 |

Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
Lesson
25
SALES
PROMOTION
OVERVIEW
This
lecture will review the
features of sales promotion as
described in the last
lecture.
Moreover
the types of sales promotion
activities its growing
importance and the way to
use
consumer
promotion and the trade promotion,
the push pull strategy of
trade promotion will be
explained
with its primary goals.
The tools of trade promotions and
how to deal with it and
other
promotional techniques besides
loyalty programs and their
mandates will be addressed.
FEATURES
OF SALES PROMOTION:
Following
the feature of sales
promotion:
·
Involves inducement to provide
incentive to buy.
·
Incentive is the key
element in a promotional
program.
·
Attempts to add value to
the product or service by
appealing to "value"
(pocket).
·
Acts as an acceleration tool.
Designed to speed up sales.
·
Targeted at different parties with
different types & levels of
incentives.
TYPES
OF SALES PROMOTION ACTIVITIES:
There
are different types of sales
promotion activities and the
two main categories in
this
regard
are explained below, while
the consumer oriented
promotion is known as Pull
strategy
and
the Trade oriented promotion
is known as Push strategy:
Consumer
Oriented Promotion:
Also
known as PULL strategy.
Targeted to Consumers, e.g. samples,
coupons, refunds,
rebates,
contests
etc.
Trade
Oriented Promotion:
Also
known as the PUSH strategy.
Targeted to Dealers / Distributors., e.g. contests and
dealer
incentives,
trade shows, trade allowances, point of
purchase displays etc.
GROWING
IMPORTANCE OF SALES
PROMOTION:
The
reasons of growing important of
the sales promotion is
explained below:
·
Retailers' Power: In these days
there is the shift at the
market place from manufacturer
to
retailer.
·
Declining brand loyalty:
Over the last few years
brand loyalty is on the
decline and the
customers
are purchasing more on the
basis of price value and
convenience. When
they
view
all brands equal they may
shift from one brand to
another.
·
Brand proliferation:
·
The market has become
saturated with new brands across
all product categories.
·
Competition: To maintain
competitive advantages manufacturers
are increasingly
using
sales
promotion.
·
Increased accountability: The
companies now demand results from
sale promotions
expenditures.
·
Short term focus: The
brand managers receive
requests from the sales
force retailers and
wholesalers
for sales promotional
activities to meet short term
targets.
·
Fragmentation of consumer market:
The large numbers of
marketers are also using
sales
promotion
techniques to target ethnic
markets. As consumers markets
are getting
fragmented,
the fragmentation due to which
mass media advertising is becoming
less
effective.
73
Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
HOW
TO USE CONSUMER
PROMOTION:
Following
are the way to use
consumer promotion:
1.
Awareness: In order to make a consumer
promotion successful it is essential to
create
awareness
in the minds of the target
audience.
2.
Trial: By creating awareness
the mind set of the
target audience to convince them to at
least
try
the product which will lead to
their using the
product.
3.
Maintain market presence: It is essential
that effective advertising
campaign is backed up
by
product supply chain to
maintain market
presence.
4.
Brand Reminder: Necessary advertising
will be required to remind consumer
about a brand
ensuring
that it doesn't go out of
the mind of the
consumers.
HOW
TO USE TRADE
PROMOTION:
There
are three primary goals to be
taken into consideration for
using trade promotion:
·
To stimulate in-store
merchandising. e.g. feature pricing,
superior store location, or
shelf
space.
·
To create a high level of
excitement about the product
among those responsible for its
sale.
·
To manipulate levels of inventory
held by whole sellers &
retailers & expanding
product
distribution
to new areas of the country
or new classes of trade.
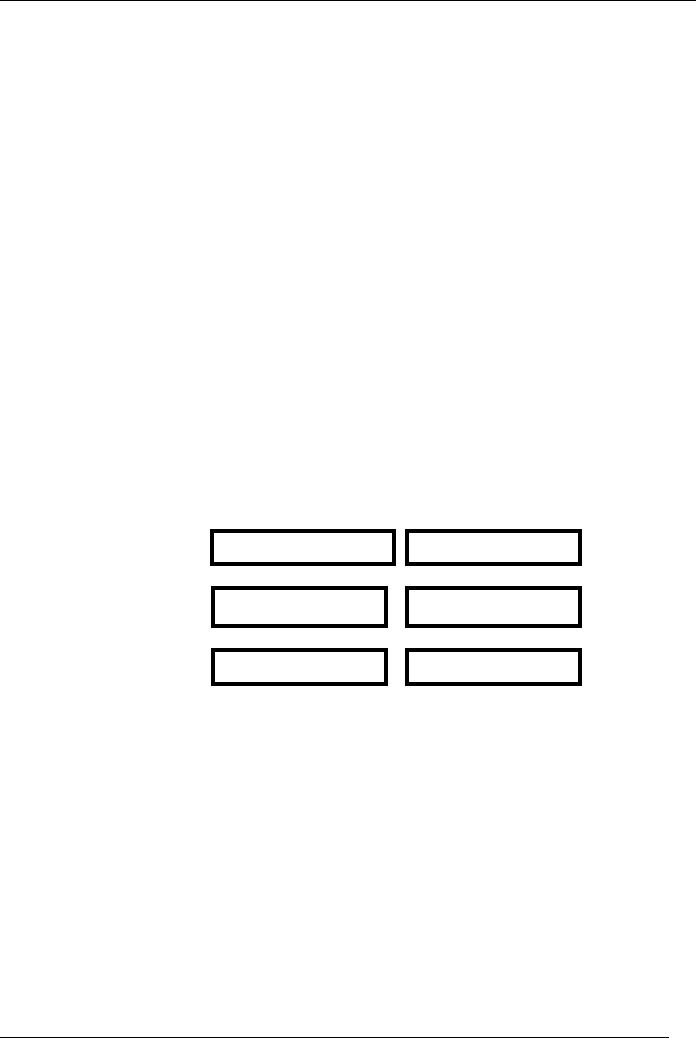
The
following chart explains the
push pull strategies for
trade promotion from
promotional
effort
to demand creation:
PUSH
- PULL STRATEGIES
PUSH
PULL
Promotional
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Effort
Reseller
Reseller
Consumer
Consumer
Demand
Creation
TOOLS
OF TRADE PROMOTION:
There
are different tools used
for trade promotion which
are described as
below:
·
Point of Purchase (POP)
Displays: A manufacturer designed
display distributed to
retailers
for
customers' attention is called
POP display.
·
Merchandise Display: Another
popular POP form is the
merchandizing display
which
retailers
used to show case their
products and create a personality
for their stores.
·
Dealer Display: Dealers displays
the product to attract
customers.
·
Trade Deals: Similar to
consumer price deal a manufacturer
may reward a reseller
financially
for purchase of a certain level of a
product or support of a
promotion.
·
Contests: Advertisers can develop
contests to motivate resellers.
·
Trade Shows and Exhibits:
The trade show is where companies
with in the same
industry
gather
to present and sell their merchandize as
well as to demonstrate their
products.
74

Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
Dealing
with the Trade:
There
are various methods of deal
with the trade to lure them
for increasing sales.
·
Bonuses: A monitory bonus is paid
to a sales person who sells
units/product over a
period
of
time.
·
Dealer Loaders: These are
premiums that a manufacturer
gives to a retailer for
buying a
certain
amount of a product.
·
Buying Allowances: A manufacturer
pays a reseller a set amount of
money or a discount
for
purchasing a certain amount of
the product during a
specified period of
time.
·
Advertising Allowances: The
manufacturer pay the
wholesaler and retailer a certain
amount
of
money to advertise the
manufacturers' product.
·
Cooperative Advertising: The
manufacturer agrees to pay a
part or all of the
advertising
expenses
incurred by the retailer
under a contractual agreement.
·
Display Allowances: A direct
payment of cash and goods is
given to the retailer agreeing
to
setup
the point of sale
display.
OTHER
PROMOTION TECHNIQUES:
Following
are the few other
promotional techniques being
used now days.
·
Sponsorships.
·
Event Marketing.
·
Aerial Advertising
Support.
·
Interactive and Internet
Promotions.
·
Loyalty Programs.
·
Partnership Programs.
·
Licensing.
·
Tie Ins.
Loyalty
Programs:
Amongst
the other promotional
techniques an important technique
being used these days
is
called
loyalty program which also
called a continuity or frequency
program (such as
airline
frequent
flyer programs) in fact
these programs are a
promotional activity to increase
customer
attention.
Following are the four
mandates of loyalty
programs.
·
Identify your best
customers.
·
Connect with those best
customers.
·
Retain the best
customers, usually by rewarding
them for their
patronage.
·
Cultivate new "best
customers."
75
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:Its growing importance, Explanation of Personal and non-personal selling
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:ADVANTAGES, Communication, Information, Various Media
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:FUNCTIONS OF ADVERTISING, IMPACT OF ADVERTISING
- ADVERTISING AND SOCIETY:PRACTICAL BENEFITS, ETHICS IN ADVERTISING, Marketplace & Market space
- MARKETING TOOLS:COMPONENTS OF MARKETING MIX, PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE (PLC) CURVE
- MARKETING TOOLS:SWOT Analysis, Contents & Structure, ROLE & FUNCTION OF ADVERTISING
- ROLE AND FUNCTIONS OF ADVERTISING:Structure of an Advertising Agency, How to Select an Advertising Agency
- ADVERTISING PLANNING:ADVERTISING OBJECTIVES, Types of Advertising, Positioning Strategies
- POSITIONING:BRANDING, 7 Steps of Creative Process, UNIVERSAL ADVERTISING STANDARDS
- ADVERTISING MESSAGE:Message Content, BASIC TERMS & CONCEPTS
- ADVERTISING BUDGET:4 Methods to determine, ADVERTISING RESEARCH, ADVERTISING RESEARCH
- ADVERTISING REACH:BROAD COMMUNICATION OBJECTIVES, ADVERTISING COPY METHODS, MEDIA RESEARCH
- PRE – PLACEMENT EVALUATION:ACCOUNT PLANNING, MARKET, COMPETITION
- WORKING OF ADVERTISING:12 Steps to develop effective campaign, SOURCE or THE ADVERTISER
- ADVERTISING RESPONSE HIERARCHY MODELS:AIDA MODEL, PROCESS REQUIRED TO GET BIG IDEA
- PROBLEM SOLVING STRATEGIES:Procedure to Handle Problems, In brief, Eight principles apply to consumer behavior
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR:ADVERTISING APEALS, MEDIA MIX DECISIONS, Target Rating Point (TRP)
- CREATIVITY IN ADVERTISING:Three aspects are most accepted, Four Rules of Creativity
- COPY WRITER:CHARACTERISTICS OF COPYWRITER, IMPORTANCE OF LANGUAGE
- WHY ADVERTISING:Advertising & Market Education, ADVERTISEMENT CAMPAIGNS
- METHODS TO APPRECIATE A PROBLEM:SPONSORSHIP—an important tool, Special Characteristics
- IMPORTANT TOOL OF ADVERTISING:TELEVISION ADVERTISING, TRANSIT ADVERTISING
- ONLINE ADVERTISING:Banners, Logos, Email Ads, Keywords on Search Engines, New Developments
- ONLINE ADVERTISING:Structural Challenges, Adobe Photoshop, JAVA, HTML, DHTML, ASP & JSP
- SALES PROMOTION:Consumer Oriented Promotion, HOW TO USE TRADE PROMOTION, Dealing with the Trade
- PUBLICITY:PERSONAL SELLING, ROLE OF SALES PERSON, FUTURE OF GLOBAL ADVERTISING
- MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:Competitors, The Target Buyer, Segmenting your Market, FUTURE OF MARKET GROWTH
- MARKETING PLAN:Situational Analysis, Macro – Environment Situation, Marketing Objectives, Financial Objectives
- MARKETING PLAN:PROMOTING BUSINESS IN LOW COST, SUPPLY CHAIN, BUYER IDENTIFICATION
- HOW TO BE GOOD CLIENTS:CHANNEL BUYERS, HOW TO BE GOOD CLIENTS 14 RULES
- CLIENT – AGENCY RELATIONSHIP:HOW TO KEEP CLIENTS (10 Ways), Three Points for Consideration
- CLIENT – AGENCY RELATIONSHIP:ADVERTISING WITHOUT AN AGENCY, LOGO AND CORPORATE IDENTITY
- NEWSPAPER ADVERTISING:AD PRODUCTION,TYPES OF NEWSPAPER ADS, CIRCULATION
- OTHER ADVERTISING MEDIUM:HOW TO USE MAGAZINES, HOW TO USE RADIO, Daypart buying options
- UTILITY OF VARIOUS MEDIA:TAPE OR FILM, UTILITY OF TV, DIRECT MAIL PACKAGE
- OTHER ADVERTISING MEDIA:POINT OF PURCHASE (POP), TRANSIT ADVERTISING, LIMITS OF ADVERTISING
- CONTINUOUS TRACKING:PLANNING CAMPAIGN, HOW TO UNDERSTAND ADS, ASK BASIC QUESTIONS
- SEASONAL ADVERTISING:MAXIMIZING IMPACT, THE WEB ADVERTISING, MEASURING ADVERTISING
- COMPONENTS OF ADVERTISING:BUY - OLOGY OF MIND, BUY - OLOGY OF MIND
- CRITICISM ON ADVERTISING:SHOULD ADVERTISING BE ABOLISHED,
- EFFECT OF ADVERTISING:HOW TO PROMPT AWARENESS, CREATING DESIGN THAT SELLS
- CREATING EFFECTIVE DESIGN:LANGUAGE OF TYPOGRAPHY, HEADLINES THAT COMMUNICATE
- WORKSHEETS:DEMOGRAPHICS OF YOUR TARGET, YOUR COMPETITOR
- GLOSSARY OF ADVERTISING:ACCOUNT EXECUTIVE, PROOF, VOICE OVER
- CONCEPT OF AN AD:HOW TO DEVELOP A CONCEPT OF AN AD