 |
Human
Relations MGMT611
VU
Lesson
07
PERSONAL
MOTIVATION AND ACHIEVEMENT
Every
individual can be well
motivated to achieve success in
work and in personal life.
High motivation
facilitates
achieving high productivity
and quality. It is important
for career building and
promotion. Self-
discipline
can motivate you and
help achieve your
goals.Motivation is an internal force to do
and achieve
personal
and organizational goals.
Needs,
wants and motivation
Personal
needs and wants drive to
work towards achieving
certain goals. In other
words, Motives are
linked
with
personal needs or
desires.
The
Need Theory of Motivation
Personal
needs and wants motivate
people until these are
satisfied. The need cycle
shows the relationship
with
work and achievement:
Need
Drive
Actions
Satisfaction
The
need cycle repeats itself, making it
difficult to every truly
satisfy people.
Needs
and Motivation
Work
and personal life offer the
opportunity to satisfy several
needs and wants.
Achievement:
Personal
achievement of needs lead people to
find joy and
satisfaction.
Power:
The
need or want for power compel people to
control resources including people
and money.
Affiliation:
People
who value relations tend to be
loyal to organizations and
also with other people.
Recognition:
People
with a strong need for
recognition wish to be acknowledged
for their contribution
and
efforts.
Discipline:
People
with a strong need for discipline
and order have the urge to
put things in order.
Risk
Taking and Thrill Seeking:
People
with a strong need for risk
taking and thrill seeking
need exciting
events
and stimulation.
There
may be a multitude of other
needs and wants that
drive or motivate people to do different
things or
tasks.
Variation
of Need
People
have different needs based
on their different
values.
A
value
is the importance a
person attaches to something
that influences the personal
action.
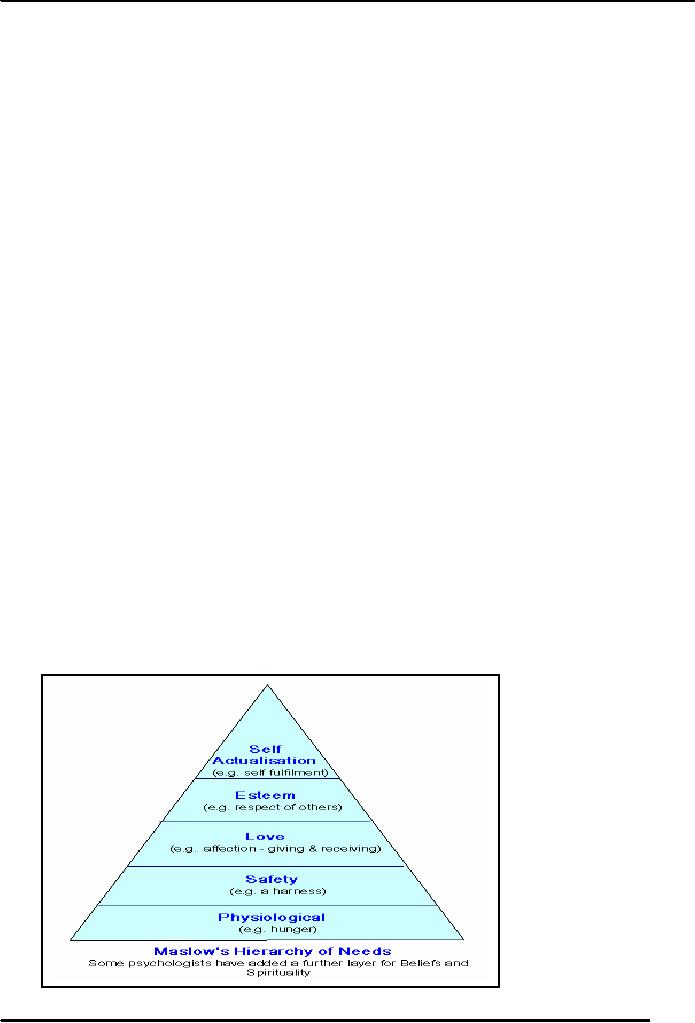
Maslow's
Hierarchy of Needs
19

Human
Relations MGMT611
VU
Maslow's
hierarchy of needs show that
people strive to satisfy the following
needs in a sequential order:
(1)
Physiological
(2)
Safety
(3)
Social
(4)
Esteem
(5)
Self-actualizing
A
person is a perpetually wanting animal.
The higher the level of need, the less
likely it is to be satisfied.
People
will make efforts to satisfy
those needs which are
important for the individual.
The first step,
however,
is the identification of a need or set of
needs.
Goal
Setting and Motivation
Success
demands identifying goals.
Almost all successful people
set goals and write them
down for personal
reminding.
A
goal is an event, circumstance, object or
condition a person strives to
achieve.
Goals
are useful because they: (a)
provide a consistent direction, (b)
improve the chances for
success and (c)
serve
as self-motivators and energizers. Combined
with self-efficacy, the contribution of
goals is even more
important.
Goals
create a discrepancy between what
exists and personal
aspirations. Such a discrepancy
leads to
dissatisfaction
and turn into a drive or
motive to eliminate the discrepancy. From
a neurological perspective,
goals
arouse the sympathetic nervous
system to action. Overly demanding
goals, however, may produce
over-arousal;
the person becomes over-stimulated and
may back away from
achieving the set
goal.
Goals
may be of different types. It
may involve learning or doing things or
tasks. A learning-goal orientation
means
that an individual is focused on
acquiring new skills and
mastering new
situations.
A
proving-goal orientation is aimed at
wanting to demonstrate and validate the
adequacy of one's
competence
by seeking favorable judgments about
one's competence.
People
with a learning-goal orientation are
more likely to seek feedback
on how well they are
performing.
Goal
Setting on the
Job
Goal
setting is important in both
profit and nonprofit firms,
especially in technical, professional
and
managerial
jobs.
Executives
set strategic goals. Workers
at lower levels establish
goals that support the
top-level strategic
goals.
An important part of goal
setting, both on and off the
job, is priority setting. If
you want to lead a
rewarding
personal life, you should
have goals and plans to
achieve them. Personal goals
heavily influence
the
formulation of career goals as well.
Integrating personal and
career goals creates balance
and stability in
life.
Types
of personal goals
Personal
goals can be divided into
different groups:
Social
and family, hobbies and
interests, physical and
mental health, financial,
etc.
Guidelines
for Goal Setting
An
action plan is needed to achieve
goals.
Specify
Goals: Vague
goals may delay action.
Concise
Goals: Use a
short, punchy statement.
Set
Realistic Goals: A
realistic goal represents the
right amount of challenge for the
person pursuing the
goal.
The higher a person's self-efficacy, the
more likely he or she may
think that a goal is
realistic.
Set
Goals for Different Time
Periods: Include
daily, short-range, medium-range,
and long-range goals.
20

Human
Relations MGMT611
VU
Include
Some Fantasy in Personal
Goal Setting: Fantasy
goals reflect a vision of the ideal type
of life
one
would like to lead. Such
goals also facilitate relaxation.
Review
Goals from Time to Time:
Some
goals lose their relevance
and therefore must be
changed.
Problems
related with
goals
A
major problem related with
goals is that goals
can
create inflexibility. They
can contribute to a narrow
focus,
thus
neglecting other worthwhile
activities.
Performance
goals can sometimes
detract from an interest in the
task.
Another
problem is that goals
can interfere with
relaxation.
Techniques
of Self-Motivation
Identifying
your most important needs
could enhance motivation. Some
other techniques are also
important
to
learn about.
Set
goals for yourself:
Goal
setting is fundamental to motivation.
Find
intrinsically motivating work:
Intrinsic
motivation refers to the natural tendency
to seek out novelty
and
challenges, to extend and use
one's capabilities.
Get
feedback on your performance:
Feedback
acts as a reward.
Apply
behavior modification to yourself:
In
using behavior modification,
remember that self-rewards
may
be more effective than self-punishments
in sustaining the right
behavior.
Improve
your skills relevant to your
goals: According
to the expectancy theory of motivation,
people
need
confidence in their skills to be
motivated.
Raise
your level of self-expectation:
The
Galatea effect is the technical term for
improving performance
through
raising one's
expectations.
Develop
a strong work ethic:
If you
are committed to the idea that
most work is valuable and
that it is
joyful
to work hard, you will
automatically become strongly motivated.
Self-discipline
and motivation
Achieving
goals and staying motivated
requires self-discipline.
The
ability to work systematically
and progressively toward a
goal until it is achieved.
The components
of
the self-discipline are as
follows:
1.
Formulate
a mission statement related
to your life.
2.
Develop
role models of self-disciplined
achievers.
3.
Develop
goals for each task.
4.
Develop
action plans to achieve
goals.
5.
Use
visual and sensory stimulation.
Self-disciplined
people form mental images of the
act of
accomplishing
what they want.
6.
Search
for pleasure within the
task. A self-disciplined
person finds joy,
excitement, and
intense
involvement
in the task at hand (intrinsic
motivation).
7.
Compartmentalize
spheres of life. Self-disciplined
people have a remarkable capacity to
divide up
(compartmentalize)
the various spheres of life to
stay focused on what they are
doing at the moment.
8.
Minimize
excuse making. Self-disciplined
people concentrate their energies on
goal accomplishment
rather
than making excuses for why
work is not
accomplished.
References
Dubrin,
A.J. (2005). Human Relations
for Career and Personal
Success. Upper Saddle River,
New Jersey,
07458.
21
Table of Contents:
- HUMAN RELATIONS:Some Guidelines for Effective Human Relations, Communication has 3meanings
- CULTURE AND PERSONALITY:Definition of sub culture, Definition of Personality, Types of Persons
- PERSONALITY AND STRESS:Personality, PERSONAL TOOLS TO CONTROL STRESS
- PERCEPTION AND INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOUR:Three concepts of personality, Bias in Perception
- PERCEPTION AND GROUP BEHAVIOR:Characteristics of Groups, Individual and Group Behavior
- ATTITUDE AND BEHAVIOUR:Types of Attitudes, Steps to turn attitude into action
- PERSONAL MOTIVATION AND ACHIEVEMENT:Needs and Motivation, Self-discipline and motivation
- SOLVING PROBLEMS SKILLFULLY:Problem solving and cognition, Ways to solve problems
- CREATIVITY IN PROBLEM SOLVING:Barriers to creativity, Tips to solve problems creatively
- HANDLING PERSONAL ISSUES:Self-Defeating Behaviour, Positive attitude to tackle personal problems
- CONFLICT RESOLUTION:WHY SO MUCH CONFLICT EXISTS, TECHNIQUES FOR RESOLVING CONFLICTS
- COMMUNICATION AND HUMAN RELATIONS:Process of communication, Improving gender barriers to communication
- ORGANIZATIONAL COMMUNICATION:To improve listening skills, Types of organizational communication
- UNDERSTANDING COMMUNICATION STYLES:Modeling communication style, Sociability continuum
- SELF-ESTEEM:Building process of self-esteem, Self-esteem and public image
- BUILDING SELF-CONFIDENCE:The importance of self-confidence and self-efficacy, Balanced Self-Confidence:
- BECOMING A LEADER-1:Assessing leadership role, Traits and Characteristics of Effective Leaders
- BECOMING A LEADER-II:Theories of leadership, Developing leadership potential
- GLOBALIZATION AND CROSS-CULTURAL DIFFERENCES:Religious Values and Bicultural Identities
- IMPROVING CROSS-CULTURAL COMPETENCE:Strategies to improve cross-cultural relations, More steps to improve Cultural Relations
- BUILDING GOOD RELATIONS WITH MANAGERS:Impressing your manager, Coping with a problem manager
- BUILDING GOOD RELATIONS WITH CO-WORKERS:Make Co-workers feel important, Maintain Honest and Open Relationships
- BUILDING GOOD RELATIONS WITH CUSTOMERS:Salesperson Represents the Business, Approaching the Customer, Excuses vs. Objections
- CHOOSING A CAREER-1:Ten Myths about Choosing a Career, Attitude toward and Perceptions about Myself
- CHOOSING A CAREER-II:Choosing a career and developing a portfolio Career, Suggestions for career Preparation
- FINDING A JOB:Targeting your job search, The Internet and Résumé Database Services, Extreme Job Hunting
- SIGNIFICANCE OF RESUME:Major types of resumes, Electronic Submission of the Résumé
- IMPROVING INTERVIEW SKILLS:Successful interview, Knowing the employer or Organization
- IMPROVING WORK HABITS-1:Reasons of procrastination, Techniques for Reducing Procrastination
- IMPROVING WORK HABITS-2:Developing the proper attitudes and values, Time-management techniques
- NEW MODEL OF CAREER ADVANCEMENT:Career portability, HUMAN RELATIONS SELF-ASSESSMENT
- TAKING CONTROL OF YOURSELF:Develop Outstanding Interpersonal Skills, Business etiquettes
- EXERTING CONTROL ON OUTSIDE ENVIRONMENT:Important communication tip, Exerting control over the outside world
- MANAGING PERSONAL FINANCES-1:Your personal financial plan, Steps in budget making
- MANAGING PERSONAL FINANCES-2:Basic investment principles, Tolerance for Investment Risks, Types of investments
- ACHIEVING HAPPINESS-1:Finding happiness and enhancing your personal life, The key to happiness
- ACHIEVING HAPPINESS-2:The Five Principles of Psychological Functioning, Your mind and Happiness
- ACHIEVING HAPPINESS-3:Need for intimacy, Working out issues with relationships
- APATHY AND ITS REMEDIES:Let us try to understand the various definitions of apathy, Coping strategies for apathy
- ENHANCING PERSONAL ETHICS-1:Influence of Culture, Common ethical problems
- ENHANCING PERSONAL ETHICS-2:Common ethical problems, Guidelines for Behaving Ethically
- HELPING OTHERS GROW:Being a Nurturing, Positive Person, A list of mentoring behaviour, Coaching skills and techniques
- REVIEW-I:What is a Human Relation?, Meanings of Communication, Two types of stress, Some personal problem, Communication style
- REVIEW-II:Steps to build self-confidence, Globalization, Building Good Relations with Co-workers, Good work habits
- REVIEW-III:New model of career advancement, Choosing your investment, Tactics for Dealing with Difficult People