10,000 and paid by
cheque.
11
Jan
19
He returned
defective goods to Mr. Afzal
worth Rs. 1,000.
12
Jan
25
Goods
are returned by Mr. Naeem
Rs. 500 to the
business.
13
Jan
30
Cash
paid to Mr. Afzal Rs. 9,000
in full settlement of his
claim.
14
Jan
31
Cash
received from Mr. Naeem
Rs. 4,500 in full settlement
of his
account.
15
Jan
31
Cash
withdrawn from the bank Rs.
500.
Now
first document that we prepare in
accounting is the voucher. We will book
first entry in voucher,
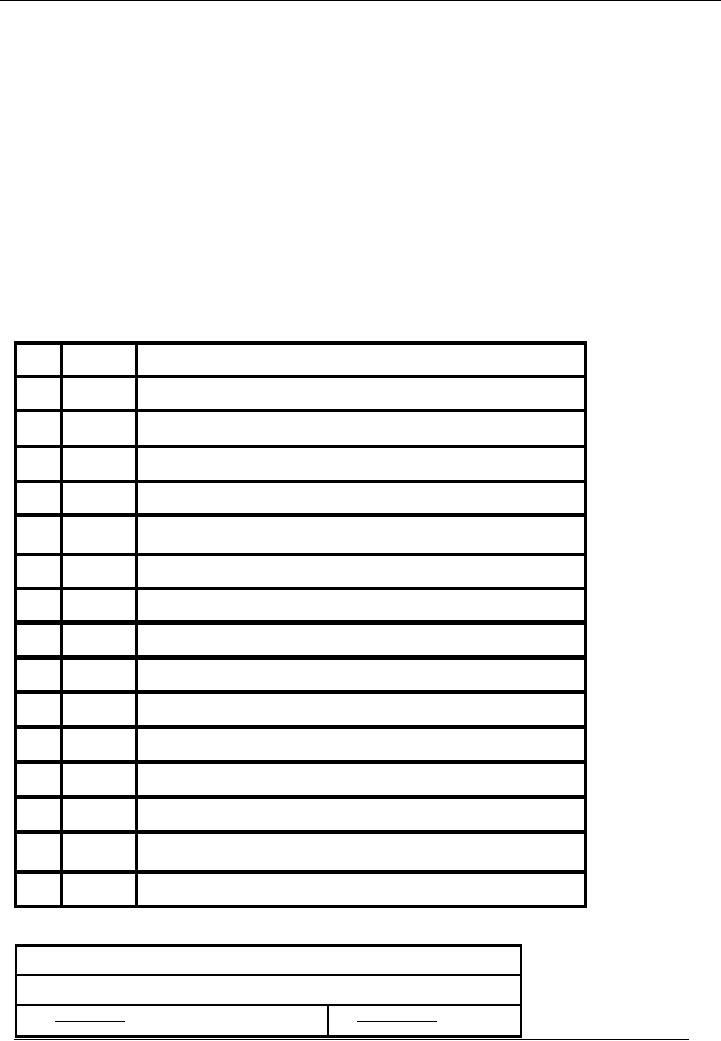
i.e.
Name Of
Company
Type
Of Voucher
Date:
1-1-02--
No:
01
63
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Description
Code
Debit
Credit
Amount
#
Amount
Cash
01
100,000
Capital
02
100,000
Total:
100,000
100,000
Narration:
Capital
Introduced in Cash by Mr.
Rizwan.
Prepared
By:
Checked
by:
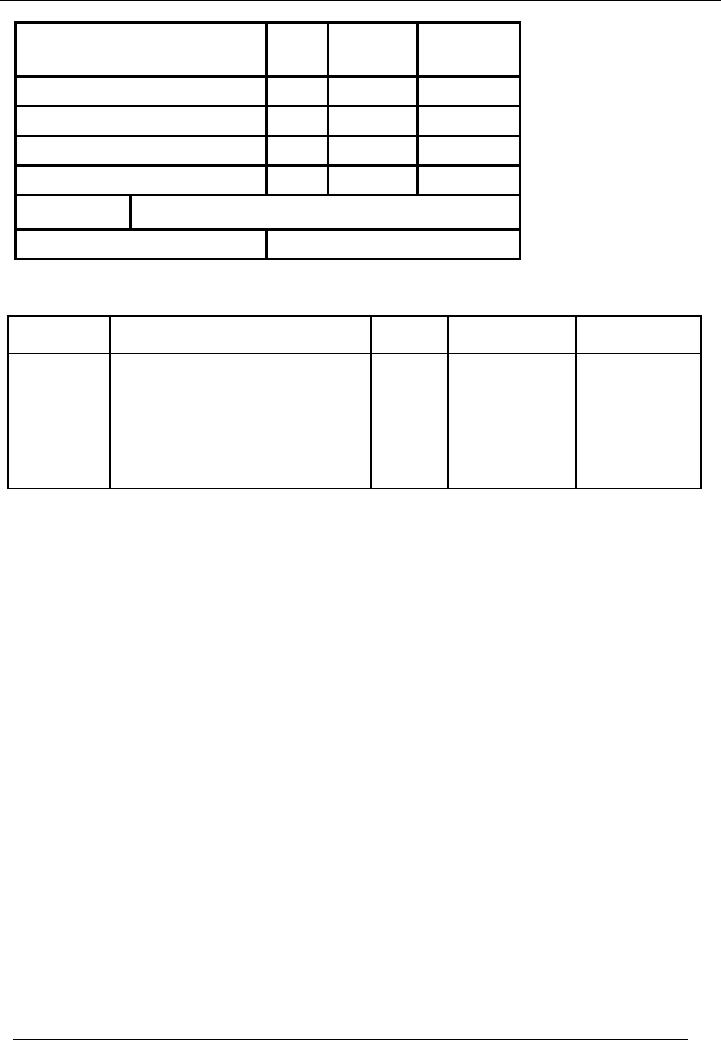
Same
entry is presented in simpler
form:
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
01-01-2002
Cash
A/c
01
100,000
Capital
A/c
02
100,000
Capital
Introduced in Cash by
Mr.
Rizwan
In this
case, cash account is debited
because cash account has
obtained benefit and Capital account
is
credited
because business has obtained
benefit because of capital
account.
This
statement can also be
interpreted like
this:
As
cash is an asset and it is
increased in this case, so cash is
debited. Capital is a liability and
increase in
liability
is credit. In this case capital is
increased, hence it is
credited.
64
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
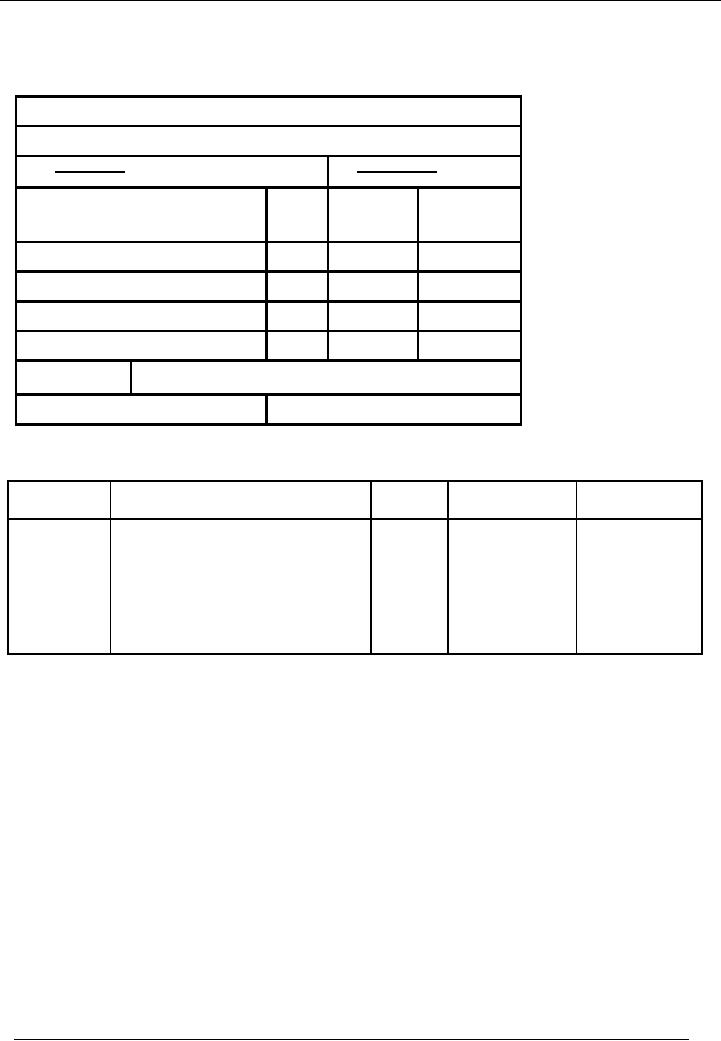
ENTRY
# 2
First, we
will book this entry in
voucher.
Name Of
Company
Type
Of Voucher
Date:
3-1-02--
No:
01
Description
Code
Debit
Credit
Amount
#
Amount
Bank
03
30,000
Cash
01
30,000
Total:
30,000
30,000
Narration:
Deposited
cash in bank.
Prepared
By:
Checked
by:
Again,
the same entry in simple
form
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-01-2002
Bank
A/c
03
30,000
Cash
A/c
01
30,000
Deposited
cash in bank.
Again,
bank account is debited because bank
account has obtained benefit
and Cash account is
credited
because
business has obtained benefit
because of cash
account.
This
statement can also be
interpreted like
this:
As bank is an
asset and it is increased in this
case, so bank is debited. Cash is an
asset and decrease in asset
is
credit. In this
case cash is decreased,
hence it is credited
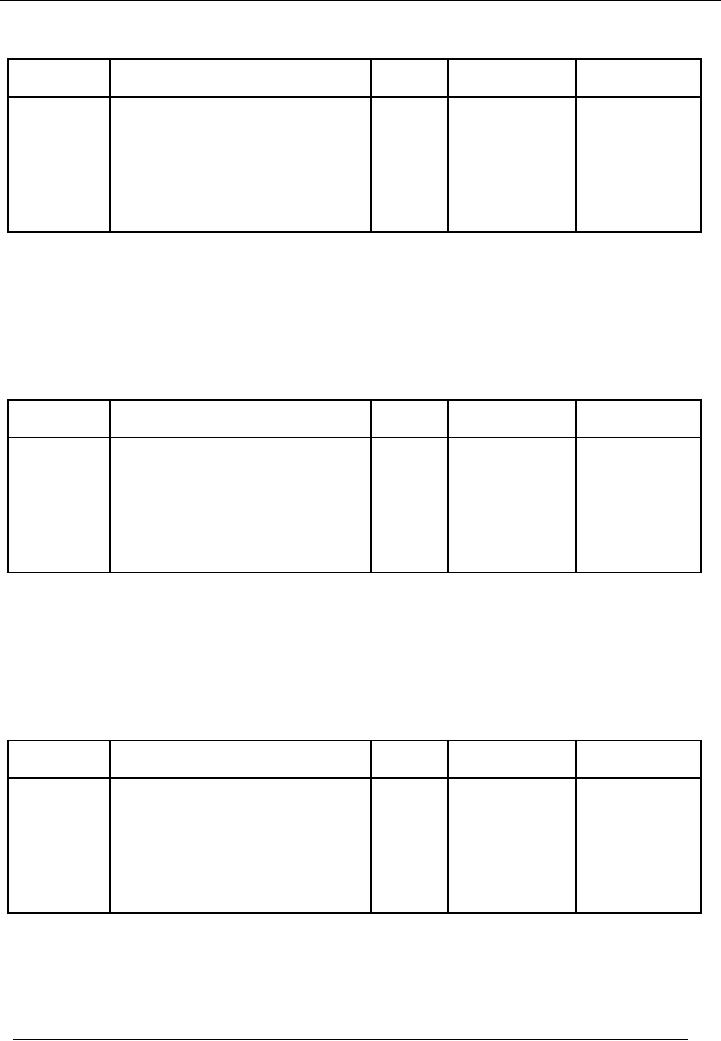
From
now onward, we will present
entry in simple
form.
65
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
ENTRY
# 3
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
05-01-2002
Cash
A/c
01
50,000
Loan
A/c
04
50,000
Obtained
loan from Mr. Saleem.
Cash
account is debited because cash
account has obtained benefit
and Loan account is credited
because
business
has obtained benefit because of
Loan account.
This
statement can also be
interpreted like
this:
As
cash is an asset and it is
increased in this case, so cash is
debited. Loan is a liability and
increase in liability
is credit. In this
case Loan is increased,
hence it is credited
ENTRY
# 4
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
07-01-2002
Furniture
A/c
05
20,000
20,000
Cash
A/c
01
Purchased
furniture for cash
Again,
furniture account is debited because
furniture account has obtained
benefit and Cash account
is
credited
because business has obtained
benefit because of cash
account.
This
statement can also be
interpreted like
this:
As
furniture is an asset and it is
increased in this case, so furniture is
debited. Cash is an asset and
decrease in
asset
is credit. In this case cash is
decreased, hence it is
credited.
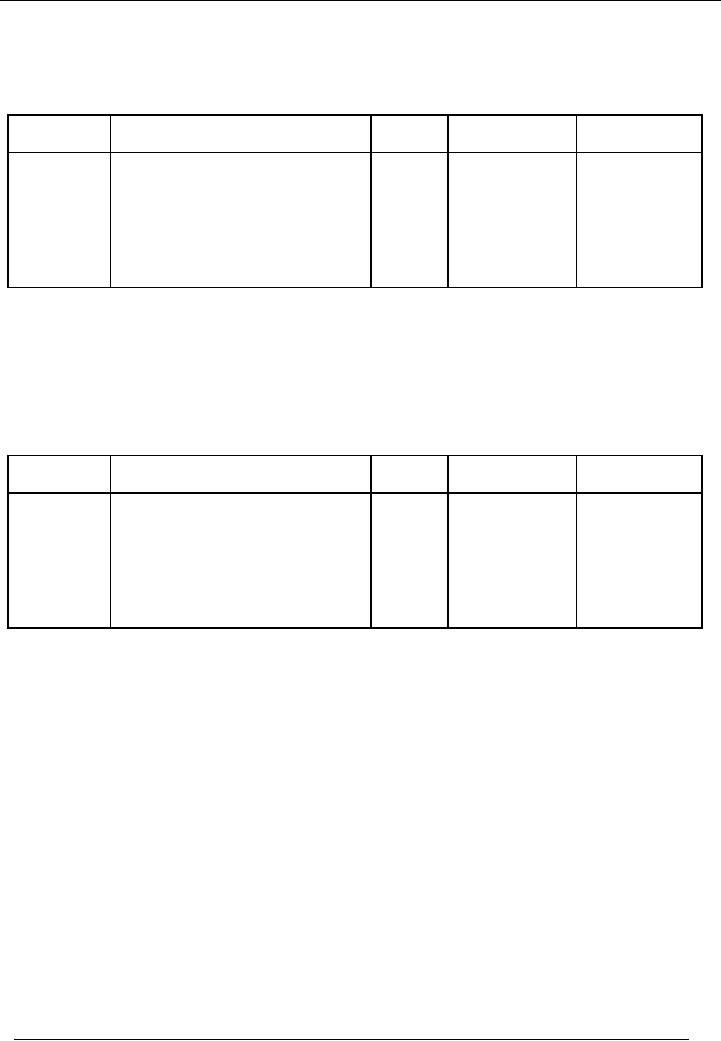
ENTRY
# 5
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
09-01-2002
Purchases
A/c
06
10,000
Mr.
Afzal(Creditors) A/c
07
10,000
Purchased
goods from Mr. Afzal
on
credit
Purchase
account is debited because purchase
account has obtained benefit
and Creditors account is
credited
because
business has obtained benefit
because of Creditors account.
This
statement can also be
interpreted like
this:
As
purchase is an expense and it is
increased in this case, so purchase is
debited. Creditors are liabilities
and
increase
in liability is credit. In this case Creditors
are increased, hence it is
credited.
66
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Creditor
is any third person or organization, to
whom business has to pay in
future.
ENTRY
# 6
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
10-01-2002
Cash
A/c
01
5,000
Sale
A/c
08
5,000
Sold
goods for cash
Cash
account is debited because cash
account has obtained benefit
and Sale account is credited
because
business
has obtained benefit because of
Sale account.
This
statement can also be
interpreted like
this:
As
cash is an asset and it is
increased in this case, so cash is
debited. Sale is an income and
increase in income
is credit. In this
case income is increased,
hence it is credited
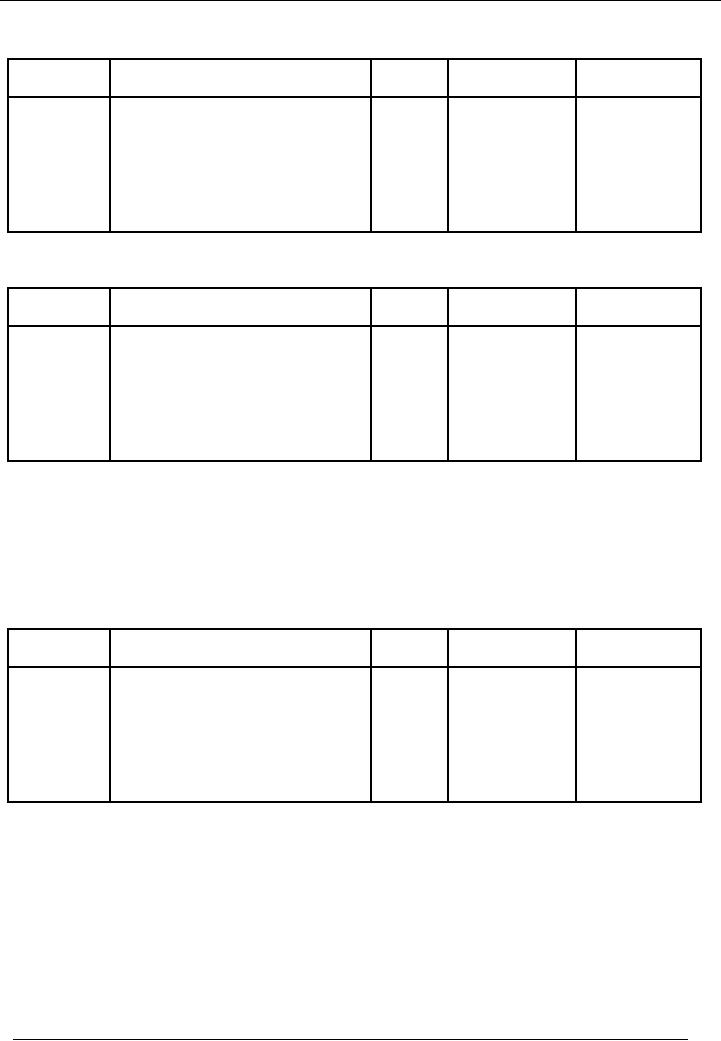
ENTRY
# 7
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
12-01-2002
Mr.
Naeem(Debtors) A/c
09
5,000
Sale
A/c
08
5,000
Sold
goods to Mr. Naeem on
credit
Debtors
account is debited because Debtors
account has obtained benefit
and Sale account is
credited
because
business has obtained benefit
because of Sale
account.
This
statement can also be
interpreted like
this:
As
Debtors is an asset and it is
increased in this case, so debtors
account is debited. Sale is an income
and
increase
in income is credit. In this case income
is increased, hence it is
credited
Debtor is
any third person or organization,
from whom cash is receivable
by the business.
67
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
ENTRY
# 8
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
15-01-2002
Bank
A/c
03
5,000
Cash
A/c
01
5,000
Cash
deposited in bank
ENTRY
# 9
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
16-01-2002
Stationery
A/c
10
3,000
Cash
A/c
01
3,000
Stationery
purchased for cash
Stationery
account is debited because stationery
account has obtained benefit
and Cash account is
credited
because
business has obtained benefit
because of Cash
account.
This
statement can also be
interpreted like
this:
As stationery is an
expense and it is increased in this
case, so stationery is debited. Cash is an
asset and
decrease
in asset is credit. In this case Cash is
decreased, hence it is
credited
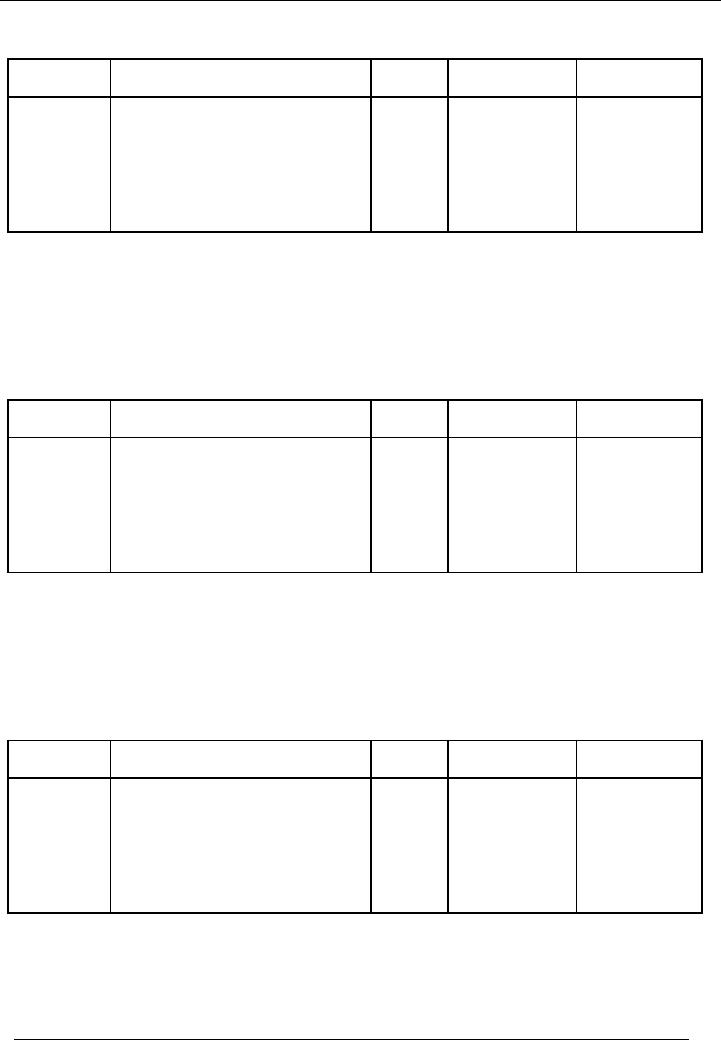
ENTRY
# 10
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
18-01-2002
Office
Equipment A/c
11
10,000
Bank
A/c
03
10,000
Office
equipment purchased by
cheque
Office
Equipment account is debited because
Office Equipment account has
obtained benefit and Bank
account
is credited because business has obtained
benefit because of Bank
account.
This
statement can also be
interpreted like
this:
As
Office Equipment is an asset
and it is increased in this case, so
Office Equipment is debited. Bank is
an
asset
and decrease in asset is credit. In this
case bank account is decreased,
hence it is credited
68
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
ENTRY
# 11
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
19-01-2002
Mr.
Afzal(Creditors) A/C
07
1,000
Purchase
return A/C
12
1,000
Creditors
account is debited because Creditors
account has obtained benefit
and Purchase return account
is
credited
because business has obtained
benefit because of Purchase
return account.
This
statement can also be
interpreted like
this:
As Creditors is a
liability and it is decreased in this
case, so Creditors is debited. Purchase
return is an
expense
and decrease in expense is credit, So it
is credited.
ENTRY
# 12
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
25-01-2002
Sales
return A/C
13
500
09
500
Mr.
Naeem(Debtors) A/C
Goods
returned by Mr.
Naeem(Debtors)
Sales
return account is debited because
Sales return account has
obtained benefit and Debtors is
credited
because
business has obtained benefit
because of Debtors
account.
This
statement can also be
interpreted like
this:
As
sales return is decrease in
income and decrease in
income is debit, so it is debited.
Debtors account is
decreased
and decrease in asset is credit, so it is
credited.
ENTRY
# 13
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
30-01-2002
Mr.
Afzal(Creditors) A/C
07
9,000
Cash
A/C
01
9,000
Cash
paid to Mr. Afzal(Creditors)
69
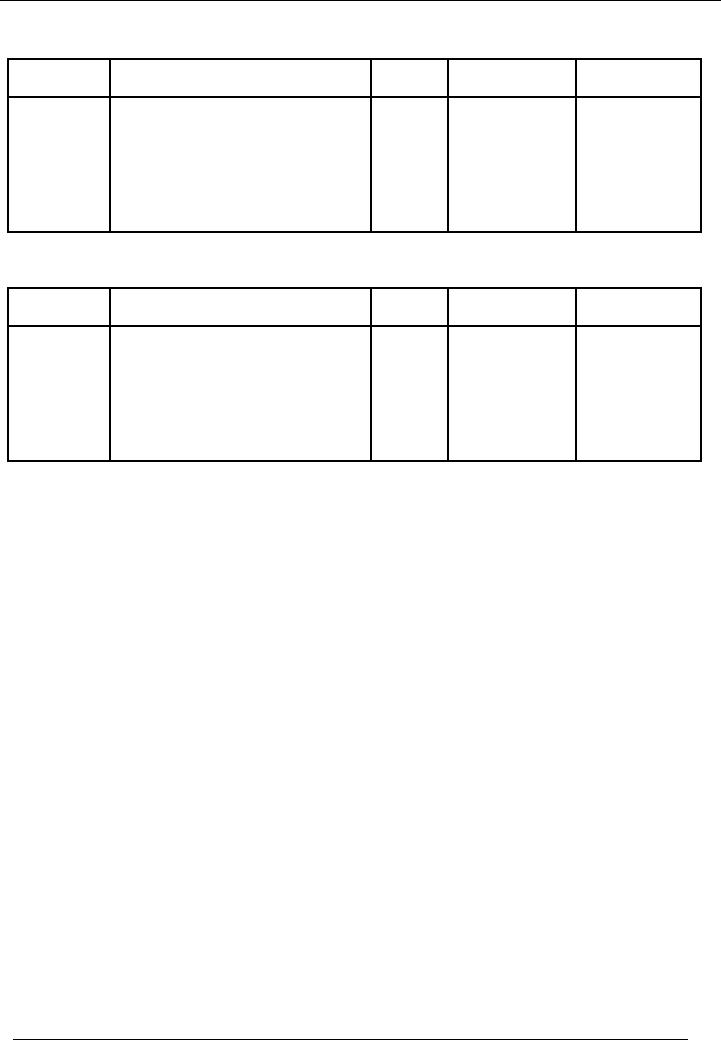
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
ENTRY
# 14
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
31-01-2002
Cash
A/C
01
4,500
Mr.
Naeem(Debtors) A/C
09
4,500
Cash
received from Mr.
Naeem(Debtors)
ENTRY
# 15
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
31-01-2002
Cash
A/C
01
500
Bank
A/C
03
500
Cash
withdrawn from bank
CASH
AND BANK BOOK
·
Ledger
is a book that keeps
separate record for each
account;
·
The
Account or Head of Account is a
systematic record of transactions of
one type; and
·
Like
other things, a separate account is
also required to record the movements in
cash (usually called
cash
in hand) and bank account
(usually called cash at
bank).
·
If the
volume of transactions is high
then we can separate books
for cash and bank
account.
·
These
separate books for cash and
bank account are called cash
book and bank book
respectively.
·
The
Cash Book records all the
movements in the cash
account.
·
A cash
book would look like
one of the two samples shown
here
70
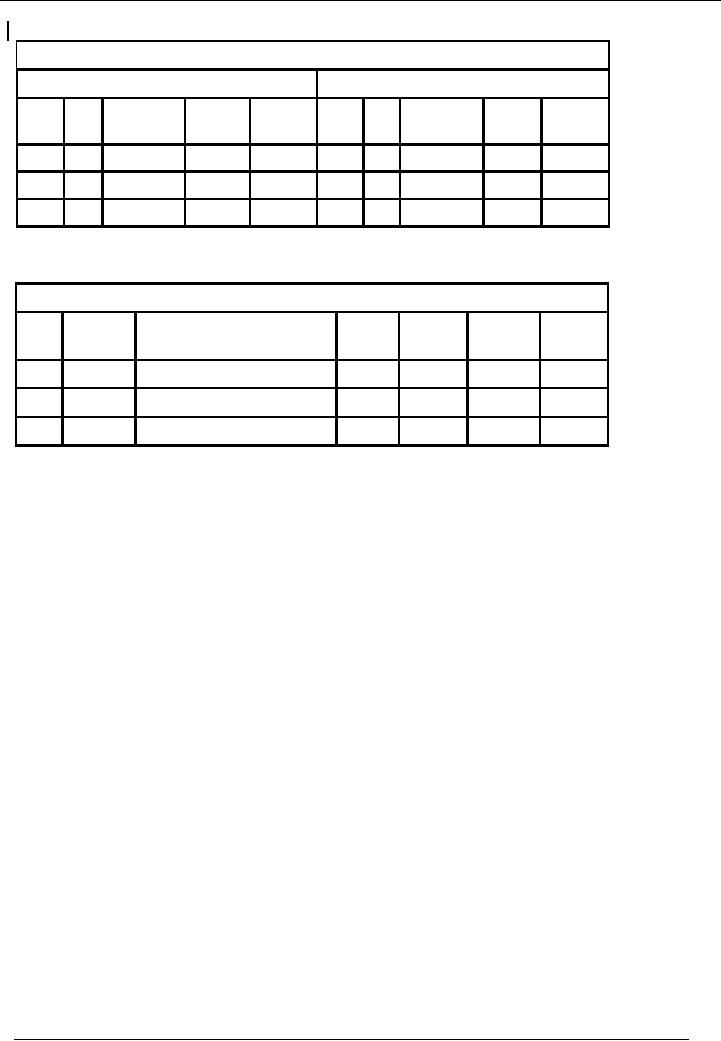
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Cash
Book
Account
Code 01
Receipt
Side
Payment
Side
Date
No. Narration /
Ledger
Receipt
Date No. Narration / Ledger
Payment
Particulars
Code
Amount
Particulars
Code Amount
OR
Cash
Book
Account
Code 01
Date
Voucher
Narration
/
Ledger
Receipt
Payment
Balance
Number
Particulars
Code
Amount
Amount
Dr/(Cr)
THE
CASH BOOK
·
In the
first format / presentation,
receipts (Debits) are written on
left hand side of the page
and
payments
(Credits) on the right hand
side.
·
In the
second presentation, instead of
using two pages, we use
two columns on the same
page.
·
Both
these presentations are
correct.
·
In the
second format, we have an
additional facility of knowing the
balance of the account after
every
transaction.
·
Whereas
in the first one, we have to
add up the receipts and
payments every time we need to
know
the
balance.
·
Moreover,
the second format utilizes
less space, therefore, we
will use this format in our
future
discussions
THE
BANK BOOK
·
The
Bank book records all the
movements in the bank account.
·
The
format of the bank book is the same as
that of cash book axcept
for an additional column
for
Cheque
Number.
·
Again,
we can use either two pages
OR two columns to present the bank
book.
71
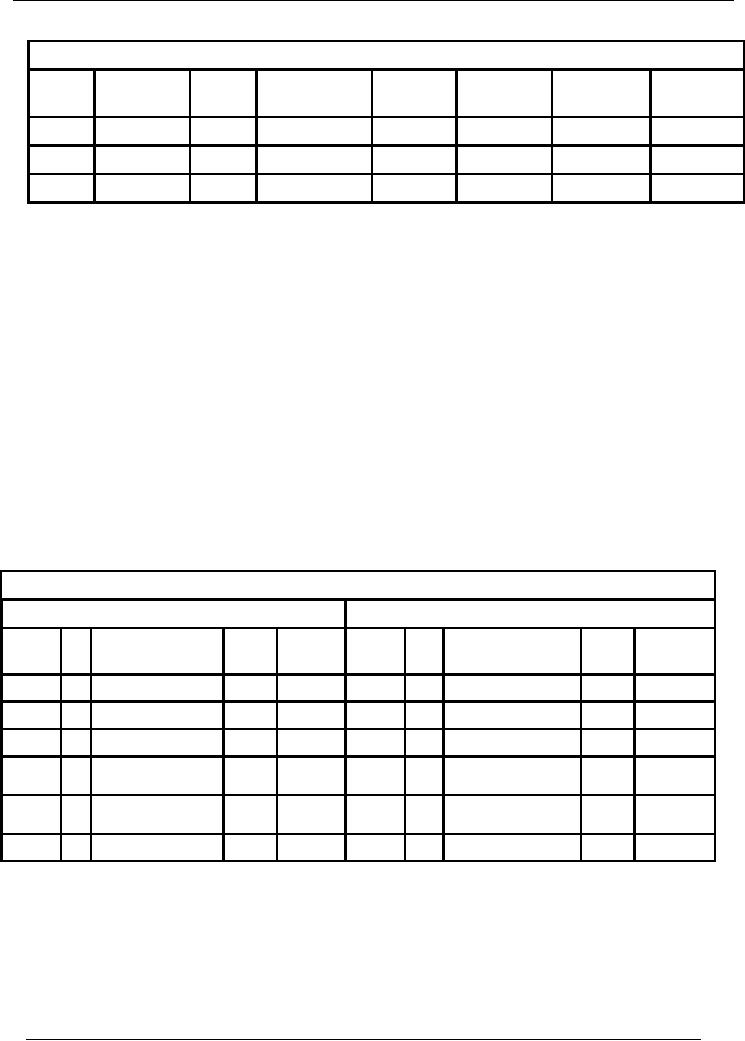
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Bank
Book (Bank Account
Number)
Account
Code 02
Date
Voucher
Chq.
Narration
/
Ledger
Receipt
Payment
Balance
Number
No.
Particulars
Code
Amount
Amount
Dr/(Cr)
·
As you
can see that except
for a few minor differences,
the formats of Cash and Bank book
are
almost
similar to that of the General
Ledger.
·
The
differences are explained
here:
·
The
title of debit and credit
columns has been changed to
receipt and payment
respectively. It is not
necessary
to make this change. But, it is done to
simplify things as we know that in
case of cash and
bank,
debit side would signify
receipt and credit side
would represent
payment.
·
There is an
additional column titled ledger
code. In this column, we write the code
of the other head
of
account that is affected by the
transaction. This helps in understanding the
complete transaction
at a
glance.
·
There
may be a column for cheque number in the
bank book.
·
It may
be noted that in case the organization
operates more than one bank
account, separate
ledger
accounts
will be opened in bank book
for each account.
Now we
will summarize all cash
transactions in both two
page cash book & one
page cash book for
the
convenience
of the reader.
Two
page cash book will be
presented asunder:
Cash
Account
Account
Code 01
Receipt
Side
Payment
Side
Date
No.
Narration
/
Ledger
Receipt
Date
No.
Narration
/
Ledger
Payment
Particulars
Code
Amount
Particulars
Code
Amount
Jan-1
Capital
introduced
02
100,000
Jan-3
Deposited in
bank
03
30,000
Jan-5
Loan
received
04
50,000
Jan-7
Furniture
purchased
05
20,000
Jan-10
Goods
sold
08
5,000
Jan-15
Deposited in
bank
03
5,000
Jan-31
Received
from
09
4,500
Jan-16
Stationery
purchased
10
3,000
debtors
Jan-31
Cash
drawn from
03
500
Jan-30
Paid
to creditors
07
9,000
bank
72
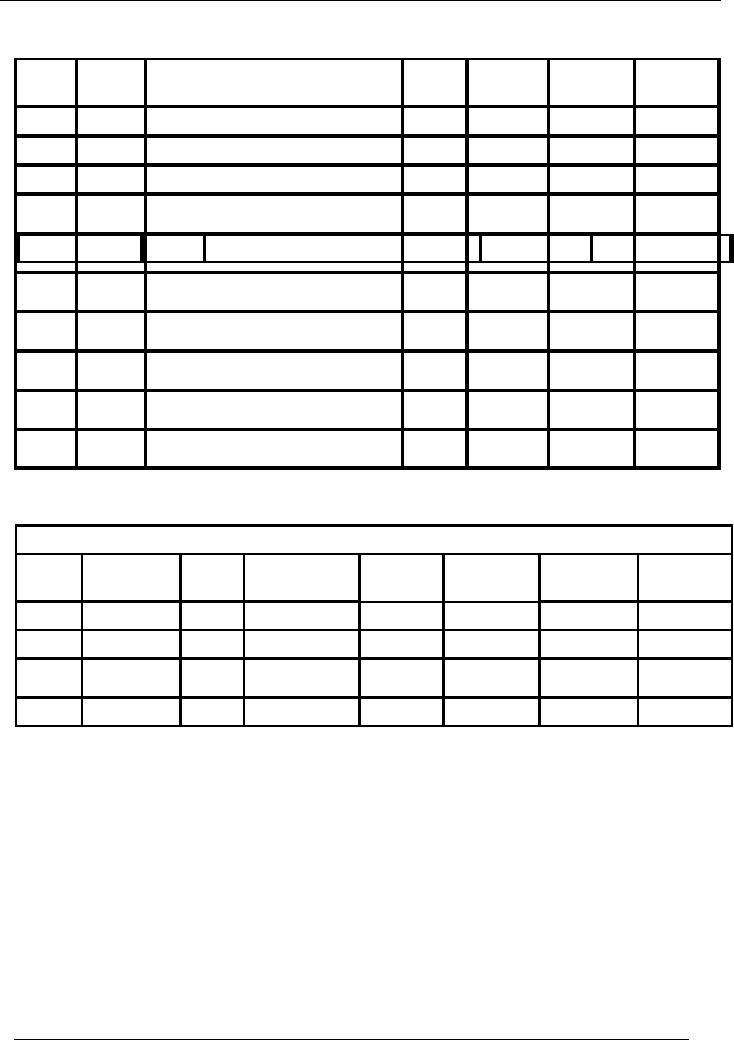
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Same
record will be presented in
two column cash book
now
Date
Voucher
Narration
/
Ledger
Receipt
Payment
Balance
Number
Particulars
Code
Amount
Amount
Dr/(Cr)
Jan-1
Capital
introduced
02
100,000
100,000
Jan-3
Deposited in
bank
03
(30,000)
70,000
Jan-5
Loan
received
04
50,000
120,000
(20,000)
Jan-7
Furniture
purchased
05
100,000
Goods
soGoods sold
ld
08
5,000
105,000
0
Jan-10
5,00
(5,000)
Jan-15
Deposited in
bank
03
100,000
(3,000)
Jan-16
Stationery
purchased
10
97,000
(9,000)
Jan-30
Paid
to creditors
07
88,000
Jan-31
Received
from debtors
09
4,500
92,500
Jan-31
Cash
drawn from bank
03
500
93,000
Now,
we will present Bank entries in bank
book.
Bank
Book (Bank Account # xxx)
Account Code 02
Date
Voucher
Chq.
Narration
/
Ledger
Receipt
Payment
Balance
Number
No.
Particulars
Code
Amount
Amount
Dr/(Cr)
Jan-3
Cash
deposited
01
30,000
30,000
Jan-15
Cash
deposited
01
5,000
35,000
Jan-18
Off.
Equip.
11
(10,000)
25,000
purchased
Jan-31
Cash
drawn
01
(500)
24,500
RECOMMENDED
READING
After
reading this lecture, you
will be able to read
· Chapter
# 2 of business accounting by Frank
Woods
· Chapter
# 2, 3 of accounting by M. Arif &
Sohail Afzal
73
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
ILLUSTRATION
Nawab
Sons started their business
in the month of March, 2002.
Following are their
transactions for the
month.
Pass journal entries,
prepare ledger accounts, and
make their profitability
analyses.
No.
Date
Particulars
01
Mar.
01
Started
business with Rs.
150,000
02
Mar.
05
Purchased
office furniture for cash
Rs. 2,000
03
Mar.
07
Purchased
goods for cash Rs.
9,000
04
Mar.
10
Paid
carriage on purchases Rs.
250
05
Mar.
12
Purchased
goods from Saleem &co.
Rs. 7,000
06
Mar.
13
Sold
goods for cash Rs.
12,000
07
Mar.
15
Sold
goods to Usman & Sons
Rs. 25,000
08
Mar.
21
Received
cash From Usman & Sons
Rs. 25,000
09
Mar.
21
Paid
cash to Saleem &co Rs.
7,000
10
Mar.
23
Paid
salaries for the month Rs.
2,500
11
Mar.
25
Paid
rent Rs. 3,000
12
Mar.
29
Purchased
stationery Rs.2,000
13
Mar.
31
Utility
bills are accrued Rs.
5,000
JOURNAL
ENTRIES
ENTRY
# 1
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-01-2002
Cash
A/c
01
150,000
Capital
A/c
02
150,000
Started
business with cash.
74
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
ENTRY
# 2
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
01-05-2002
Office
Furniture A/c
03
2,000
Cash
A/c
01
2,000
Purchased
office furniture
ENTRY
# 3
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-07-2002
Purchases
A/c
04
9,000
Cash
A/c
01
9,000
Purchased
goods for cash.
ENTRY
# 4
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-10-2002
Carriage
on purchase A/c
05
250
Cash
A/c
01
250
Paid
carriage on purchase.
ENTRY
# 5
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-12-2002
Purchases
A/c
04
7,000
Salim
& co.(Creditors)
06
7,000
Purchased
goods on credit
75
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
ENTRY
# 6
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-13-2002
Cash
A/c
01
12,000
Sale
A/c
07
12,000
Goods
sold for cash.
ENTRY
# 7
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-15-2002
Usman
& Sons(Debtors) A/c
08
25,000
25,000
Sale
A/c
07
Goods
sold on credit.
ENTRY
# 8
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-21-2002
Cash
A/c
01
25,000
Usman
& Sons(Debtors A/c
08
25,000
Cash
received from Usman &
Sons
ENTRY
# 9
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-21-2002
Salim
& co.(Creditors) A/c
06
7,000
Cash
A/c
01
7,000
Paid
cash to Salim &
co.
76
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
ENTRY
# 10
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-23-2002
Salaries
A/c
09
2,500
Cash
A/c
01
2,500
Started
business with cash.
ENTRY
# 11
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-25-2002
Rent
A/c
10
3,000
Cash
A/c
01
3,000
Paid
rent..
ENTRY
# 12
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-29-2002
Stationery
A/c
11
2,000
2,000
Cash
A/c
01
Stationery
purchased.
ENTRY
# 13
Date
Particulars
Code
#
Amount(Dr.)
Amount(Cr.)
Rs.
Rs.
03-31-2002
Utility
Bills A/c
12
5,000
Accrued
Expenses A/c
13
5,000
Accrual of
utility bills for the
month..
77
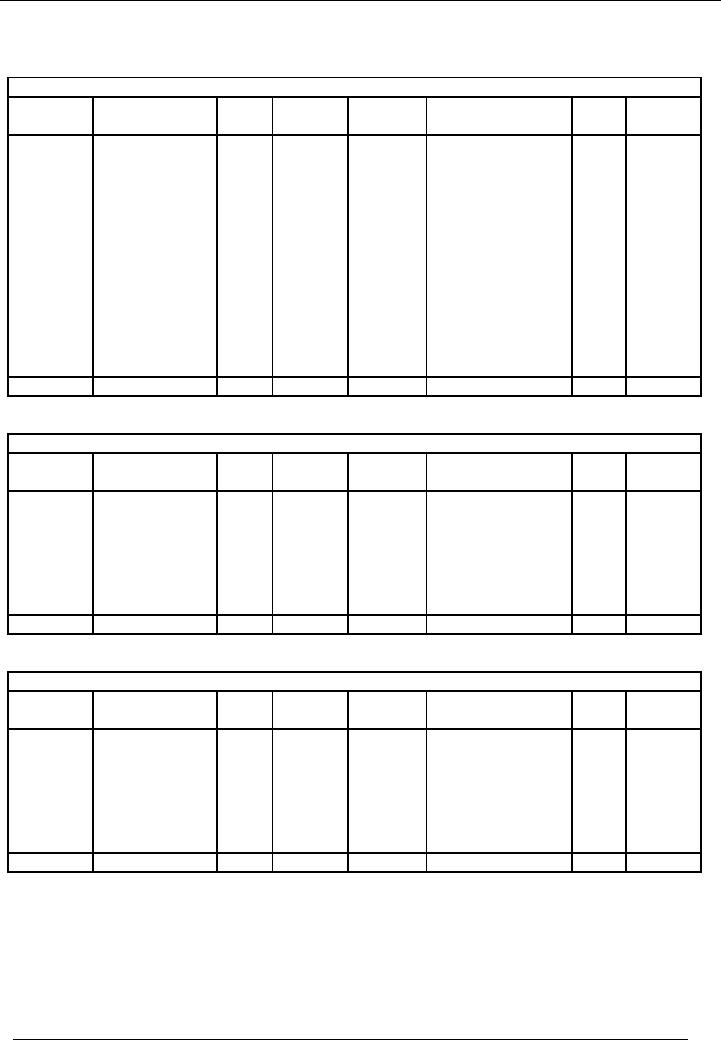
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
LEDGER
ACCOUNTS
Cash
Account
Account
code # 1
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
1-3-02
Commenced
02
150,000
5-3-02
Office
furniture
03
2,000
business
purchased
13-3-02
Goods
sold
07
12,000
7-3-02
Goods
purchased
04
9,000
21-3-02
Received
from
10-3-02
Carriage
paid
05
250
debtors
08
25,000
21-3-02
Paid
to creditors
06
7,000
23-3-02
Paid
salaries
09
2,500
25-3-02
Paid
rent
10
3,000
29-3-02
Paid
for stationery
11
2,000
BALANCE
161,250
Total
187,000
Total
187,000
Capital
Account
Account
code # 2
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
1-3-02
Cash
introduced
01
150,000
BALANCE
150,000
Total
150,000
Total
150,000
Office
furniture Account
Account
code # 3
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
5-3-02
Office
furniture
01
2,000
purchased
BALANCE
2,000
Total
2,000
Total
2,000
78
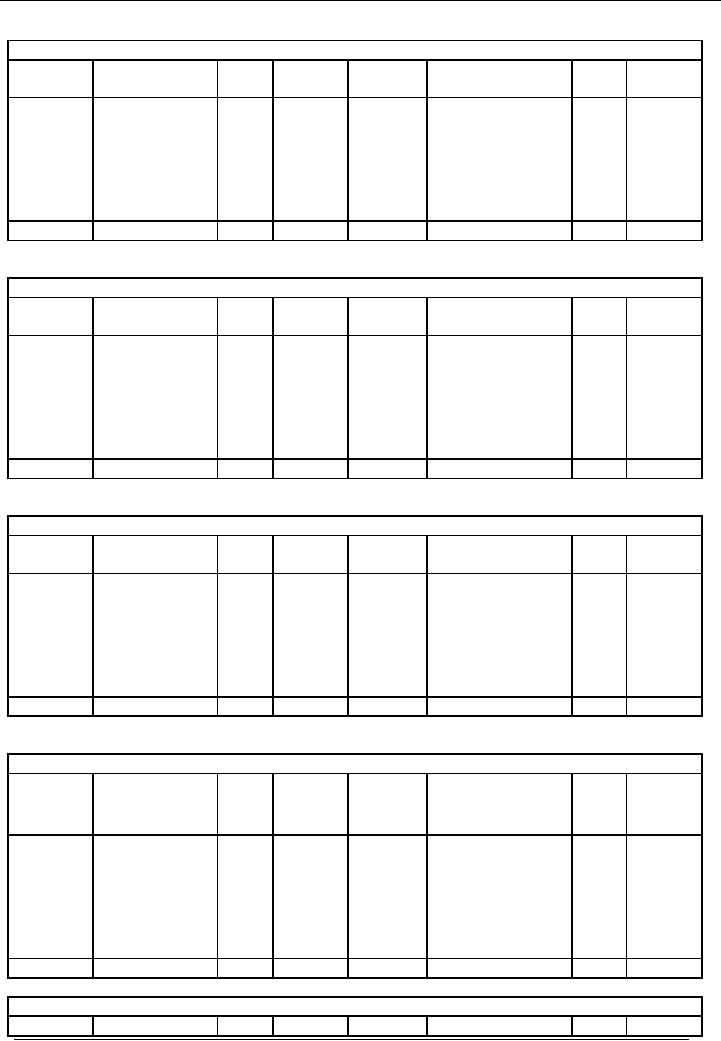
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Purchases
Account
Account
code # 4
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
7-3-02
Purchased
01
9,000
goods
12-3-02
Purchased
7,000
goods
on credit
BALANCE
16,000
Total
16,000
Total
16,000
Carriage
on purchase Account Account
code # 5
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
10-3-02
Paid
carriage on
01
250
purchase
BALANCE
250
Total
250
Total
250
Salim
& co.(Creditors) Account
Account
code # 6
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
12-3-02
Purchased
04
7,000
21-3-02
Paid
cash
01
7,000
goods
BALANCE
0
Total
7,000
Total
7,000
Sale
Account Account code #
7
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
13-3-02
Goods
sold
01
12,000
15-3-02
Goods
sold on
08
credit
25,000
BALANCE
37,000
Total
37,000
Total
37,000
Usman
& sons(Debtors) Account
Account
code # 8
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
79
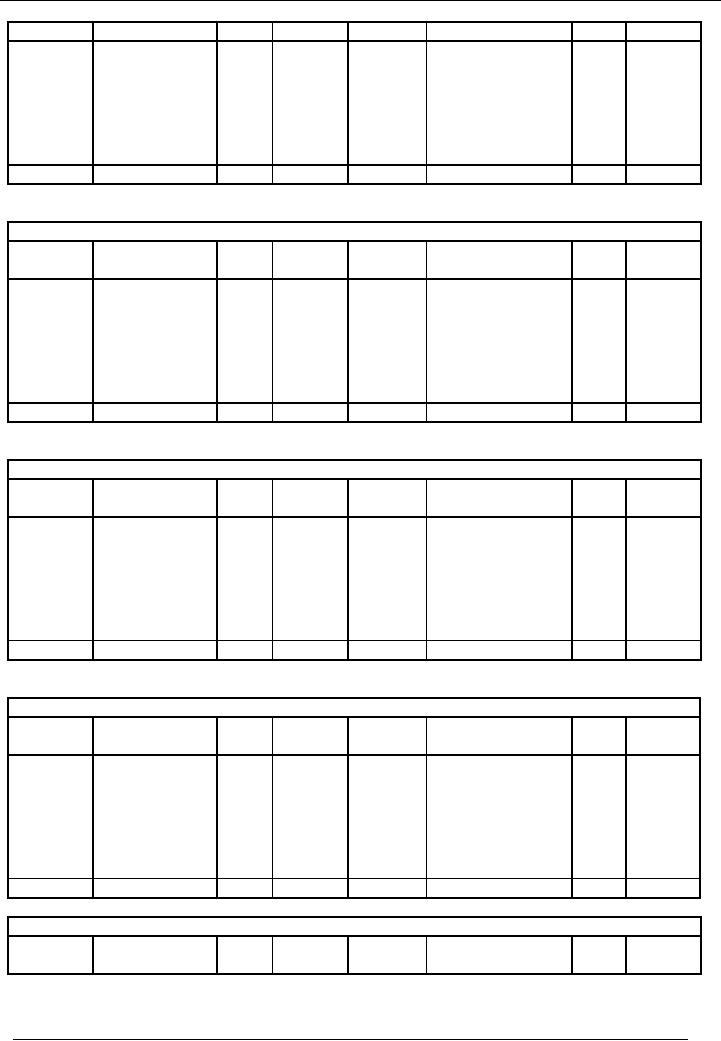
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
15-3-02
Goods
sold
07
25,000
21-3-02
Received
cash
01
25,000
BALANCE
0
Total
25,000
Total
25,000
Salaries
Account
Account
code # 9
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
23-3-02
Salaries
paid
01
2,500
BALANCE
2,500
Total
2,500
Total
2,500
Rent
Account Account code #
10
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
Rent
paid
01
3,000
25-3-02
BALANCE
3,000
Total
3,000
Total
3,000
Stationery
Account
Account
code # 11
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
29-3-02
Stationery
01
2,000
purchased
BALANCE
2,000
Total
2,000
Total
2,000
Utility
Bills Account
Account
code # 12
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
80
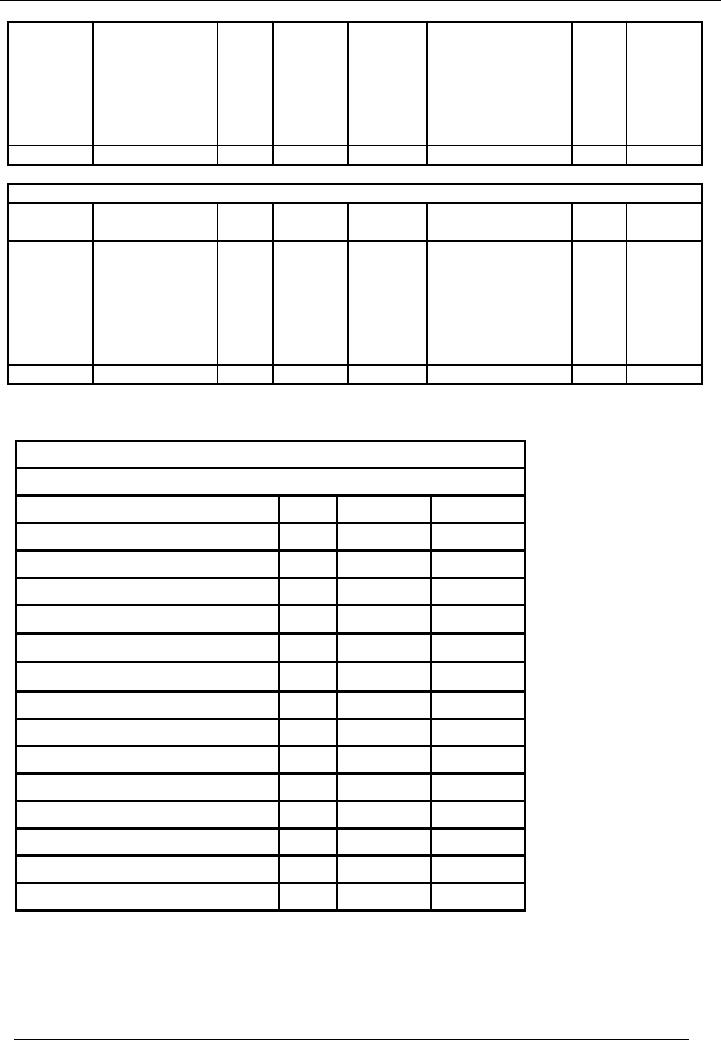
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
31-3-02
Accrued
utility
13
5,000
bills
BALANCE
5,000
Total
5,000
Total
5,000
Accrued
Expenses Account Account
code # 13
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
31-3-02
Accrued
utility
12
5,000
bills
BALANCE
5,000
Total
5,000
Total
5,000
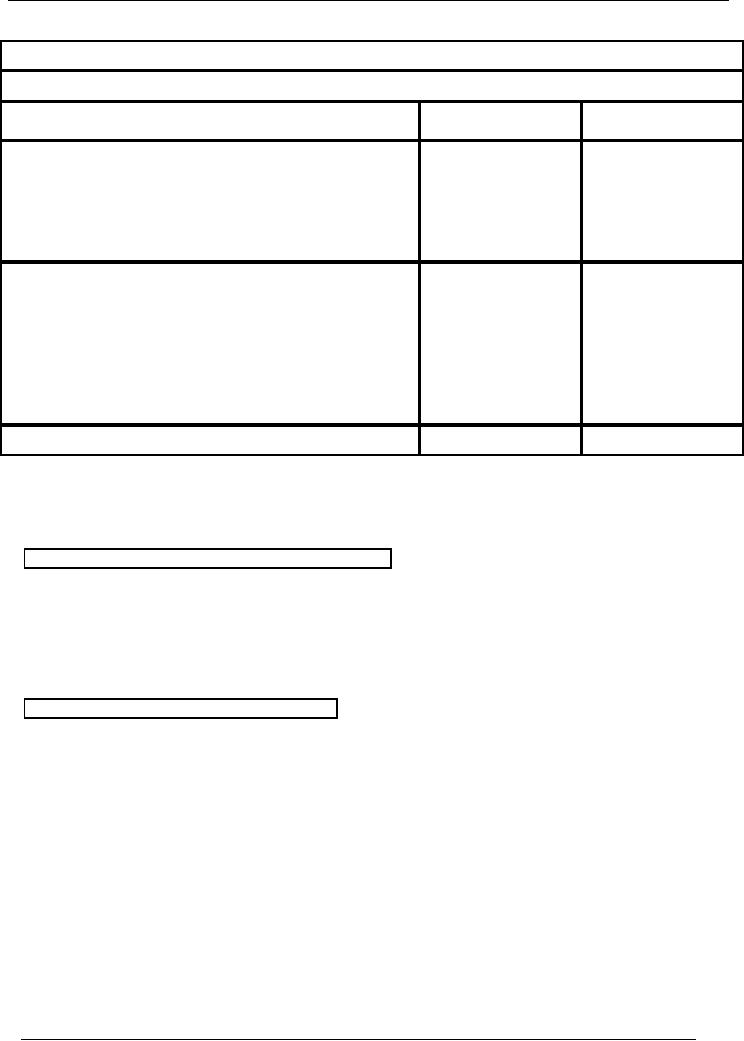
TRIAL
BALANCE
Saeed
& co.
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
2002)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
161,250
Capital
Account
02
150,000
Furniture
Account
03
2,000
Purchases
Account
04
16,000
Carriage
on purchase account
05
250
Salim&
co. (Creditor)
06
0
Sales
07
37,000
Usman
& co. (Debtor)
08
0
Salaries
09
2,500
Rent
10
3,000
Stationery
11
2,000
Utility
billst
12
5,000
Accrued
expenses
13
5,000
Total
192,000
192,000
81
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Saeed
& Co.
Profit &
Loss Account for the
period ended January 31,
2002
Particulars
Amount
Amount
Rs.
Rs.
37,000.
Income
/ Sales / Revenue (See Note
#1)
Less:
Cost of Goods
Sold
(16,250)
(See
Note # 1)
Gross
Profit
20,750.
Less:
Admin. Expenses
(12,500)
(See
Note # 2)
Net
Profit/ (Loss)
8,250
Note
# 1 Cost of goods
sold
Purchases
16,000
Add:
carriage on purchase
250
Cost
of goods sold
16,250
Note
# 2 Admin. Expenses
Salaries
2,500
Rent
3,000
Stationery
2,000
Utility
bills
5,000
Total
Admin. Expenses
12,500
RECOMMENDED
READING
After
reading this lecture, you
will be able to read
· Chapter
# 3 of business accounting by Frank
Woods
· Chapter
# 5 of accounting by M. Arif & Sohail
Afzal.
82
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES