 |
PERSUASION & COMMUNICATION THEORIES:Message Orientation |
| << PROBLEMS SOLVING STRATEGIES:Communicate results |
| COMMUNICATION CONCEPTS & THEORIES:Research and Persuasion >> |
Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
Lesson
35
PERSUASION
& COMMUNICATION THEORIES
Overview
Basically
while improving upon the
definition of public relations the word
mutual understanding between
the
organization and its publics
was rethought and defined to
be persuasion for better understanding
and
the
philosophy pertaining to the persuasion
and communication theories in the modern
perspective.
Main
Definitions Of Public
Relations
·"It is a planned
& sustained effort to establish &
maintain
Mutual
understanding between
an organization & its
publics."
·"It is a phenomenon
& necessity of our times."
---
Edward Bernays
·Word
Persuasion would be better than
mutual
understanding.
Quentin
Bell
Public
Opinion is the
collective opinion of groups of
people.
2
things sure about public
opinion:
·It
will change
·Those
who hold an opinion were somehow
persuaded to think as they do.
PERSUASION
& COMMUNICATION THEORIES
2
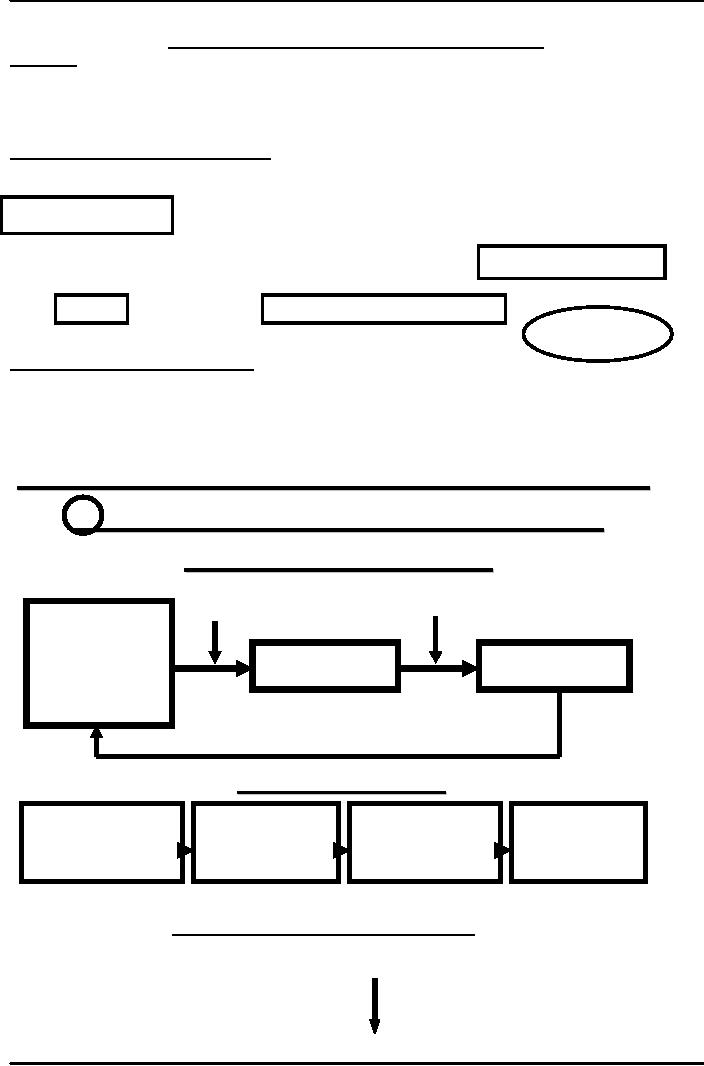
Theoretical Model of PR Practice
Communication
Model
Medium
Decoding
Sender
encoding
Audience
Response
message
FEED
BACK
Behavioral
Model
Awareness
Latent
Triggering
Behavior
readiness
event
Persuasive
Strategies Based On 3 Elements
Media
Orientation
Whom
to tell How to
tell
What
Media to communicate
85

Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
(
Choice of medium is very critical. It
must be believable e.g.
Television
Which
is highly credible with mass
penetration?
Message
Orientation
1.
Actually message must be
evaluated.
2.
To be effective persuasive appeals must
combine the rational & the emotional.
3.
To be persuasive, a message has to
present something of value to the
target public.
4.
Must be compatible with that public's
motives.
·Source
Orientation.
1.
Source
of information has big effect on
persuasion.
2.
People
tend to believe sources that
are like them, like they
want to be , or like they perceive
themselves
to be.
3.
Research
has suggested that source
credentials may not matter
as much as a message's plausibility
&
message
quality.
Propaganda
& Persuasion Appeals
Some
misleading propaganda devices.
1.
Name
Calling.
Positive
or negative.
2.
Glittering
Generalities.
Throngs
of greeters. Enthusiastic
crowds
3.
Transfer.
Famous
person's aura is transferred to
less known persons.
4.
Testimonial.
Actual
endorsement - not transfer.
5.
Card
stacking.
Telling
one side of story.
6.
Emotional
stereotypes.
All
kinds of images are so designed
like "good
Pakistani",
"housewife",
"foreigner"
etc.
7.
Illicit
Silence.
Basically
holding information that
would correct a false
impression.
Persuasion
& Communication Theories
There
are 5
important
elements
---
Robert
Cialdini.
1.
Consistency
2.
Reciprocity
3.
Social
validation
4.
Authority
5.
Scarcity
Based
on the above 5
elements
there are 4
principles of
persuasion to be kept in
mind--
Earl
Newman
(Built
on concept of personal identification
with an idea or a problem).
1.
Identification.
2.
Suggestion
of action.
3.
Familiarity
& Trust.
4.
Clarity.
86
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION & BRIEF HISTORY:Definitions Of Public Relations
- HOW DOES PR WORK?:OVERVIEW, Formulation of policy
- PUBLIC RELATIONS DISTINGUISHED:Size of a PR Department.
- PUBLICS OF PR:Expanded Publics, Few Examples Of Publics
- PLANNING PUBLIC RELATIONS PROGRAMMES:Print Media, Electronic Media
- MEDIAS OF PR:Media for External Publics, Principles of Good Press Relations
- PRESS RELATIONS IN PR:What is News, Secrets Of Good News Release.
- CREATED PRIVATE MEDIA:Private Media, New Forms of House Journals
- SPECIAL USES OF PUBLIC RELATIONS:Crisis Management, Skills Of PR
- BUDGETING IN PR:Labour, Office Overheads, PR & Photographs
- PUBLIC RELATIONS PROBLEMS:Defining PR problems, C’s of PR explained
- METHODS OF COMMUNICATION:Psychology of Public Relations
- PR IN VARIOUS ORGANIZATIONS:Techniques of Trade Association PR
- PR IN LABOUR UNIONS & RELIGIOUS GROUPS:Community Public Relations
- PR IN EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS & IN MEDIA CHANNALS
- USING ADVERTISING FOR P R COMMUNICATION:Role Of PR
- ROLE OF PUBLIC RELATIONS IN MARKETING:How To Educate The Market
- PUBLIC RELATIONS AND CORPORATE STRUCTURE:Corporate Identity Essentials
- E-PR & ITS TOOLS:Immediate Points To Consider, Using Email As PR Tool
- SPONSORSHIP—AN IMPORTANT PR TOOL:PR & Communication Audit
- HOUSE JOURNALS:Possible Publics Of House Journals, Exhibitions & PR
- CRISIS MANAGEMENT IN PR:Plan Of Action Adopted, Interview at your place
- ADVERTISING IN PR:Broad Objectives Of Advertising, Direct Advertising.
- INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC RELATIONS:Media Used, Within Store Contacts
- PUBLIC RELATIONS CONSULTANCY:Disadvantages, Mass Communication
- PUBLIC RELATION’S ROLE IN MARKET EDUCATION:Kinds Of Markets
- MODERN DAY VALUES OF PR:Ethics Of Public Relations
- CHOICE OF MEDIA FOR PR COMPAIGN:Communication Channels & Media
- PR TECHNIQUES:Tactics & Techniques
- DESIGNING PR COMPAIGNS:Definitive Mission statement, Reputation.
- PUBLIC OPINION:Identifying Priority Publics, If Goal Is Attitude Change
- PUBLIC RELATIONS AND RESEARCH:Planning Phase Of Research
- PR AND RESEARCH:Unobtrusive Measures, Questionnaires For Survey
- PROBLEMS SOLVING STRATEGIES:Communicate results
- PERSUASION & COMMUNICATION THEORIES:Message Orientation
- COMMUNICATION CONCEPTS & THEORIES:Research and Persuasion
- PUBLIC RELATIONS & LAW:How To Stay Out Of Trouble
- PUBLIC RELATIONS & CASE STUDIES:Case Analysis, Images Of Public Relations
- PR AND PRINTING PROCESSES:Fundamentals Of Printing
- PUBLIC SPEAKING -- A PR TOOL:Key Benefits, How To Prepare
- PR -- COPING WITH UNEXPECTED:Some Possible PR Ideas
- DREAMS & REALITIES OF PR:Who Takes Charge Of Identity?
- CHANGING INTO OVERDRIVE:How International Is PR?
- GETTING ON WITH PR:Where does PR fit in the structure?
- FUNDAMENTALS OF A SUCCESSFUL NEWSLETTER:RESEARCH, WRITING