 |
Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
Lesson
35
UTILITY
OF VARIOUS MEDIA
OVERVIEW
In
this lecture we will recap
the procedure the choosing a
production company and the
two
important
elements for producing TV
spots like tape or film and
like hiring talent. Besides
this
we
will also review the utility of
radio, TV, newspapers and magazines. The
use of direct mail
as
an important advertising tool, we will
also be discussed including the
rules and benefits.
TAPE
OR FILM:
While
preparing a good TV spot it is important to
answer the following two
questions.
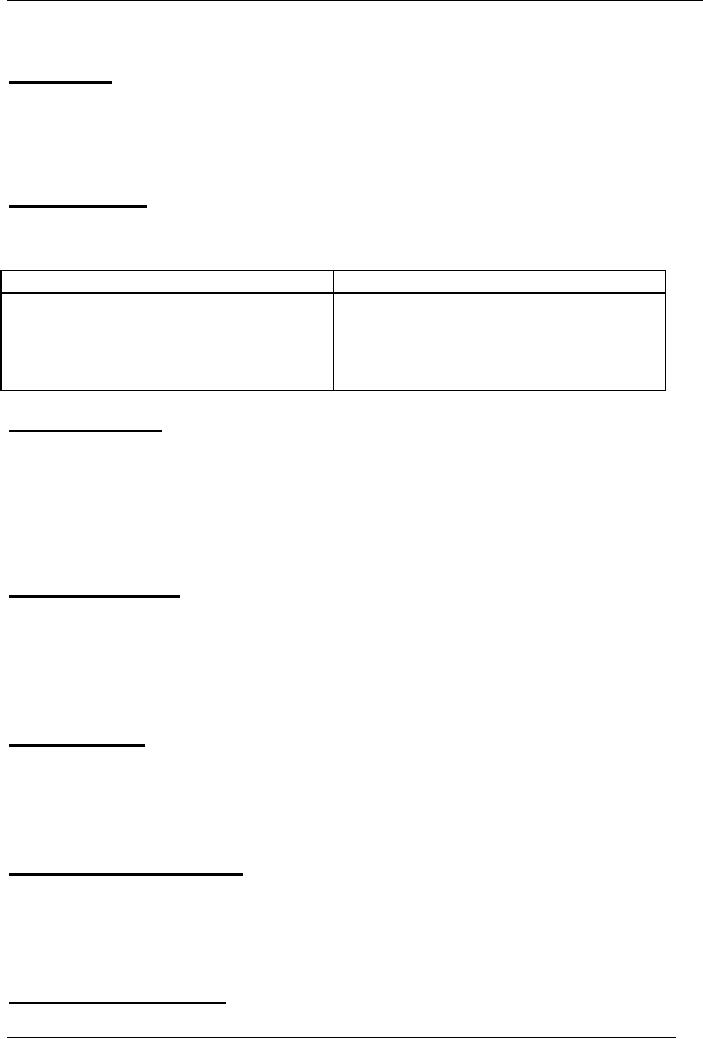
Following
is the comparison between
the usage of tape and film
and its features for
preparing a
TV
spot.
TAPE
FILM
·
Good
for low budget
spots
·
Expensive
& more subtle
quality
·
Less
depth & range of tones
·
More
depth & range of tones.
·
Expensive
spots both in tape &
film.
HIRING
TALENT:
No
spot can be complete without the
use of the actors or announcers
who read your copy
or
perform
"live" in the spot. In this
context the hiring of talent
of different type is given
below:
Announcer:
Who reads your copy,
(on or off camera).
Actors:
Who perform "live" in the
spot or both.
Using
yourself, your staff, or family members
in commercials: Be cautious
Get third party
opinion.
UTILITY
OF RADIO
We
will try to review the
utility of different mediums
like Radio, TV, Newspapers and
magazines
as under:
·
Any
business serving a consumer
market can use Radio.
·
Bring
immediate response for sale
& promotion.
·
Equally
good at increasing awareness.
UTILITY
OF TV
·
Ideal
for Advertisers need to demonstrate
their product.
·
Creates
sense of Excitement.
·
Those
needing to reach a specific
Market.
·
Creates
advertising opportunities for
businesses aiming at narrower
target.
UTILITY
OF NEWSPAPERS
·
Those
who want to influence a broad
market.
·
Newspapers
provide a good medium for
conveying specific, detailed
information such as
price,
percentage discounts & product
features.
·
Local
daily & weekly newspapers
are No.1 advertising choice
of most small
businesses.
UTILITY
Of MAGAZINES
·
Where
potential market is highly targeted
&/or scattered over a wide
geographical area.
105

Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
·
Where
advertisers want broader target & a
more narrow geographic
range.
·
Where
advertisers who have patience &
are more interested in
building long term
business
than in rapid sales.
HOW
TO USE DIRECT MAIL:
Direct
mail refers to brouchers,
letters, post cards and catalogs that
are sent through mails
and
are
expected to bring an immediate sale or
inquiry.
Who
should use direct
mail?
The
following categories of advertisers can
use direct mail for
effective results:
·
For
advertisers with a highly specific
target market.
·
For
those who do not have a store or
walk in office.
·
Great
for reaching working women
& other business people.
·
For
those who don't mind making
a relatively high initial
investment to get a high rate of
response.
Costs
of direct mail:
The
costs of direct mail vary
greatly as explained
below:
·
From 5
Rs. to Send a letter to
thousands for sending modest
catalog mailing.
·
One
way is to send through JOINT
Mailing.
Mailing
List Three Types
1.
Your customer list: Your sales
data.
2.
Compiled lists: From
directories.
3.
Responder lists: Who responded to
direct mailings.
RULES
OF DIRECT MAIL:
Before
you begin to plan your
package of direct mail
following principles of any
direct mail
should
be kept in mind:
Stress
Benefits: Benefit
statement most important,
Headline must state primary
benefit of
offer.
Repeat
offer more than once:
Three
times - in letter, brochure,
response device.
Offer
an incentive: Buy
within 30 days & receive the
free book.
Offer
a Guarantee: "Guaranteed
for life" or "life time
guarantee".
Give
more than one option to
respond: Like
giving option to call or
order by mail.
Put
your copywriter in charge:
Use
experienced copywriter for direct
mailing.
Don't
be afraid of long copy two
purposes: A long
copy should not be avoided
as it can
serve
to purposes as under:
1.
Gives casual reader more to
capture attention.
2.
Helps close sales by giving
more information.
Make
copy easily understandable: Don't make
people work too hard, you
will lose them.
106

Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
DIRECT
MAIL PACKAGE:
"A
direct mail package can be
anything from a letter to an elaborate
package containing
product
sample, videotape, and or gifts." And
this package should be based
on following
factors.
·
The
size of budget.
·
Complexity
of message to be delivered.
·
Your
positioning.
·
Amount
of time your audience will give to
your mailing.
A
typical direct mail package
can contain several pieces
e.g.:
1.
A Mailing Envelope: Try to make your
envelop as inviting as possible by using
various
proven
techniques.
i.
Chose a size and color of envelop
that doesn't look like
junk mail.
ii.
Use the right stamp
2.
Sales Letter: A good sales
letter should be as personal as possible
and as packed with
selling
copy as possible.
3.
Direct Mail Brochure: It
should be a complete, stand alone
sales piece it can be almost
of
any
length and the plain or
fancy.
4.
The Response Device: A
response device is known as
the reply card or reply
coupon this
should
contain a brief of your
offer, all price information
and your address.
107
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:Its growing importance, Explanation of Personal and non-personal selling
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:ADVANTAGES, Communication, Information, Various Media
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:FUNCTIONS OF ADVERTISING, IMPACT OF ADVERTISING
- ADVERTISING AND SOCIETY:PRACTICAL BENEFITS, ETHICS IN ADVERTISING, Marketplace & Market space
- MARKETING TOOLS:COMPONENTS OF MARKETING MIX, PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE (PLC) CURVE
- MARKETING TOOLS:SWOT Analysis, Contents & Structure, ROLE & FUNCTION OF ADVERTISING
- ROLE AND FUNCTIONS OF ADVERTISING:Structure of an Advertising Agency, How to Select an Advertising Agency
- ADVERTISING PLANNING:ADVERTISING OBJECTIVES, Types of Advertising, Positioning Strategies
- POSITIONING:BRANDING, 7 Steps of Creative Process, UNIVERSAL ADVERTISING STANDARDS
- ADVERTISING MESSAGE:Message Content, BASIC TERMS & CONCEPTS
- ADVERTISING BUDGET:4 Methods to determine, ADVERTISING RESEARCH, ADVERTISING RESEARCH
- ADVERTISING REACH:BROAD COMMUNICATION OBJECTIVES, ADVERTISING COPY METHODS, MEDIA RESEARCH
- PRE – PLACEMENT EVALUATION:ACCOUNT PLANNING, MARKET, COMPETITION
- WORKING OF ADVERTISING:12 Steps to develop effective campaign, SOURCE or THE ADVERTISER
- ADVERTISING RESPONSE HIERARCHY MODELS:AIDA MODEL, PROCESS REQUIRED TO GET BIG IDEA
- PROBLEM SOLVING STRATEGIES:Procedure to Handle Problems, In brief, Eight principles apply to consumer behavior
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR:ADVERTISING APEALS, MEDIA MIX DECISIONS, Target Rating Point (TRP)
- CREATIVITY IN ADVERTISING:Three aspects are most accepted, Four Rules of Creativity
- COPY WRITER:CHARACTERISTICS OF COPYWRITER, IMPORTANCE OF LANGUAGE
- WHY ADVERTISING:Advertising & Market Education, ADVERTISEMENT CAMPAIGNS
- METHODS TO APPRECIATE A PROBLEM:SPONSORSHIP—an important tool, Special Characteristics
- IMPORTANT TOOL OF ADVERTISING:TELEVISION ADVERTISING, TRANSIT ADVERTISING
- ONLINE ADVERTISING:Banners, Logos, Email Ads, Keywords on Search Engines, New Developments
- ONLINE ADVERTISING:Structural Challenges, Adobe Photoshop, JAVA, HTML, DHTML, ASP & JSP
- SALES PROMOTION:Consumer Oriented Promotion, HOW TO USE TRADE PROMOTION, Dealing with the Trade
- PUBLICITY:PERSONAL SELLING, ROLE OF SALES PERSON, FUTURE OF GLOBAL ADVERTISING
- MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:Competitors, The Target Buyer, Segmenting your Market, FUTURE OF MARKET GROWTH
- MARKETING PLAN:Situational Analysis, Macro – Environment Situation, Marketing Objectives, Financial Objectives
- MARKETING PLAN:PROMOTING BUSINESS IN LOW COST, SUPPLY CHAIN, BUYER IDENTIFICATION
- HOW TO BE GOOD CLIENTS:CHANNEL BUYERS, HOW TO BE GOOD CLIENTS 14 RULES
- CLIENT – AGENCY RELATIONSHIP:HOW TO KEEP CLIENTS (10 Ways), Three Points for Consideration
- CLIENT – AGENCY RELATIONSHIP:ADVERTISING WITHOUT AN AGENCY, LOGO AND CORPORATE IDENTITY
- NEWSPAPER ADVERTISING:AD PRODUCTION,TYPES OF NEWSPAPER ADS, CIRCULATION
- OTHER ADVERTISING MEDIUM:HOW TO USE MAGAZINES, HOW TO USE RADIO, Daypart buying options
- UTILITY OF VARIOUS MEDIA:TAPE OR FILM, UTILITY OF TV, DIRECT MAIL PACKAGE
- OTHER ADVERTISING MEDIA:POINT OF PURCHASE (POP), TRANSIT ADVERTISING, LIMITS OF ADVERTISING
- CONTINUOUS TRACKING:PLANNING CAMPAIGN, HOW TO UNDERSTAND ADS, ASK BASIC QUESTIONS
- SEASONAL ADVERTISING:MAXIMIZING IMPACT, THE WEB ADVERTISING, MEASURING ADVERTISING
- COMPONENTS OF ADVERTISING:BUY - OLOGY OF MIND, BUY - OLOGY OF MIND
- CRITICISM ON ADVERTISING:SHOULD ADVERTISING BE ABOLISHED,
- EFFECT OF ADVERTISING:HOW TO PROMPT AWARENESS, CREATING DESIGN THAT SELLS
- CREATING EFFECTIVE DESIGN:LANGUAGE OF TYPOGRAPHY, HEADLINES THAT COMMUNICATE
- WORKSHEETS:DEMOGRAPHICS OF YOUR TARGET, YOUR COMPETITOR
- GLOSSARY OF ADVERTISING:ACCOUNT EXECUTIVE, PROOF, VOICE OVER
- CONCEPT OF AN AD:HOW TO DEVELOP A CONCEPT OF AN AD