 |

Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
Lesson
19
COPY
WRITER
OVERVIEW
This
lecture will discuss creativity
for profit in advertising.
Moreover in the lecture we
will
discuss
in detail about the copy
writer, its role, work,
tasks and characteristics. We will
also
explain
about the importance of
language in advertising and illustrate
the anatomy of an ad and
general
adjectives and verbs used
while designing an ad and preparing a
copy.
CREATIVITY
vs. PROFIT:
The
basic purpose of any advertisement
within a business or commercial
environment is to
ensure
how much it helps in
promoting the business of
the company thereby being an
essential
part
of its profitability. Therefore,
the only judge of creativity
is how it helps to achieve
profits.
The
important points in this regard
for the creative artists
should be to first make sure that
the
message
is driven home and then add
all the creative stuffs
desired without spoiling the
main
purpose.
The two parameters in this
regard or consequence are i.e.: "Impact"
and
"Relevance"
and
in this context following
points of creativity should
not be ignored.
·
Creativity should include
not only brand communication
but also brand experiences
collected
over a period of
time.
·
It should not only
include compelling words &
visuals but also have
catching ideas that
add
value
to the brand.
COPY
WRITER:
The
purpose of each appealing message in
advertisements is to motivate people to
buy the
advertised
goods and services. Advertising
copywriters are the people
who write slogans
like
(Nike's
"Just do it") and other slogans
carefully making punchy
phrases to coax the
target
audience
into buying deluge of
product and services. Following
description will explain
regarding
copywriter and his/her assignments in
advertising environment.
·
A copy writer is who
writes the most interesting
and original copy that will get
people
appreciating
and buying.
·
A copywriter works in creative
partnership with art
director to conceive, develop &
produce
effective
advertisements.
·
While art director
deals mainly with visual
images, copy writer provides
verbal or written
aspect.
COPYWRITER'S
WORK:
A
copywriter's work depending
upon the type of agency
may include as under:
·
Meeting with account management
team to discuss client's requirements
& background to
the
product.
·
Working in close-knit creative
partnership with art
director to generate workable
concepts
and
ideas.
·
Writing clear, persuasive and
original copy.
·
Submitting ideas & discussing
progress with the creative
director.
·
Amending &revising campaigns according to
feedback from creative director or
clients.
·
Working on several campaigns at once
under pressure & tight
deadlines.
·
Carefully proof reading
copy to check spellings &
grammar.
·
Overseeing campaign through
the production stage to
final completion.
·
Keeping up to date with
popular culture &
trends.
·
Advising would be creative &
reviewing portfolios.
51
Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
COPYWRITER'S
TASK:
Copywriting
is a job i.e. proceeds as
creative, stimulating and even
glamorous. The
copywriter's
work is often stressful since
being creative on a tight
schedule isn't all that
easy.
The
task of the copywriters
includes:
·
Writing ads for
various media.
·
Analyzing marketing
data.
·
Consulting with
clients.
·
Consulting with other members of
creative team.
·
Editing and re writing
copy.
CHARACTERISTICS
OF COPYWRITER:
The
skills abilities and personal
characteristics of a copywriter are as
follows:
·
Writing creatively &
persuasively.
·
Working under pressure.
·
Meeting deadlines.
·
Working in team.
·
Working cohesively with
clients.
·
Keeping abreast of market
trends.
·
Translating client's
preferences.
·
Having amazing sense of
humor.
·
Working on various projects
simultaneously.
·
Being a wordsmith.
IMPORTANCE
OF LANGUAGE:
In
fields of marketing & advertising
language has powerful
influence over people and
their
behavior.
First of all let us have a
look at the various
components of an advertisement.
·
HEADLINE: To grab attention.
·
ILLUSTRATION: To retain
interest.
·
BODY COPY: Details & sales
pitch.
·
SIGNATURE LINE: Brand name,
slogan & trade mark.
·
STANDING DETAILS: Address of
company.
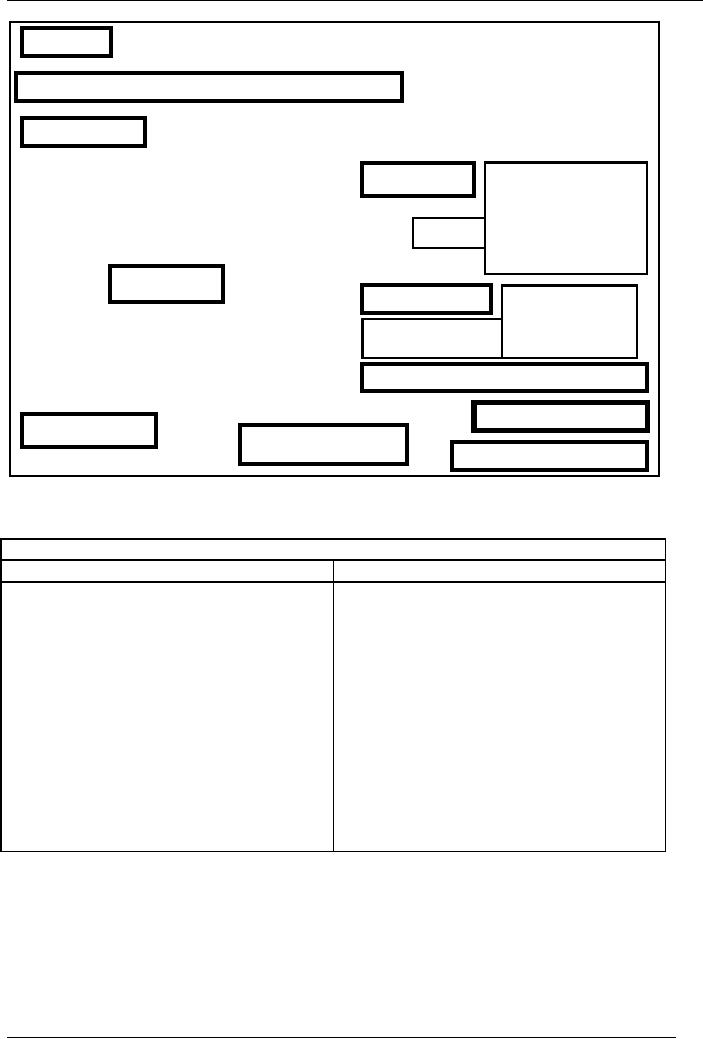
These
components are further
explained and illustrated in the
chart no. 22 namely
Anatomy
of
an Advertisement.
52
Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
ANATOMY
OF AN ADVERTISEMENT
Overline
Headline
Underline
Lead
BODY
VISUAL
Elaborator
Subheads
Wrap
up
Product
name
Caption
Facilitator
Slogan
/ Logo
VOCABULARY
USED IN ADVERTISING
ADJECTIVES
VERBS
New
Make
Good
/Better / Best
Get
Free
Give
Fresh
Have
Delicious
See
Full
Buy
Sure
Come
Clean
Go
Wonderful
Know
Special
Keep
Crisp
Look
Fine
Need
Great
Use
The
study of vocabulary used in
advertising listed above in chart
no. 23, contains
most
common
adjectives and verbs as the
language of advertising is of course
normally very
positive
and
emphasizes about one product
standing out in comparison
with another e.g.
comparatives
are
often used when no real
comparison is make such as an
advertisement of a detergent
may
say
"it gets clothes whiter"
but the question is whiter
than what.
53
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:Its growing importance, Explanation of Personal and non-personal selling
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:ADVANTAGES, Communication, Information, Various Media
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:FUNCTIONS OF ADVERTISING, IMPACT OF ADVERTISING
- ADVERTISING AND SOCIETY:PRACTICAL BENEFITS, ETHICS IN ADVERTISING, Marketplace & Market space
- MARKETING TOOLS:COMPONENTS OF MARKETING MIX, PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE (PLC) CURVE
- MARKETING TOOLS:SWOT Analysis, Contents & Structure, ROLE & FUNCTION OF ADVERTISING
- ROLE AND FUNCTIONS OF ADVERTISING:Structure of an Advertising Agency, How to Select an Advertising Agency
- ADVERTISING PLANNING:ADVERTISING OBJECTIVES, Types of Advertising, Positioning Strategies
- POSITIONING:BRANDING, 7 Steps of Creative Process, UNIVERSAL ADVERTISING STANDARDS
- ADVERTISING MESSAGE:Message Content, BASIC TERMS & CONCEPTS
- ADVERTISING BUDGET:4 Methods to determine, ADVERTISING RESEARCH, ADVERTISING RESEARCH
- ADVERTISING REACH:BROAD COMMUNICATION OBJECTIVES, ADVERTISING COPY METHODS, MEDIA RESEARCH
- PRE – PLACEMENT EVALUATION:ACCOUNT PLANNING, MARKET, COMPETITION
- WORKING OF ADVERTISING:12 Steps to develop effective campaign, SOURCE or THE ADVERTISER
- ADVERTISING RESPONSE HIERARCHY MODELS:AIDA MODEL, PROCESS REQUIRED TO GET BIG IDEA
- PROBLEM SOLVING STRATEGIES:Procedure to Handle Problems, In brief, Eight principles apply to consumer behavior
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR:ADVERTISING APEALS, MEDIA MIX DECISIONS, Target Rating Point (TRP)
- CREATIVITY IN ADVERTISING:Three aspects are most accepted, Four Rules of Creativity
- COPY WRITER:CHARACTERISTICS OF COPYWRITER, IMPORTANCE OF LANGUAGE
- WHY ADVERTISING:Advertising & Market Education, ADVERTISEMENT CAMPAIGNS
- METHODS TO APPRECIATE A PROBLEM:SPONSORSHIP—an important tool, Special Characteristics
- IMPORTANT TOOL OF ADVERTISING:TELEVISION ADVERTISING, TRANSIT ADVERTISING
- ONLINE ADVERTISING:Banners, Logos, Email Ads, Keywords on Search Engines, New Developments
- ONLINE ADVERTISING:Structural Challenges, Adobe Photoshop, JAVA, HTML, DHTML, ASP & JSP
- SALES PROMOTION:Consumer Oriented Promotion, HOW TO USE TRADE PROMOTION, Dealing with the Trade
- PUBLICITY:PERSONAL SELLING, ROLE OF SALES PERSON, FUTURE OF GLOBAL ADVERTISING
- MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:Competitors, The Target Buyer, Segmenting your Market, FUTURE OF MARKET GROWTH
- MARKETING PLAN:Situational Analysis, Macro – Environment Situation, Marketing Objectives, Financial Objectives
- MARKETING PLAN:PROMOTING BUSINESS IN LOW COST, SUPPLY CHAIN, BUYER IDENTIFICATION
- HOW TO BE GOOD CLIENTS:CHANNEL BUYERS, HOW TO BE GOOD CLIENTS 14 RULES
- CLIENT – AGENCY RELATIONSHIP:HOW TO KEEP CLIENTS (10 Ways), Three Points for Consideration
- CLIENT – AGENCY RELATIONSHIP:ADVERTISING WITHOUT AN AGENCY, LOGO AND CORPORATE IDENTITY
- NEWSPAPER ADVERTISING:AD PRODUCTION,TYPES OF NEWSPAPER ADS, CIRCULATION
- OTHER ADVERTISING MEDIUM:HOW TO USE MAGAZINES, HOW TO USE RADIO, Daypart buying options
- UTILITY OF VARIOUS MEDIA:TAPE OR FILM, UTILITY OF TV, DIRECT MAIL PACKAGE
- OTHER ADVERTISING MEDIA:POINT OF PURCHASE (POP), TRANSIT ADVERTISING, LIMITS OF ADVERTISING
- CONTINUOUS TRACKING:PLANNING CAMPAIGN, HOW TO UNDERSTAND ADS, ASK BASIC QUESTIONS
- SEASONAL ADVERTISING:MAXIMIZING IMPACT, THE WEB ADVERTISING, MEASURING ADVERTISING
- COMPONENTS OF ADVERTISING:BUY - OLOGY OF MIND, BUY - OLOGY OF MIND
- CRITICISM ON ADVERTISING:SHOULD ADVERTISING BE ABOLISHED,
- EFFECT OF ADVERTISING:HOW TO PROMPT AWARENESS, CREATING DESIGN THAT SELLS
- CREATING EFFECTIVE DESIGN:LANGUAGE OF TYPOGRAPHY, HEADLINES THAT COMMUNICATE
- WORKSHEETS:DEMOGRAPHICS OF YOUR TARGET, YOUR COMPETITOR
- GLOSSARY OF ADVERTISING:ACCOUNT EXECUTIVE, PROOF, VOICE OVER
- CONCEPT OF AN AD:HOW TO DEVELOP A CONCEPT OF AN AD