 |
Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
LESSON
9
JOINT
STOCK COMPANY
JOINT
STOCK COMPANY
Joint
Stock Company is the third
major form of business
organization. It has entirely
different
organizational
structure from sole
proprietorship and partnership.
There are two
advantages
of
Joint Stock Company. First
of all, it enjoys the
advantage of increased capital.
Secondly,
the
company offers the
protection of limited liability to
the investors.
The
law relating to Joint Stock
Company has been laid in
Companies Ordinance,
1984,
which
came into force on January
1, 1985 in Pakistan.
DEFINITION
Following
are some important
definition of Joint Stock
Company:
1.
Simple
Definition
"A
company may be defined as an
association of persons for
the purpose of making
profit."
2.
According
to Kimball,
"A
corporation by nature is an artificial
person, created or authorized by a
legal statue
for
some specific
purpose."
3.
According
o S.E. Thomas,
"
A company is an incorporated association
of persons formed usually
for the pursuit of
some
commercial purpose."
Structural
Diagram
Joint
Stock Company
Specific
Purpose
Association
of
Persons
Legal
Statute
FEATURES
OF JOINT STOCK
COMPANY
Following
are the main features of a
Joint Stock Company.
46

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
1.
Creation of Law
A
joint stock company is the
creation of law or special
`Act' of the state. It is
formed and
governed
by the Companies Ordinance or by a
special Act of the
legislature. Pakistani
companies
are incorporated under the
Companies Ordinance,
1984.
2.
Capital Borrowing
The
company can borrow capital
in its own name to expand
the business.
3.
Separate Legal
Entity
A
Joint Stock Company has
separate legal entity, apart
from its members. It can
sue in a
court
of law in its own
name.
4.
Legal Person
A
Joint Stock Company, as a
legal person, has the
usual rights of any person
to carry on the
business
in its own name, to own
property, to borrow or lend
money and to enter into
contract.
5.
Long Life
A
joint stock company has
long life as compared to
other forms of business
organizations.
6.
Limited Liability
The
liability of the shareholder is
limited to the extent of the
face value of the shar4es
they
hold.
7.
Large Scale
Business
Because
of more members, a company
has larger capital as
compared to sole trade ship
and
partnership,
which helps in doing
business on large
scale.
8.
Management of Company
The
shareholders elect the Board
of Directors in the Annual
General Meeting and all
the
management
is selected by the Board of
Directors.
9.
Number of members
In
case of private limited
company, minimum number of
shareholders is `2' and
maximum is
`50';
but in case of public
limited company, minimum
number is `7' and there is
no limit for
maximum
number.
10.
Transferability of Shares
A
shareholder of a company can
easily transfer his shares
to other persons. There is
no
restriction
on the purchase and sale of
shares.
11.
Trade Agreement
A
joint stock company enjoys
separate existence, so it can
join the trade agreements
with
other
firms in its own
name.
12.
Purchases and Sale of
Property
A
joint stock company can
purchase and sale the
property in its own
name.
13.
Payment of Taxes
A
joint stock company pays
double taxes to the
government.
14.
Object
The
basic object of a joint
stock company is to earn
profit. Whole profit is not
distributed
among
the shareholders. Some
portion is transferred to General
Reserve for
emergencies.
47

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
15.
Government Control
A
joint stock company has to
comply with the rules of
the government. It has to
audit its
accounts.
16.
Easy Mode of
Investment
The
capital of a joint stock
company is divided into the
shares of small value. So,
every
person
can purchase these shares
according to his income and
saving.
17.
Common Seal
Since
a company is an artificial person
created by law, therefore, it
cannot sign documents
for
itself.
The common seal, with
the name of the company is
used as a substitute for
its
signature.
ADVANTAGES
AND DISADVANTAGES OF JOINT STOCK
COMPANY
ADVATNAGES
OF JOINT STOCK
COMPANY
Following
are the advantages of Joint
Stock Company:
1.
Expansion of Business
A
joint stock company sells
the shares, debentures and
bond s on large scale. So, a
joint
stock
company can collect a large
amount of capital and can
expand its business.
2.
Easy Access to
Credit
A
joint stock company can
get a huge amount of capital
from banks and other
institutions.
3.
Easy to Exit
It
is easy to separate oneself
from a joint stock company
by selling his
shares.
4.
Experts' Services
Because
a joint stock company has a
strong financial position, so it
may hire the service
of
qualified
and technical
experts.
5.
Employment
Joint
stock companies are also
playing very important role
to provide employment to
unemployed
persons of the
country.
6.
Flexibility
There
is flexibility in such business
organizations.
7.
Limited Liability
The
liability of the owner is
limited. In case of loss,
the shareholders are not
required to pay
anything
more than the face
value of the shares.
8.
Large Scale
Production
Availability
of huge amounts of capital
makes possible for a joint
stock company to
produce
goods
on very large scale, at a
lower cost.
9.
Larger Capital
There
is no problem of capital in a joint
stock company because there
is not limit for
maximum
number
of members. So, a joint
stock company collects
capital from many
people.
10.
Long Life
A
joint stock company has a
permanent life. If one or
more than one shareholder
die, or sell
their
shares, it makes no difference to
the company. New
shareholders take their
place.
48

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
11.
Long-term Projects
A
joint stock company has a
permanent and long life
and huge capital. Such
organizations
can
undertake the projects,
which may give profit
after many years.
12.
Spread of Risk
In
joint stock company, the
risk of business is spread
over a large number of
people. Such
organizations
can undertake risky
projects, which other types
or organization do not
take.
13.
Transfer of Shares
In
joint stock company, the
shares of public limited
company can be easily
transferred or
disposed
off. There is no restriction on
the transfer of shares in a
joint stock company.
14.
Increase in Saving and
Investment
The
shares are in large number
but their value is small.
The shares of a company may
have a
value
of Rs. 10, Rs. 100
etc. So, rich as well as
poor can purchase the
shares of a company.
This
leads to increase in savings
and investment.
15.
Better Management
Such
organization is administered by the
elected directors. These
directors are
generally
experienced
and qualified in business
field. This increases the
efficiency of the
company.
16.
Beneficial Advices
A
joint stock company can
take beneficial advices from
the government at the time
of need
which
reduces the chances of its
failure.
17.
Public Confidence
A
joint stock company is
created by law and is
supervised by legal authority.
So, a joint stock
company
can easily win the
public confidence.
18.
Higher Profits
With
the help of larger capital
and technical skill, the
cost of production is reduced,
which
increases
the rate of profit.
DISADVANTAGES
OF JOINT STOCK
COMPANY
Some
of the disadvantages of the
joint stock company are
given below:
1.
Initial Difficulties
It
is more difficult to establish a
joint stock company as
compared to other
business
organizations.
2.
Lack of Interest
Most
shareholders become relaxed
and leave all the
functions to be carried out by
the
directors.
This usually encourages the
directors to promote their
own interest at the cost of
the
company.
3.
Labor Disputes
In
such organization there is no
close contact of the workers
with the owners or
the
shareholders.
This leads to formation of
labor unions to fight
against the company's
management.
4.
Lack of Responsibility
There
is lack of personal interest
and responsibility in the
business of a joint stock
company. If
any
mistake occurs, everybody
tries to shift or transfer
his responsibilities to other
persons and
he
remains safe.
49

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
5.
Lack of Secrecy
A
joint stock company cannot
maintain its secrecy due to
the reason that a company
has to
submit
various reports to the
registrar.
6.
Lack of Freedom
A
joint stock company cannot
perform its functions freely
because it has to submit
various
reports
to the registrar form time
to time.
7.
Monopoly
Due
to larger size and
resources, a joint stock
company is in a position to create
monopoly.
Sometimes
a few customers make
agreement and exploit the
consumers.
8.
Speculation
Due
to free transfer of shares
and limited liability,
speculation in the stock
market takes place,
which
may affect the economy of
the country.
9.
Corruption
The
directors of the company do
not show the picture of
the company to the public
and
encourage
corruption by changing the
policies for their personal
interest.
10.
Complicated Process
The
formation of a joint stock
company is a complicated process
due to many legal
formalities.
11.
Centralization of Power
In
joint stock company, all
the powers have in a few
hands and due to this, an
ordinary
shareholder
cannot participate in the
affairs of a company.
12.
Double Taxes
A
joint stock company has to
pay double taxes to the
government. Firstly, company
pays tax
on
the whole profit of the
company. Secondly, every
shareholder pays tax on his
individual
income.
13.
Exploitation
Ordinary
shareholders do not have
full information about the
affairs of their company.
So, they
are
exploited.
14.
Problem of Large-Scale
Production
Since
joint stock company produces
on large-scale, so many problems
arise in the economy.
15.
Nepotism
In
a joint stock company, the
directors of company employ
their inefficient and
incapable
relatives
and friends and give
key jobs to them. As a
result, the company suffers
a loss.
16.
Late Decision
In
joint stock company, the
decision making process in
time consuming because a
meeting is
necessary
to solve the business
problems and matters.
Distinguish
between Public Limited
Company and Private Limited
Company.
PUBLIC
COMPANY
It
is a company which is formed by a
least `7' members, and
there are no
restrictions:
for
the transfer of
shares.
for
maximum numbers, and
for
subscription of shares and
debentures.
50

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
PRIVATE
COMPANY
It
is a company which is formed by at
least `2' members and
has certain
restrictions:
for
the transfer of
shares
for
maximum number of
members,
for
subscription of shares and
debentures.
DISTINCTION
BETWEEN PUBLIC
LIMITED
COMPANY
AND PRIVATE LIMITED
COMPANY
________________________________________________________________________
Public
Limited Company
Private
Limited Company
________________________________________________________________________
1.
Number of Members
Minimum
number of members
There
must be at least `2'
should
be `7' and there is
no
members
and maximum
restriction
for the maximum
number
should not exceed
number
of members
`50'.
2.
Number of Directors
Minimum
number of directors
Its
shareholders may elect
at
Is
`7' and maximum
number
least
`2' directors and
of
directors is appointed
maximum
number of directors
according
to its Articles of
is
appointed according to
its
Association.
Articles
of Association.
3.
Issue of Security
It
can invite the public
for
It
cannot invite the public
for
subscription
of its shares and
subscription
of any type of
debentures.
security.
4.
Prospectus
It
is compulsory for
public
It
is not compulsory to file
the
company
by law of file the
prospectus
with registrar's
prospectus
with the registrar's
office.
office.
5.
Certificate of Incorporation
It
cannot start the
business
It
can commence business
after
receiving the
certificate
soon
after it receives the
of
incorporation, unless it
certificate
of incorporation.
receive
the certificate of
commencement.
6.
Certificate of Commencement
It
is necessary for
public
It
is not compulsory by law
to
limited
company to obtain the
obtain
the certificate of
certificate
of commencement
commencement
of business
of
business.
7.
Title
Every
public company has to
Every
private company has
to
use
the word "limited after
its
use
the word "Private
limited"
name.
after
its name.
51

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
8.
Publication
Public
company must publish
There
is no restriction for
its
annual performance
report.
publication
of annual report.
9.
Shares Transferability
It
shares can be transferred
to
Its
shares cannot be
others
without restriction.
transferred
and disposed off to
others
without any
restriction.
10.
Statutory Meeting
It
has to hold a
statutory
It
is not required by law
to
meeting
within prescribed
hold
statutory meeting
limited.
11.
Submission of Report
It
is required by law to
submit
It
is not required by law
to
various
types of reports to
the
fulfill
the conditions of
registrar's
office, i.e.
minimum
subscription before
Auditors'
Report, Profit and
its
incorporation.
Loss
Account, Balance
Sheet.
12.
Minimum Subscription
It
cannot obtain the
certificate
It
is not required by law
to
of
commencement of business
fulfill
the conditions of
without
fulfilling the condi-
minimum
subscription before
tion
of minimum subscription.
its
incorporation.
13.
Written Consent of
Directors
In
public company
directors
he
directors of private
have
to give written
consent
company
are not required to
that
they are ready to act
as
give
their consent for
directorship.
the
directors of the
company.
14.
Tax Payment
Public
company has to pay
Private
company only pays
tax
double
tax to the
government.
on
its whole profit.
15.
Dissolution
Public
company is dissolved
A
separate legal procedure
is
according
to Companies
adopted
for the dissolution
of
Ordinance,
1984.
private
company.
________________________________________________________________________
PROCEDURE
OF FORMATION OF A JOINT STOCK
COMPANY IN PAKISTAN.
Joint
Stock Company is the third
major form of business
organization. It has entirely
different
organizational
structure from sole
proprietorship and partnership.
There are two
advantages
of
Joint Stock Company. First
of all, it enjoys the
advantage of increased capital.
Secondary,
the
company offers the
protection of limited liability to
the investors.
The
law relating to Joint Stock
Company has been laid in
Companies Ordinance,
1984,
which
came into force on January
1, 1985 in Pakistan.
Following
are the important stages or
steps for the formation of a
joint stock company:
52

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
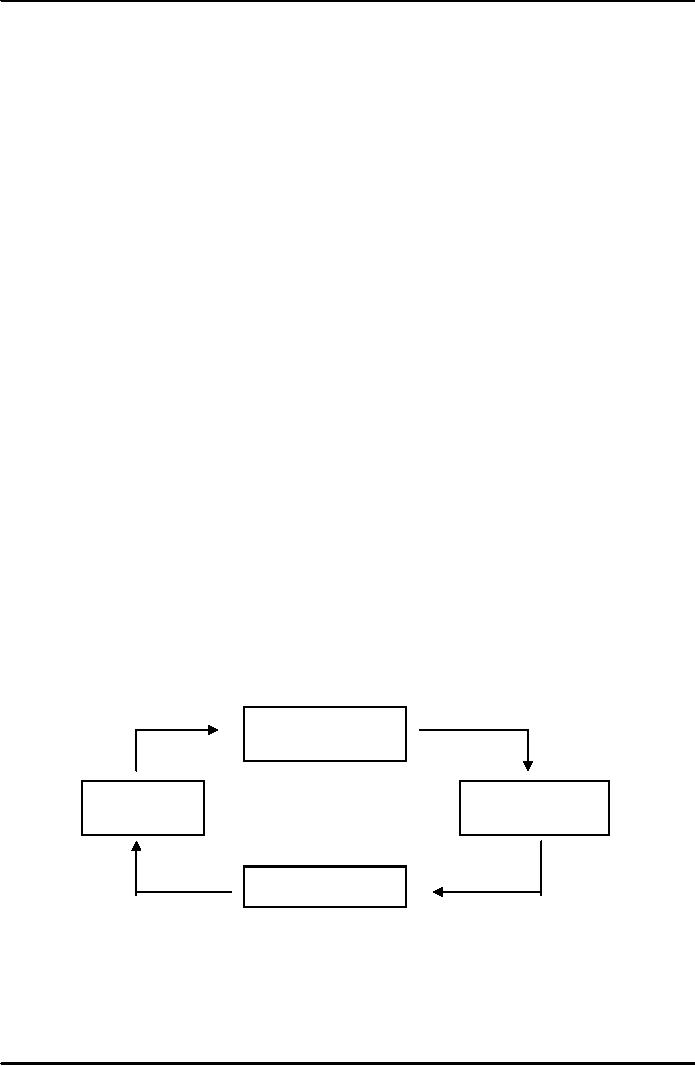
Formation
of joint Stock
Company
Promotion
Incorpo-
Capital
Certificate
Stage
ration
Subscription
of
Com-
Stage
Stage
mencement
PROMOTION
STAGE
The
promoters do the basic work
for the start of a
commercial or an industrial business
on
corporate
basis.
Promotion
is the discovery of ideas
and organization of funds,
property and skill, to run
the
business
for the purpose of earning
income. Following steps are
involved in the stage
of
promotion.
1.
Idea about
Business
Before
starting the business,
promoters have to think
about the nature and
production of
company's
business.
2.
Investigation
After
deciding the nature of
business, promoters go in preliminary
investigation and make
out
plans
as regard to the availability of
capital, means of transportation,
labour, electricity,
gas,
water
etc.
3.
Assembling various
Factors
After
making initial investigation,
the promoter starts
accumulating various factors in
order to
assemble
them. They arrange license,
copyrights, employment of necessary
employees etc.
4.
Financial Sources
The
promoters also decide the
capital sources of the
company and they work
out the ways
through
which capital can be
generated.
5.
Preparation of Essential
Documents
In
addition to above discussed
matters, the promoters also
prepare following
essential
documents
for the formation of
company:
Memorandum
of company
Articles
of company
Prospectus
of company
The
promoters carrying out these
various activities give the
company its physical form in
the
shape
of:
Giving
a name to the company
Sanctioning
of Capital Issue
INCORPORATION
STAGE
The
second stage for
establishment of a company is to get it
incorporated.
1.Filling
of Document
Following
documents are to be submitted by
the promoters in the
Registrar's office.
(a)
Memorandum of Association
A
document indicating name,
address, objects, authorized
capital etc. of a
company.
53

Introduction
to Business MGT 211
VU
(b)
Articles of Association
A
document containing laws and
rules for internal control
and management of a
company
(c)
List of Directors
A
list of the names,
occupations, addresses, along
with the declaration of
directors.
(d)
Written Consent of
Directors
A
written consent showing
their willingness to act at
directors, to be sent to the
Registrar.
(e)
Declaration of Qualifying
Shares
A
declaration certificate showing
that the directors have
taken up qualifying shares
and have
paid
up the money or pay it in
near future to the
registrar.
(f)
Prospectus
Promoters
have to file a prospectus
with the registrar.
(g)
Statutory Declaration
A
statutory declaration is to be sent to
the Registrar that all
legal formalities have
been
completed.
2.
Payment of Registration
Fee
For
the registration of company,
the registration fee is also
paid to the Registrar. For
example.
Application
and documents filing
fee
Registration
fee
Stamp
fee on Memorandum and
Articles
3.
Certificate of Incorporation
If
the registrar finds all
the documents right and
thinks that all formalities
have been fulfilled
then
he issues the certificate of
incorporation to promoters.
CAPITAL
SUBSCRIPTION STAGE
After
getting certificate of incorporation,
the next stage is to make
arrangement for
raising
capital.
For any kind of business,
the company raises its
capital through following
sources:
By
Issuing Shares
By
Issuing Debentures
By
Savings
CERTIFICATE
OF COMMENCEMENT
For
the commencement of business,
every public company has to
obtain the certificate
of
commencement,
which requires the
fulfillment of following
conditions:
1.
Issue of Prospectus
A
company has to issue
prospectus for selling
shares and debentures to
public.
2.
Allotment of Shares
The
shares and debentures are
allotted according to the
pro visions of memorandum,
when
applications
are received from the
public.
3.
Minimum Subscription
It
is also certified that the
shares have been allotted up
to an amount, not less than
the
minimum
subscription. After verifying
the foregoing documents, the
registrar issues a
certificate
of commencement of business to public
company.
54
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:CONCEPT OF BUSINESS, KINDS OF INDSTRY, TYPES OF TRADE
- ORGANIZATIONAL BOUNDARIES AND ENVIRONMENTS:THE ECONOMIC ENVIRONMENT
- BUSINESS ORGANIZATION:Sole Proprietorship, Joint Stock Company, Combination
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP AND ITS CHARACTERISTICS:ADVANTAGES OF SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- PARTNERSHIP AND ITS CHARACTERISTICS:ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF PARTNERSHIP
- PARTNERSHIP (Continued):KINDS OF PARTNERS, PARTNERSHIP AT WILL
- PARTNERSHIP (Continued):PARTNESHIP AGREEMENT, CONCLUSION, DUTIES OF PARTNERS
- ORGANIZATIONAL BOUNDARIES AND ENVIRONMENTS:ETHICS IN THE WORKPLACE, SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
- JOINT STOCK COMPANY:PRIVATE COMPANY, PROMOTION STAGE, INCORPORATION STAGE
- LEGAL DOCUMENTS ISSUED BY A COMPANY:MEMORANDUM OF ASSOCIATION, CONTENTS OF ARTICLES
- WINDING UP OF COMPANY:VOLUNTARY WIDNIGN UP, KINDS OF SHARE CAPITAL
- COOPERATIVE SOCIETY:ADVANTAGES OF COOPERATIVE SOCIETY
- WHO ARE MANAGERS?:THE MANAGEMENT PROCESS, BASIC MANAGEMENT SKILLS
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT:Human Resource Planning
- STAFFING:STAFFING THE ORGANIZATION
- STAFF TRAINING & DEVELOPMENT:Typical Topics of Employee Training, Training Methods
- BUSINESS MANAGERíS RESPONSIBILITY PROFILE:Accountability, Specific responsibilities
- COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS:THE LEGAL CONTEXT OF HR MANAGEMENT, DEALING WITH ORGANIZED LABOR
- COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS (Continued):MOTIVATION IN THE WORKPLACE
- STRATEGIES FOR ENHANCING JOB SATISFACTION AND MORALE
- MANAGERIAL STYLES AND LEADERSHIP:Changing Patterns of Leadership
- MARKETING:What Is Marketing?, Marketing: Providing Value and Satisfaction
- THE MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:THE MARKETING MIX, Product differentiation
- MARKET RESEARCH:Market information, Market Segmentation, Market Trends
- MARKET RESEARCH PROCESS:Select the research design, Collecting and analyzing data
- MARKETING RESEARCH:Data Warehousing and Data Mining
- LEARNING EXPERIENCES OF STUDENTS EARNING LOWER LEVEL CREDIT:Discussion Topics, Market Segmentation
- UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER BEHAVIOR:The Consumer Buying Process
- THE DISTRIBUTION MIX:Intermediaries and Distribution Channels, Distribution of Business Products
- PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION:Transportation Operations, Distribution as a Marketing Strategy
- PROMOTION:Information and Exchange Values, Promotional Strategies
- ADVERTISING PROMOTION:Advertising Strategies, Advertising Media
- PERSONAL SELLING:Personal Selling Situations, The Personal Selling Process
- SALES PROMOTIONS:Publicity and Public Relations, Promotional Practices in Small Business
- THE PRODUCTIVITY:Responding to the Productivity Challenge, Domestic Productivity
- THE PLANNING PROCESS:Strengths, Weaknesses, Threats
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT:Planning for Quality, Controlling for Quality
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT (continued):Tools for Total Quality Management
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT (continued):Process Re-engineering, Emphasizing Quality of Work Life
- BUSINESS IN DIGITAL AGE:Types of Information Systems, Telecommunications and Networks
- NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION MODES:Body Movement, Facial Expressions
- BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS:Organization as a System
- ACCOUNTING:Accounting Information System, Financial versus Managerial Accounting
- TOOLS OF THE ACCOUNTING TRADE:Double-Entry Accounting, Assets
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT:The Role of the Financial Manager, Short-Term (Operating) Expenditures