 |
THE PROCESS OF WRITING II:ORGANIZING, DRAFTING, REVISING |
| << THE PROCESS OF WRITING:INVENTION, WHEN YOU START TO WRITE |
| ALL ABOUT WORDS:HOW WORDS ARE FORMED?:SUFFIXES >> |
Journalistic
Writing MCM310
VU
LECTURE
7
THE
PROCESS OF WRITING II
2.
External source of
information:
1)
Libraries
2)
Internet
3)
Resource persons
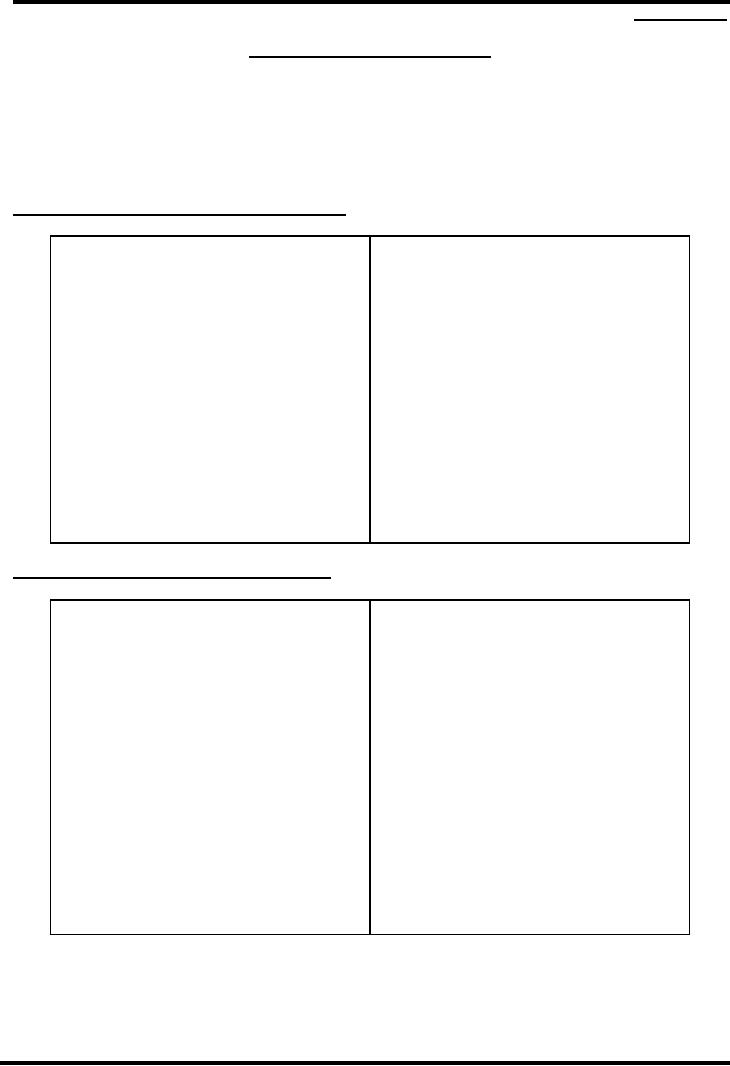
LIBRARY
OF CONGRESS CLASSFICATION
M
Music
A.
General
works
N
Fine
Arts
B
Philosophy
& Religion
P
Language
and Literature
C
History
of Civilization
Q
Science
D
General
History
R
Medicine
E-F
History
Americas
S
Agriculture
G
Geography
and Anthropology
T
Technology
H
Social
Sciences
U
Military
Science
J
Political
Sciences
V
Naval
Science
K
Law
Z
Bibliography
L
Education
SIMPLIFIED
DEWEY DECIMAL
SYSTEM
350
Administration
000
General
works
360
Welfare
100
Philosophy
&
Psychology
370
Education
200
Religion
380
Public
Services
300
Social
Sciences
390
Customs
and Folklore
310
Statistics
400
Philosophy
320
Political
Science
500
Pure
Science
330
Economics
600
Applied
Science
340
Law
700
Fine
Arts
800
Literature
900
History
Top
ten search engines:
1.
Google
2.
Alltheweb Fast and
clear.
3.
Yahoo Directories and search
engine
18

Journalistic
Writing MCM310
VU
4.
Hotbot - Directories and search
engine
5.
About sites vetted by
humans
6.
Excite - Directories and search
engine
7.
iWon
8.
MSN
9.
Completeplanet directs to various
databases
10.
Altavista - Directories and search
engine
Highly
Valuable Links:
Online
Newspapers:
http://www.ipl.org/div/news/
World
Fact File:
http://bartleby.com/151/
Encyclopedia
of Quotations: http://bartleby.com/quotations/
Columbia
Encyclopedia: http://bartleby.com/65/
Encyclopedia
of World History
http://www.bartleby.com/67/
The
Element of Style by William Strunk:
http://www.bartleby.com/141/
Encyclopedia
Britannica: http://www.britannica.com/
Encyclopedia
Americana:
http://www.americana.com/
ORGANIZING
After
writers collect information pertaining to
their topics, a useful next
step is to organize it--decide where
to
place
information in the argument, as well as
which information to omit. One
easy way to do this is
outlining.
Argumentative
and narrative papers generally
have three main
sections.
The
introduction is used to grab the
readers' attention and
introduce the main idea or
claim, often in the
form
of
a thesis statement.
The
body consists of several
supporting paragraphs that
help to elaborate upon the
main claim.
Finally,
the conclusion serves to wrap up the
argument and reemphasize the writer's
main ideas.
After
gathering information in the collection
stage, the writer should think about
where each piece of
information
belongs in the course of an argument. By
taking time to organize and plan the
paper, writers save
time
and frustration in the drafting
stage; they find that they
can follow the pattern they
have established for
themselves
in their outlines.
DRAFTING:
�
Give
yourself ample time to work on your
project.
�
Find
a comfortable place to do your
writing.
�
Avoid
distractions.
�
Take
breaks.
REVISING:
Review
higher-order concerns:
�
Clear
communication of ideas
�
Organization
of paper
�
Paragraph
structure
�
Strong
introduction and conclusion
19
Journalistic
Writing MCM310
VU
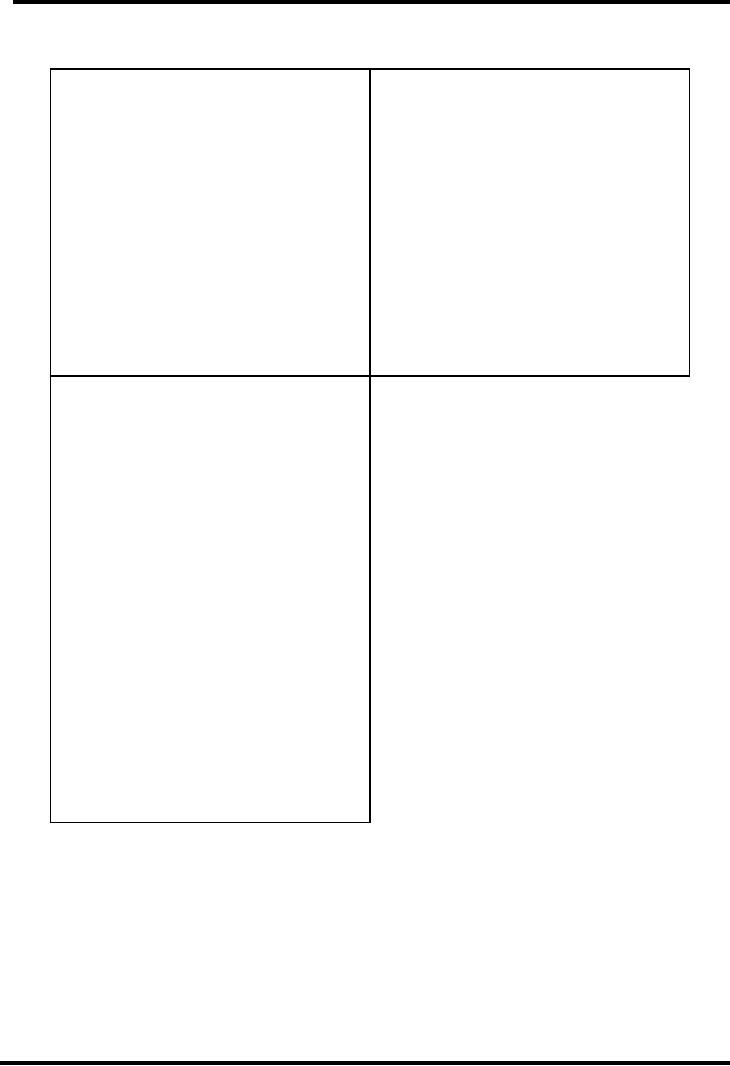
PROOFREADING:
Ask
yourself about the three
sensitive areas: Content,
format and mechanics:
B.
FORMAT:
A.
CONTENT:
Did
i:
Did
i:
1.
Choose an appropriate title?
1.
Stick to my point?
2.
Use quotations correctly?
2.
Use good source and enough
sources
3.
Use headings and
subheadings?
of
information?
4.
Label graphs, charts, and
tables?
3.
Organize my information
carefully?
5.
Include
a
list
of
resources
or
4.
Check my facts?
bibliography?
5.
Use illustration?
6.
Number the pages?
6.
Consider my readers?
7.
Use sufficient detail and
description?
C.
MECHANICS:
Did
I:
1.
Check sentences for
completeness and
sense?
2.
Check for consistent verb
tense?
3.
Check for consistent point
of view?
4.
Check for subject-verb
agreement?
5.
Check for proper use of
pronouns?
6.
Check all spellings?
7.
Check for end marks
and other
punctuation?
8.
Check
for
capital
letters
and
underlining?
9.
Check paragraph indentation?
10.
Check legibility?
Source:
Purdue University Sources.
20
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO JOURNALISTIC WRITING:Practical, THINGS TO KNOW
- QUALITIES OF GOOD WRITERS
- QUALITIES OF GOOD WRITERS
- QUALITIES OF GOOD WRITING:Achieve appropriate readability:
- QUALITIES OF GOOD WRITING:Be concise, Be creative, Be correct
- THE PROCESS OF WRITING:INVENTION, WHEN YOU START TO WRITE
- THE PROCESS OF WRITING II:ORGANIZING, DRAFTING, REVISING
- ALL ABOUT WORDS:HOW WORDS ARE FORMED?:SUFFIXES
- DICTIONARY-A WRITER’S LANGUAGE TOOL:KINDS OF INFORMATION
- PARTS OF SPEECH:Noun Gender, Noun Plurals, Countable Nouns
- BASIC CLAUSE PATTERNS
- ACTIVE AND PASSSIVE VOICE
- MODIFIERS AND SENTENCE TYPES:COMPOUND SENTENCES
- REPORTED SPEECH:Indirect Questions, Direct commands
- GRAMMATICAL SENTENCE – ISSUES:SUBJECT-VERB AGREEMENT
- GRAMMATICAL SENTENCE – ISSUES II:SENTENCE FRAGMENTS
- EFFECTIVE SENTENCE:PARALLELISM, NEEDED WORDS, SHIFTS
- STYLE: GUIDELINE AND PITFALLS I:COLLOQUIAL VS FORMAL, CIRCUMLOCUTION
- STYLE: GUIDELINE AND PITFALLS II:AMBIGUITY, REDUNDANCY, EUPHEMISM:
- PARAGRAPH WRITING: TYPES AND TECHNIQUES:STRUCTURE
- PARAGRAPH WRITING: TYPES AND TECHNIQUES:Putting on Our Play
- ESSAY WRITING:VARIOUS STRATEGIES FOR ESSAYS, PROMPTS
- SIGNAL WORDS:Non word Emphasis Signals
- EXPOSITORY WRITING:LOGICAL FALLACIES, APPEAL TO EMOTION
- THE WRITING STYLES: REPORT and NARRATIVE WRITING, SHORT REPORTS
- THE WRITING STYLES: DESCRIPTIVE AND PERSUASIVE WRITINGS, Observation
- RESEARCH WRITING AND DOCUMNETING SOURCES:Handling Long Quotations
- Summary and Précis Writing:CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD SUMMARY
- Punctuation:THE PERIOD, THE COMMA, THE SEMICOLON, THE COLON
- MECHANICS:ABBREVIATIONS, NUMBERS, SPELLING, THE HYPHEN
- READING SKILLS FOR WRITERS:EDUCATED READING, STEPS
- PARTS OF A NEWSPAPER:Box-out, By-line, Caption, Exclusive, Feature
- THE LANGUAGE OF THE NEWSPAPERS II:BROADSHEET NEWSPAPER
- News Writing and Style I:WHAT TO LOOK FOR IN A NEWSPAPER
- NEWS WRITING II:Accuracy, Clarity, Style, Qualities of Effective Leads
- EDITORIAL WRITING:WRITING AN EDITORIAL:STRUCTURING AN EDITORIAL
- WRITING FEATURES:GENERATING FEATURE STORY IDEAS
- WRITING COLUMNS:Column and a news report, Purpose, Audience
- WRITING ARTICLES FOR NEWSPAPERS:The Heading, The Lead
- WRITING ANALYSIS:purpose, scope, method, results, recommendations
- LETTERS TO EDITORS:Four important aspects about letters, Organizing letters
- BROADCAST AND WEB NEWS WRITING:WRITE CONCISELY, BROADCAST STYLE
- WRITING PRESS RELEASE, REVIEWS AND OBITUARIES:Summary of Content:
- THE ART OF INTERVIEWINGS
- FINAL THOUGHTS:Practical, Job-Related, Social, Stimulating, Therapeutic