 |
THEORIES OF GENDER DEVELOPMENT (2):The Behavioral Approach |
| << THEORIES OF GENDER DEVELOPMENT:The Biological Approach, |
| THEORIES OF GENDER DEVELOPMENT (3):The Cognitive Approach >> |
Gender
Issues In Psychology (PSY -
512)
VU
Lesson
10
THEORIES
OF GENDER DEVELOPMENT
(2)
The
Behavioral Approach
Recap
The
Biological approach
Strong
and weak points
The
Behaviorist or Learning Approach
Background
According
to this approach all behavior and
personality is a result of learning. Where the
biological approach
emphasizes
"nature", the behavioral approach
stresses upon "nurture".Early
behaviorists, like Skinner,
emphasized
the importance of reinforcement
Later
on, in addition to reward
and punishment, the significance of other
variables like the social
context,
observation,
modeling, and imitation were
also included in behaviorism, that led to the
social learning approach
According
to the behavioral approach, learning of gender
roles can be explained in terms of a
result of:
�
Classical
conditioning
�
Operant
Conditioning or the use of reinforcement: positive,
negative, punishment, or no
reinforcement
�
Learning by
observation
The
behaviorists maintain that gender
role associated behaviors
are learnt and not innate,
just like any
other
cultural
patterns. They are shaped by
reinforcement (Guerin, 1992).
Children's
upbringing is designed in such a
way that they are steered
toward learning specific, socially
desired
gender
roles.
Children,
right from birth, receive
different treatment (Maccoby & Jacklin,
1974; Pomerlau et al,
1990).
This
difference may increase in later years in
childhood and can be seen in
childcare settings, as well as in
home
(Chick
et al, 2002; Huston,
1986).
The
very fact that we can find variations in
gender roles across cultures
indicates the existence of
different
treatments
(Gibbons, 2000).
But
if different treatments are the
cause of gender differences
then how did this difference
start in first place?
Can
it be that there were small
innate differences that were
amplified after different
treatment?
Classical
Conditioning
Every
time a child sees the parent of the same
sex as his/her own, he/she
is seen as wearing a particular type
of
clothes,
using fixed type of gestures,
and using a particular style of
communication. This forms a type of
association
which leads to adoption of
gender roles. But a stronger
and more plausible explanation is the
one
based
upon operant conditioning.
Operant
Conditioning
The
type of learning in which a voluntary
response becomes stronger or
weaker depending on its positive
or
negative
consequences.The organism plays an
active role and `operates'
on environment to produce the
desired
outcome.
Now why would an organism
operate on the environment? To meet, as
well as avoid, certain
consequences--------reinforcement
in other words.
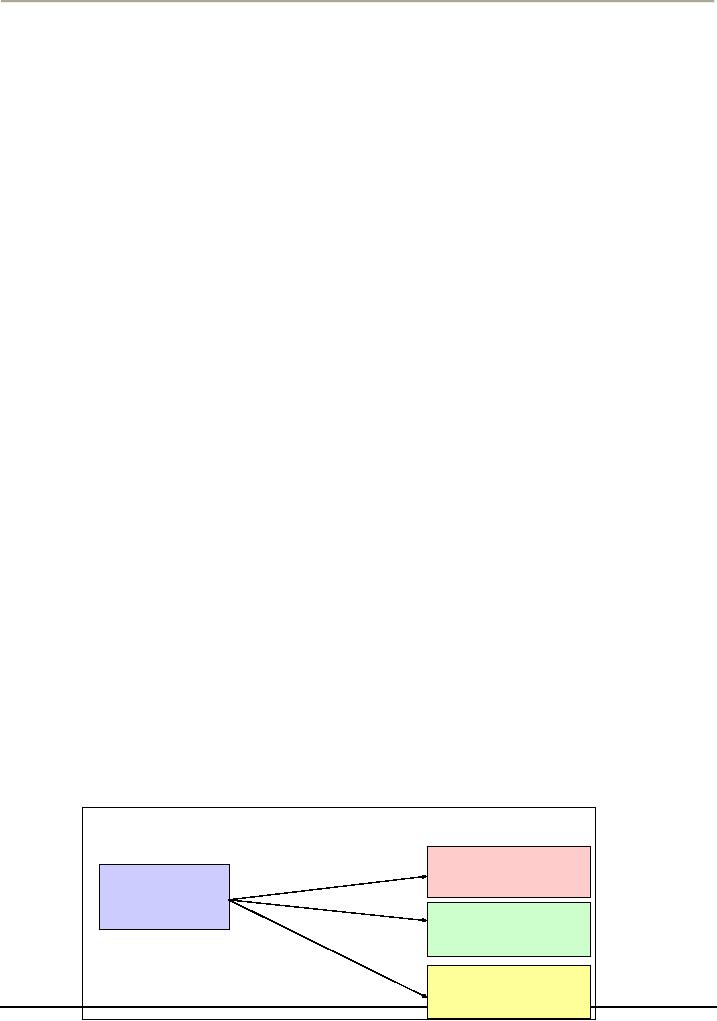
C
o n s e q u e n c e s o f B e h a v io r
P
o s it iv e
consequence
B
e h a v io r
N
e g a tiv e
consequence
No
consequence
31
Gender
Issues In Psychology (PSY -
512)
VU
The
various consequences of behavior
have different impacts on the
behavior under question.
Consequences
of Behavior and their
impact
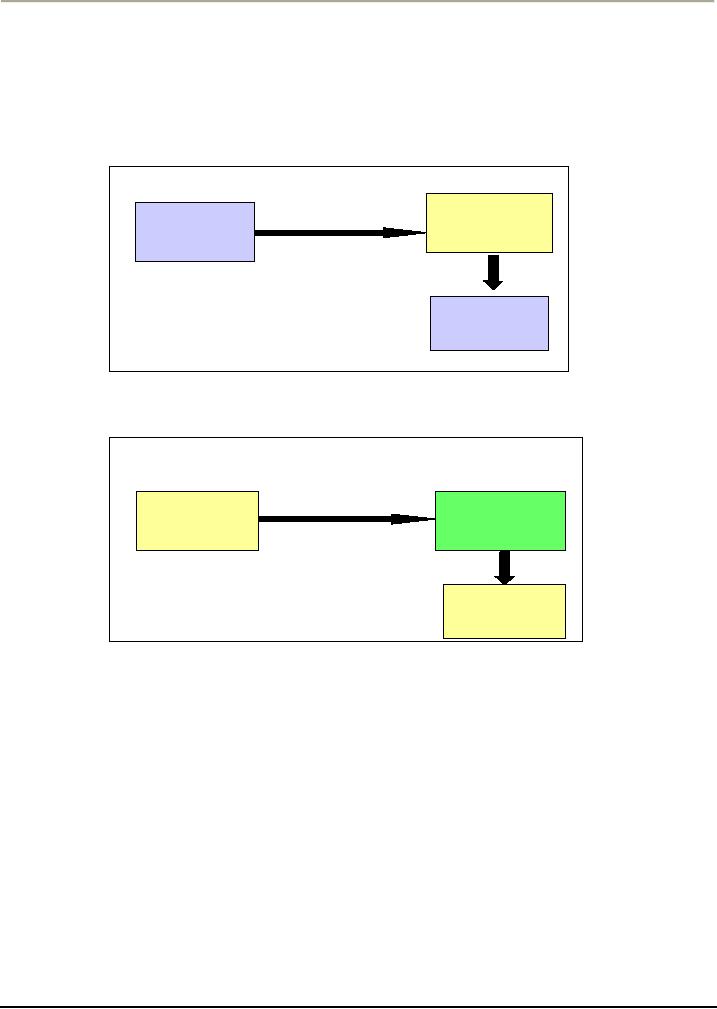
Figure:
1
Positive
reinforcement
Response/
Behavior
Response
will
be
repeated
Figure:2
Response/
Negative
Behavior
reinforcement
Response
will
be
repeated
32
Gender
Issues In Psychology (PSY -
512)
VU
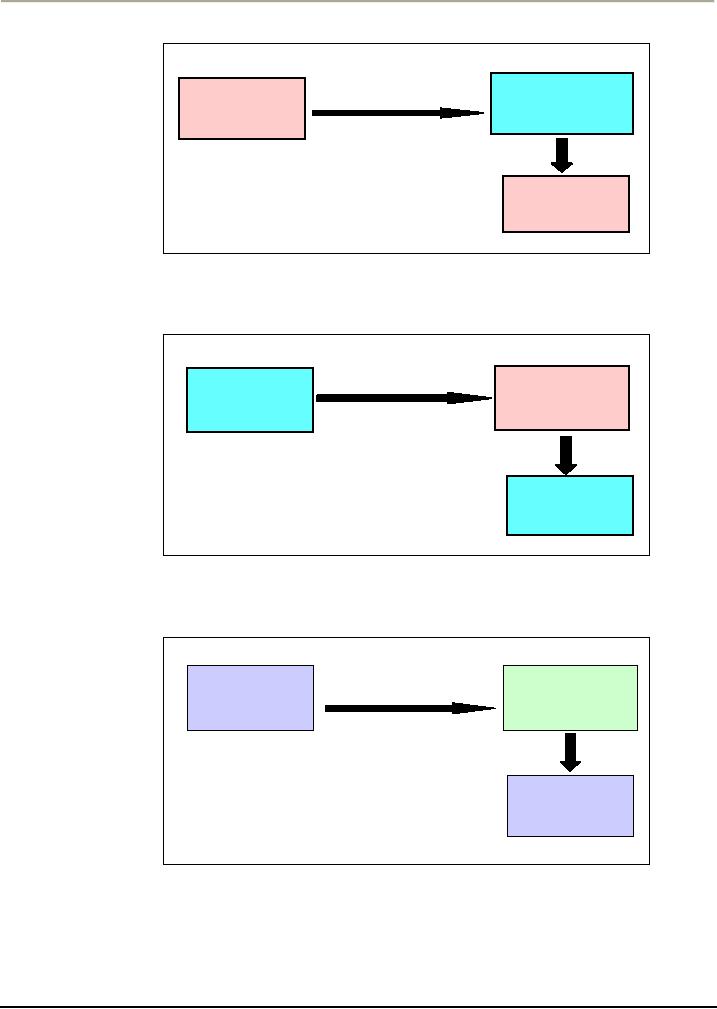
Figure:
3
Response/
Punishment
Behavior
Response
will
not be
repeated
Figure:
4
No
Response/
reinforcement
Behavior
Response
will
not be
repeated
Consequences
of behavior and learning gender
roles:
Figure:
1
Positive
Response
reinforcement
(Son
copying father)
(appreciation)
Response
will
be
repeated
33
Gender
Issues In Psychology (PSY -
512)
VU
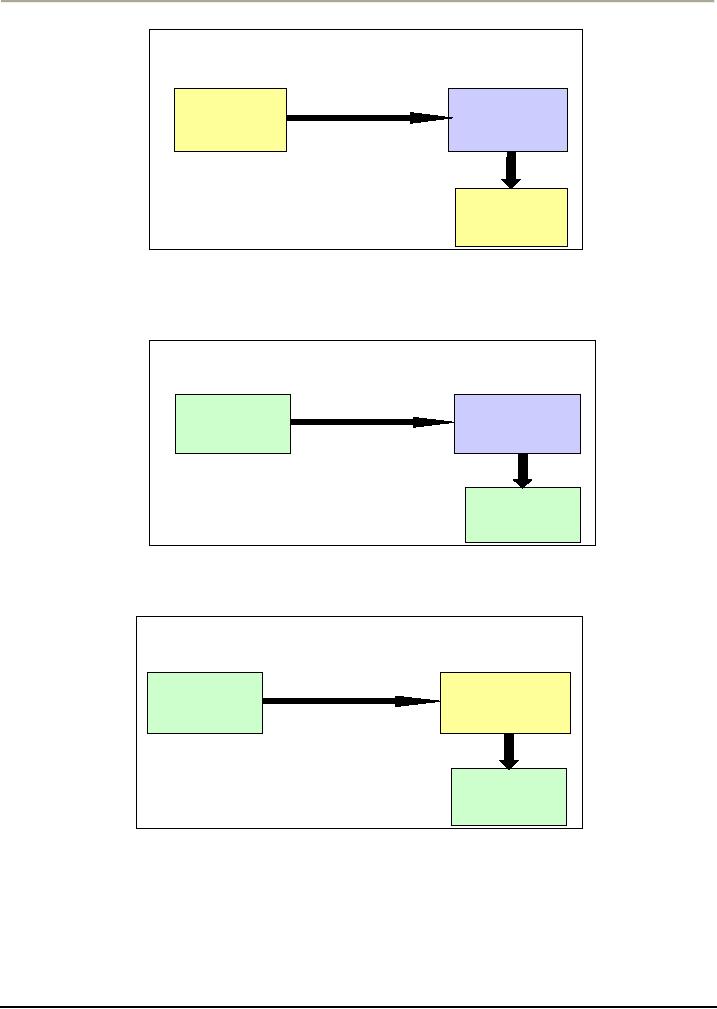
Figure:
2
No
Response
reinforcement
(boy
likes
(nobody
pays
washing
his
clothes)
attention)
Response
will
not be
repeated
Figure:
3
Negative
Response
reinforcement
(girl
works in kitchen)
(avoids
harsh
treatment)
Response
will
be
repeated
Figure:
4
Response
(S
on playing with
Punishment
dolls)
(ridiculed/scolded)
Response
will
not be
repeated
34
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Common misconception, Some questions to ponder
- FEMINIST MOVEMENT:Forms or Varieties of Feminism, First wave feminists
- HISTORICAL BACKGROUND:Functionalism, Psychoanalytic Psychology:
- Gender- related Research:Andocentricity, Overgeneralizing, Gender Blindness
- RESEARCH METHODS FOR GENDER ISSUES:The Procedure of Content Analysis
- QUALITATIVE RESEARCH:Limitations Of Quantitative Research
- BIOLOGICAL DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GENDERSHormones and Chromosomes
- BIOLOGICAL DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GENDERS: HORMONES AND NERVOUS SYSTEM
- THEORIES OF GENDER DEVELOPMENT:The Biological Approach,
- THEORIES OF GENDER DEVELOPMENT (2):The Behavioral Approach
- THEORIES OF GENDER DEVELOPMENT (3):The Cognitive Approach
- THEORIES OF GENDER DEVELOPMENT (3):Psychoanalytic Feminism
- OTHER APPROACHES:The Humanistic Approach, Cultural Influences
- GENDER TYPING AND STEREOTYPING:Development of sex-typing
- GENDER STEREOTYPES:Some commonly held Gender Stereotypes
- Developmental Stages of Gender Stereotypes:Psychoanalytic Approach, Hostile sexism
- CULTURAL INFLUENCE & GENDER ROLES:Arapesh, Mundugumor
- DEVELOPMENT OF GENDER ROLE IDENTIFICATION:Gender Role Preference
- GENDER DIFFERENCES IN PERSONALITY:GENDER DIFFERENCES IN BULLYING
- GENDER DIFFERENCES IN PERSONALITY:GENDER, AFFILIATION AND FRIENDSHIP
- COGNITIVE DIFFERENCES:Gender Differences in I.Q, Gender and Verbal Ability
- GENDER AND MEDIA:Print Media and Portrayal of Genders
- GENDER AND EMOTION:The components of Emotions
- GENDER, EMOTION, & MOTIVATION:Affiliation, Love, Jealousy
- GENDER AND EDUCATION:Impact of Educational Deprivation
- GENDER, WORK AND WOMEN'S EMPOWERMENT:Informal Work
- GENDER, WORK AND WOMEN'S EMPOWERMENT (2):Glass-Ceiling Effect
- GENDER, WORK & RELATED ISSUES:Sexual Harassment at Workplace
- GENDER AND VIOLENCE:Domestic Violence, Patriarchal terrorism
- GENDER AND HEALTH:The Significance of Women’s Health
- GENDER, HEALTH, AND AGING:Genetic Protection, Behavioral Factors
- GENDER, HEALTH, AND AGING:Physiological /Biological Effects, Changes in Appearance
- GENDER DIFFERENCES IN AGING:Marriage and Loneliness, Empty Nest Syndrome
- GENDER AND HEALTH PROMOTING BEHAVIORS:Fitness and Exercise
- GENDER AND HEALTH PROMOTING BEHAVIOR:The Classic Alameda County Study
- GENDER AND HEART DISEASE:Angina Pectoris, The Risk factors in CHD
- GENDER AND CANCER:The Trend of Mortality Rates from Cancer
- GENDER AND HIV/AIDS:Symptoms of AIDS, Mode of Transmission
- PROBLEMS ASSOCIATED WITH FEMALES’ REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
- OBESITY AND WEIGHT CONTROL:Consequences of Obesity, Eating Disorders
- GENDER AND PSYCHOPATHOLOGY:Gender, Stress and Coping
- GENDER AND PSYCHOPATHOLOGY:The Diagnostic Criteria
- GENDER AND PSYCHOTHERAPY:Traditional Versus Feminist Theory
- FEMINIST THERAPY:Changes targeted at societal level
- COURSE REVIEW AND DISCUSSION OF NEW AVENUES FOR RESEARCH IN GENDER ISSUES