 |
FM – A NEW GENERATION IN BROADCASTING:Low Cost, The Difference |
| << ADVERTISERS’ APPROACH:Dramatized, Dialogue based, News |
| MICROPHONE TO TRANSMITTER:Amplifiers, Modulator, Transmitter >> |
Introduction
to Broadcasting MCM
411
VU
LESSON
18
FM
A NEW GENERATION IN
BROADCASTING
FM
very much heard these
days. For long, listeners
have been accustomed to
hearing
medium
wave and short wave
points of transmission, or say
frequencies at which one
can
tune
to a radio station of one's
choice. With the advancement
in programs side of
broadcasting,
progress has also been
made in the technical side
of broadcasting. In fact
the
two
sides lead each other in
the mutual growth of the
subject of broadcasting.
FM,
frequency modulation, the
nomenclature set for new
type of transmission, are
not long
range
radio stations like the
old fashioned radio stations
many of which are called
global
stations
due to their large range of
beaming across the
world.
It
should not sound too
technical to students of mass
communication to understand
some
technical
aspect of the FM radio
broadcasts. Here we may not
indulge in understanding
how
wave
theory and electromagnetic
way of sending message
affects communication through
air,
but
it is certainly like a doctor
understanding some equipment
for better usage, or an
architect
perceiving
some vital functions of some
new software meant for
designing and construction
of
buildings
on modern lines.
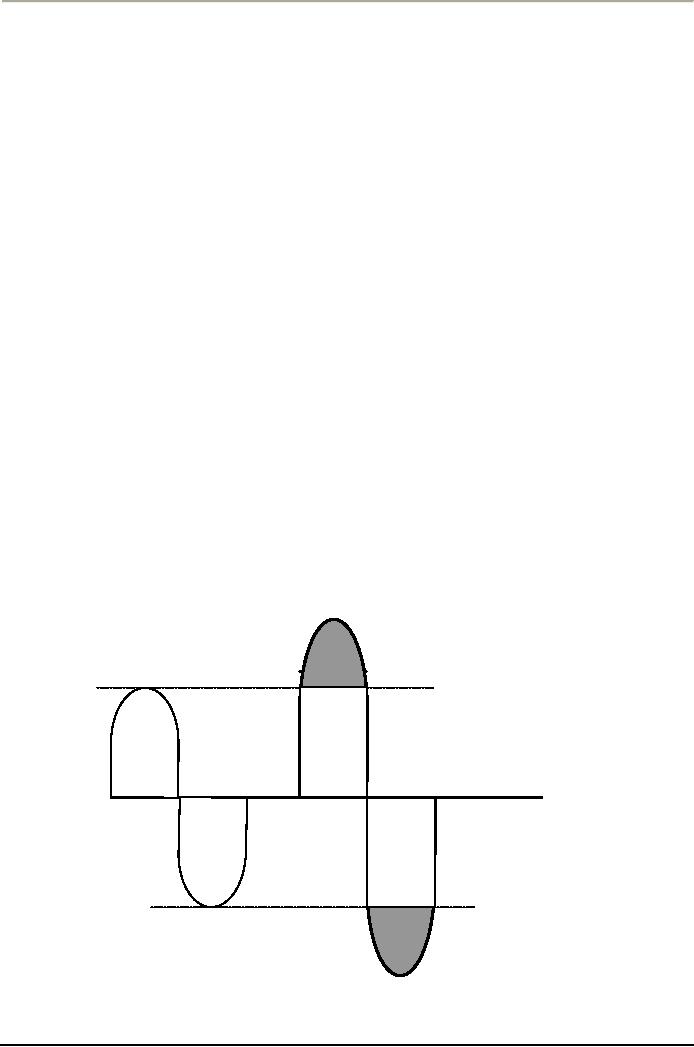
Amplitude
& Frequency Modulation
In
the case of Amplitude
Modulation, or the AM broadcast,
the sound waves after
put along the
electromagnetic
waves, are only given a
treatment to the amplitude of
the wave, and not
its
frequency.
Measured in volts, the
amplitude is the number of
times you can amplify a
wave to
give
it a strength to a desired
level.
It
is like this;
AM
Diagram
A
B
38
Introduction
to Broadcasting MCM
411
VU
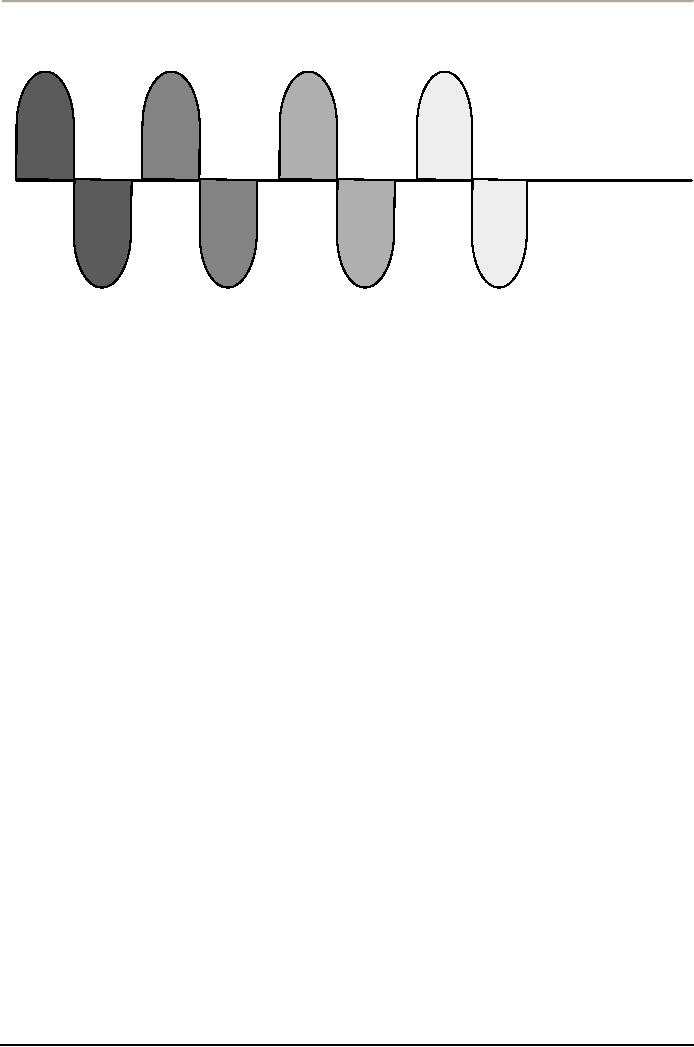
FM
Diagram
The
same wave in the case of FM
is treated differently; the
number of times it spins
have been
increased
instead of its height, or
amplitude be disturbed.
Advantages
& Disadvantages
The
AM has been strong and
could be transmitted to more
distance as compared to FM
but
problem
with AM is that it interacts
more with static charge
like coming from the
thundering
clouds,
or the waves emitting from
other sources as a spark
plug of a motorbike and the
likes.
At
times the interference goes
to a level that distortion so
created does not allow a
listener to
hear
what is being broadcast. The
quality of transmission has to be
compromised, sometime,
beyond
normal level of tolerance of
your target
listeners.
On
the contrary, the FM way of
transmission is less prone to
interferences caused by
static
charges
or electrical sparks. Due to
high frequency, its waves
show resistance to other
waves
and
take the original broadcast
strongly to end point of its
range of transmission which is
fairly
less
than the one possible
with AM mainly because the
transmission of the FM is based on
the
physics
principle of Line-in -Sight.
More it rubs with the
ground, weaker it becomes as a
signal.
So
a higher and powerful
transmitter will ensure a
clear transmission by an FM station
from
listeners'
point of view.
Low
Cost
The
cost of setting up an FM radio
station is very low as
compared to a traditional
radio
station.
But still, the equipment
required includes; transmitter,
main studio and two
small
studios,
control room where most
equipment is installed and
one continuity studio. A set
of
computers
loaded with multimedia
software, set of headphones
and a high quality radio
set
should
suffice to make things
rolling.
The
FM Broadcasting Products
In
their nature the programs
meant for an FM station are
only little different from
the ones you
can
hear from AM station, the
fact that an FM station is
not heard at a far off
place, however,
reduces
its utility as a commercial
brand broadcasting facility.
But local area advertisers
are
much
inclined to exploit an FM station in
their region to publicize
their products, and that
earns
money
for the FMs.
39

Introduction
to Broadcasting MCM
411
VU
The
regular programs include
talawat, naat, qawwalies,
national songs and folk
songs. But as
is
the practice, film and
album songs with a touch of
pop and rock are
the hot favorites for
the
disc
jockeys, though a ghazal
here and some musical
insertion there also
continues.
Handling
the Broadcast
Well,
at the FM stations you need
back-to-back programs. The
program schedule, which
must
be
made on weekly basis, should
ensure that programs are in
hand to ensure continuity.
What
is
killing for an FM station, is a
pause, or pauses of inordinate
length. Even a couple
of
seconds
silence will lead to tuning
to other stations and
causing a permanent loss of
your
build-up
audience.
Performing
as an anchor-person on FM station is not
an ordinary broadcasting attitude.
The
talent
must be trained enough to
understand the exact
requirement
of
his/her job. The script
must be practiced regularly
and all property, of speech
should be
exploited
to keep the interest of your
listeners in tact.
The
Difference
Though
not a rule, the practice is
to avoid airing long
discussions, talk shows or
other serious
natured
current affairs programs.
Dramas are one entity
yet not known widely to
the FM
stations.
Latest music albums,
interactive-talking to listeners through
telephone, taking their
e-
mails
or ordinary mail in between
musical programs are the
hallmark of their
broadcast.
Some
FM station Services
As
a regular feature a number of FM
stations are doing some
services, very useful to
listeners,
especially
who are traveling; weather
reports after regular
intervals like it is raining at
the
highway
near Hyderabad, DG Khan,
Gujranwala or Shahrah e Karakrum.
Currency exchange
rates,
PIA flights or some train
timings also mark their
approach to keep supplying
such useful
announcements
to the listeners.
40
Table of Contents:
- BROADCASTING:Historical Facts about Radio, Wireless and Radio
- CLASSIFICATION OF PROGRAMS:NEWS, Language, Sensationalizing
- CURRENT AFFAIRS:Talk Shows, Discussions, Seminars, Live Shows
- OUTDOOR BROADCASTING I:VIP Movement, Suddenly Assigned Events
- OUTDOOR BROADCASTING II:Pakistan Day March Past, General Elections
- CURTAIN RAISER:Political, Financial, Sports, Academics
- RADIO FEATURE:Personality Features, Features on Events
- MUSICAL PROGRAMS:Classical Music, Light and Film Music, Folk Music
- RADIO DOCUMENTARY:Narrative, Dramatized, Imagination, Close to places
- DISC JOCKEY:Women in Focus, Daily/ Weekly Division, Making Titles
- VOICE IN BROADCASTING:Speech, Accent, Loudness, Stress
- NOISE:Physical, Medium itself, Problem at sender’s end, Semantics
- STUDIO:Drama Studio, Studios for Talk Shows/ Discussions, Music Studios,
- RADIO DRAMA I:Stage Dramas, Early Radio Dramas, Ethics, Classification
- RADIO DRAMA II:Selection of director, The Playwrights, Script, Voices
- ADVERTISEMENT – INCOME GENERATION:Similarities, More Analysis
- ADVERTISERS’ APPROACH:Dramatized, Dialogue based, News
- FM – A NEW GENERATION IN BROADCASTING:Low Cost, The Difference
- MICROPHONE TO TRANSMITTER:Amplifiers, Modulator, Transmitter
- WRITING SCRIPT FOR RADIO BROADCAST:NEWS Script, Interviews
- INTERACTIVE BROADCASTING:On-line, E-mails, Interview, Views in News
- REVISION:CURRENT AFFAIRS, RADIO FEATURE, MUSICAL PROGRAMS
- HISTORY OF TELEVISION:Early History, The Black & White Images, Color Television
- PAKISTAN TELEVISION (PTV):The Excitement, Timing, Live Broadcast
- BROADCASTING LAWS:Laws in the 19th century, Press Council of Pakistan
- REPLICAS OF RADIO BROADCAST:The Staff, News Reading, Programming
- NEW SCRIPT WRITING AND DIRECTION TECHNIQUES:TV Script
- SETS:Permanent Sets, Hot & Cover Sets, Special Sets, Economical
- CAMERA SHOTS – THE VISUAL LANGUAGE:Angle Shots, Movement shots
- LIGHTS IN VISUAL BROADCASTING:Light Temperature, Light and Distance
- INTERIOR AND EXTERIOR:NEWS and Interviews, Dramas and Music
- BROADCASTING AND MEDIA IMPERIALISM:The truth in the debate
- ENVIRONMENT OF TV BROADCAST:Optical Illusions, POV, Depth of Field
- BUDGET:First Part, Second Part, Third Part, The Sponsors
- COMPARISON AND CONTRAST OF DIFFERENT RADIO AND TV FORMATS:TV NEWS
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – FROM RADIO TO TV:Seminars, Interviews
- PRE-PRODUCTION:Brain Storming, Scripting a new program, Approval
- PRODUCTION & POST-PRODUCTION:Booking Shifts, Rehearsals
- TV ADVERTISEMENTS – MONEY WITH ENTERTAINMENT:Early Phase, Getting Spots
- ENIGMA OF MORE CHANNELS:The Investment, Fresh Ideas, Closure of channels
- ANCHORPERSON:Appearance and Confidence, Job Opportunities
- COMPARISON BETWEEN RADIO AND TV BROADCAST:The Difference, Script
- TERRESTRIAL TO SATELLITE TO CABLE TV:Cable Network, CD Channels
- CAREER IN BROADCASTING:Production, Direction, Lighting Director, Script Writer
- REVISION (LESSON 23 TO 44):Broadcasting Laws, PEMRA, Budget