 |
SOME USEFUL STYLE SHEETS PROPERTIES |
| << STYLE SHEETS 2 |
| JAVA SCRIPTING 1 >> |
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Lesson
12
SOME
USEFUL STYLE SHEETS
PROPERTIES
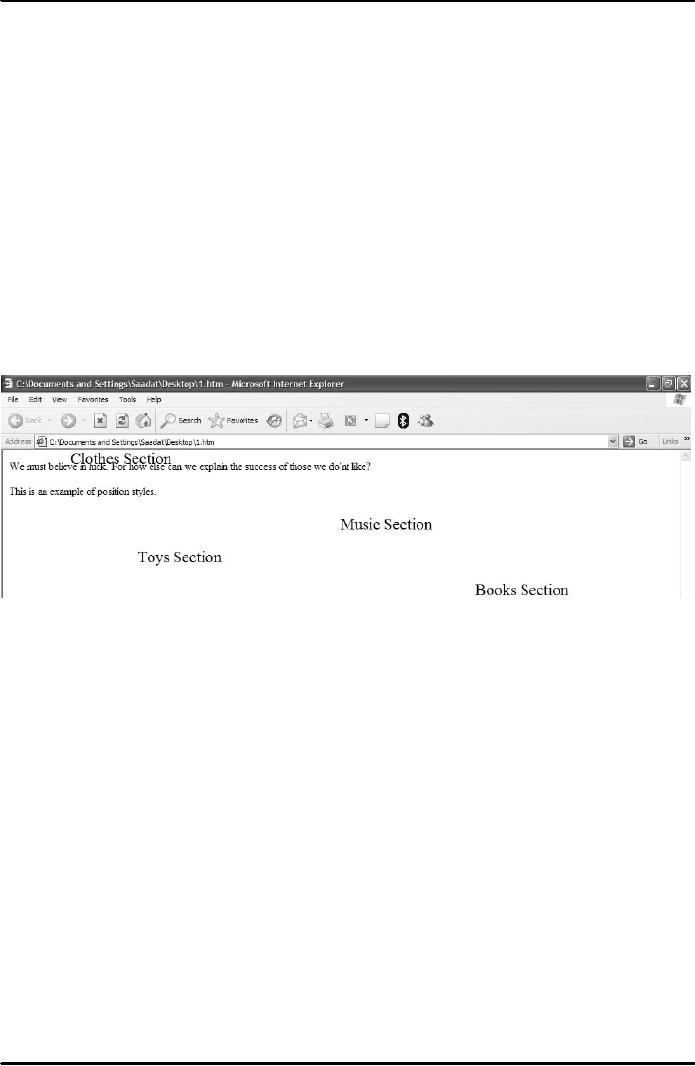
Example
position style
<HTML>
<STYLE>
DIV
{font-size: 18pt}
</STYLE>
<BODY>
<DIV
STYLE="position: absolute; left: 700px;
top: 200px">Books
Section</DIV>
<DIV
STYLE="position: absolute; left: 200px;
top: 150px">Toys
Section</DIV>
<DIV
STYLE="position: absolute; left: 500px;
top: 100px">Music
Section</DIV>
<DIV
STYLE="position: absolute; left: 100px;
top: 0px">Clothes
Section</DIV>
We
must believe in luck. For
how else can we explain the
success of those we do'nt
like?
<p
STYLE="position: static; left: 200px;
top:30px">
This
is an example of position
styles.
</BODY></HTML>
Result
is shown in Fig. 1 below.
Fig.
1
<HTML>
<STYLE>
DIV
{font-size: 18pt}
</STYLE>
<BODY>
<DIV
STYLE="position: absolute; left: 700px;
top: 200px">Books
Section</DIV>
<DIV
STYLE="position: absolute; left: 200px;
top: 150px">Toys
Section</DIV>
<DIV
STYLE="position: absolute; left: 500px;
top: 100px">Music
Section</DIV>
<DIV
STYLE="position: absolute; left: 100px;
top: 0px">Clothes
Section</DIV>
We
must believe in luck. For
how else can we explain the
success of those we do'nt
like?
<p
STYLE="position: relative; left:
200px;top:5px">
This
is an example of position
styles.
</BODY></HTML>
52

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Result
is shown in Fig. 2 below.
Fig.
2
Positioning in
the 3rd dimension
We can
use the property `z-index' for
positioning in the third dimension. For
example,
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Style
Sheet 3-D
Positioning</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<STYLE>
DIV
{font-size: 16pt; Color:red}
</STYLE>
<BODY>
<IMG
SRC="image2.gif" STYLE="z-index: 0;position: absolute;
left: 95px; top:
10px">
<DIV
STYLE="z-index: 1; position: absolute;
left: 10px; top:
60px">
<B>This
text appears on top of the
image.</B>
</DIV>
</BODY>
</HTML>
53

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Result
is shown in Fig. 3 below.
Fig.
3
Introduction
to java script
Although
JavaScript bears the name of
java, it is a very different language
that is used for a very
different
purpose.
It supports both web browser
and server side scripting.
Browser scripts are used to
create dynamic
web
pages that are more
interactive, more responsive. Before
discussing JavaScript, you should
know some
basics.
A variable defines a value stored at a
location address in the computer that
may be accessed
through
the
variable. For example Var
i=3; means
i
Location
name
3
Value
at the location
65895
Location
address
Rules
for variables
Variable
names can begin with an
uppercase letter (A-Z),
lower case letter (a-z), an
underscore character
(_),
or
dollar sign ($). Remaining
characters can be any of the
above or from digits (0-9). In
JavaScript variables
are
case sensitive. It means
that if you have a variable
`money' you cannot write
`Money' or `mONEY'.
You
don't
need to define the variable with the data
type (rather it is not allowed in
JavaScript)
General
data types
They
are as follows:
int
or integer: This
indicates the whole numbers
like 78 or 98 etc.
float :
It
is a decimal fractions like 8.9 or
6.6 etc.
Char :
It
is any alphabet from A-Z or
any digit or for that
matter any of the characters on
the
key
board you can see. Digits
defined as chars cannot have
mathematical operation on
them.
String:
When
more than one chars
join they make a string.
Boolean:
It
just has true or false
value. For example if you
have variable `pass' as boolean it
can be
true or false only.
These
data types vary in exact
definition depending on the language and
tool you are
using.
Some
might have more data
types then the ones
discussed above. JavaScript Data
types are
Number,
Boolean, String, Null and
Undefined.
Event
handler
Events
describe actions that occur
as the result of user interaction
with a web page or other
browser-related
activities.
For example, when a user
clicks a hyperlink or a button or
enters data in a form, an event
is
generated
informing the browser that action
has occurred and that
further processing is required.
The
54
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
keywords
responsible for activating certain
actions on HTML document are called
Event handlers. Some
common event
handlers are as follows: onclick,
ondbclick, onfocus , onload, onsubmit, onselect,
onblur,
onchange,
onmousedown, onmousemove, onmouseout,
onmouseover.
Changing
images using event handlers
Consider
following examples:
<HTML>
<BODY>
<IMG
SRC=contents.gif
WIDTH=170
HEIGHT=50
BORDER=0
NAME=picture
onmouseover="picture.src='search.gif';picture.width=250;
picture.height=100"
onmouseout="picture.src='contents.gif';picture.width=170;
picture.height=50">
</BODY>
</HTML>
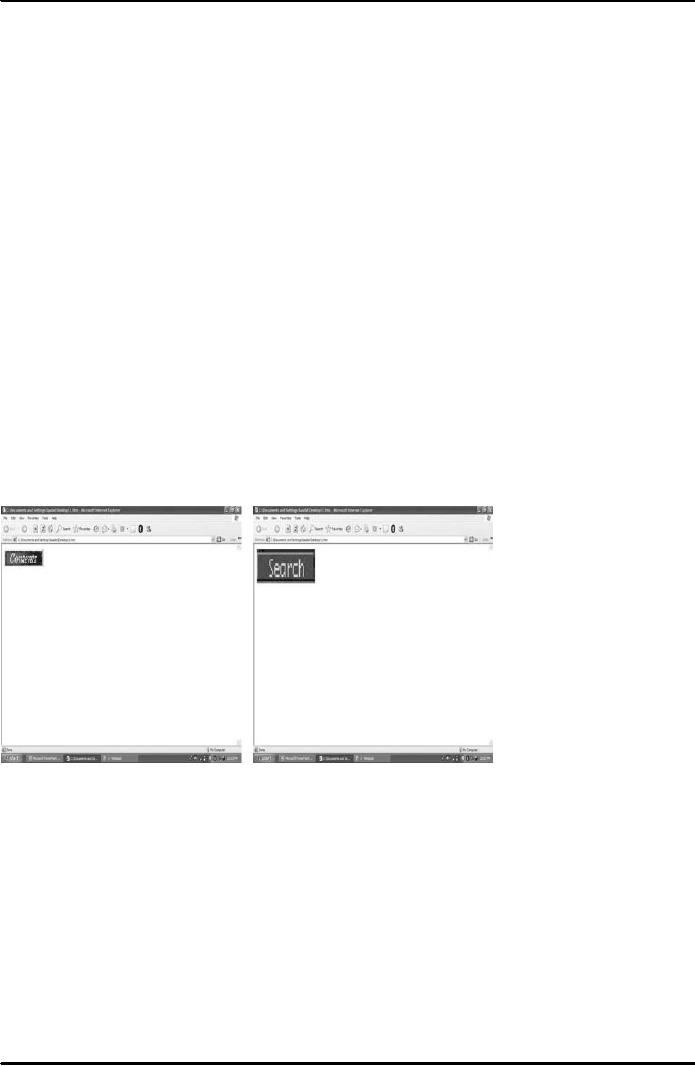
Result is
shown in Fig. 4 below. Note
that we can change the
width and height of
the
resulting
picture, that is,
`search.gif'.
Fig.
4
<HTML>
<BODY>
<A
href=image2.gif
onmouseover="picture.src='search.gif';picture.width=250;
picture.height=100"
onmouseout="picture.src='contents.gif';picture.width=170;
picture.height=50">
<IMG
SRC=contents.gif
WIDTH=170
HEIGHT=50
BORDER=0
NAME=picture>
55

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
</A>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Result
is shown in Fig. 5 below. Note that
using <A> we can make the resulting
image
`search.gif'
clikable such that when a user
clicks at it he opens a different
image `image2.gif,
as
shown
below.
Fig.
5
Objects
In computer
language an object consists of certain
properties and functions, exclusive to the object. In
all
object
oriented languages we can
create objects of our own.
In Java Script we are
provided with certain
already
defined objects which are
ready to use.
56
Table of Contents:
- E-COMMERCE
- WHAT IS A NETWORK
- HOW MANY CLASS A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE POSSIBLE
- NETWORKING DEVICES
- BASICS OF HTML 1
- BASICS OF HTML 2
- TEXT BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO BUTTONS
- FRAMES AND IMAGES IN HTML
- TAG ATTRIBUTES, SOUNDS FILES, ANIMATIONS
- STYLE SHEETS 1
- STYLE SHEETS 2
- SOME USEFUL STYLE SHEETS PROPERTIES
- JAVA SCRIPTING 1
- JAVA SCRIPTING 2
- JAVA SCRIPTING 3
- JAVA SCRIPTING AND XML
- CLIENT AND SERVER SIDE PROCESSING OF DATA
- APPLETS, CGI SCRIPTS
- MAINTAINING STATE IN A STATELESS SYSTEM
- INTEGRATION WITH ERP SYSTEMS
- FIREWALLS
- CRYPTOGRAPHY
- HASH FUNCTION AND MESSAGE DIGEST
- SYMMETRIC KEY ALGORITHMS
- VIRTUAL PIN PAYMENT SYSTEM
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 1
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 2
- SECURE SOCKET LAYER (SSL)
- E-BUSINESS: DISADVANTAGES OF E-BUSINESS
- E-BUSINESS REVENUE MODELS
- E-MAIL MARKETING
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
- META INFORMATION
- DATA MINING
- CONFIDENCE AND SUPPORT
- ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
- PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE
- SUPPLY CHAIN
- PORTERíS MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- BARRIERS TO INTERNATIONAL E-COMMERCE
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 1
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 2
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 3
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 1
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 2