 |
Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
Lesson
12:
MARKET
SEGMENTATION AND ITS
BASES
OBJECTIVES:
UNDERSTANDING:
Be
able to define market
segmentation
Learning
who uses market segmentation
and how
market
segmentation operates
Understanding
:
o
Geographic Segmentation
What
is Market?
Market
consists of:
P E O P
L E
BUT
- not just ANY people, they
have to have:
Willingness
to buy
Purchasing
power (money)
Authority
to buy
1.
Market Segmentation
The
process of dividing market
into distinct subsets of
consumers with common needs or
characteristics is called
Market
Segmentation. The concept of
segmentation goes hands in
hands with the concept of
diversity. Diversity
compliments
Segmentation
But
why do we need to segment people in
groups?
If
all consumers were alike
with same needs, wants
and desires and the same
background education and
experience
the
mass marketing be a logical
strategy.
Undifferentiated
Marketing,
Offering
the same product and marketing
mix to all consumers. When
trying to sell the same
product to every
prospect
with a single advertising campaign, the
marketer must portray its
product as a means of satisfying
a
common
or generic need and therefore,
ends up in appealing to no
one
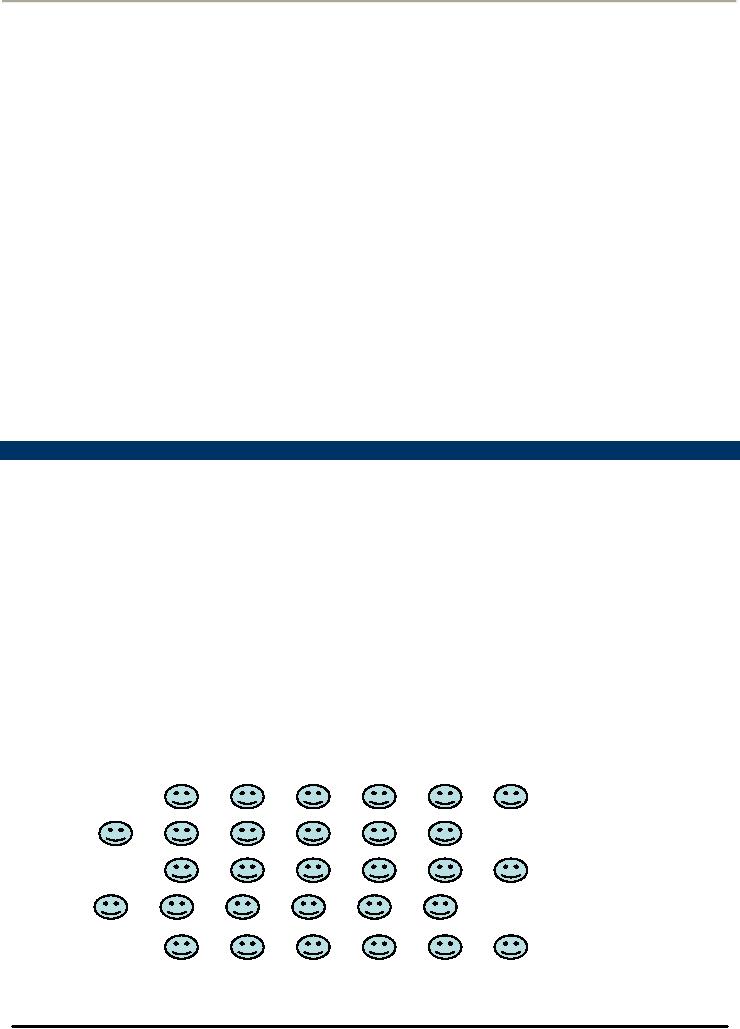
How
Market Looks Before
Segmentation
41
Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
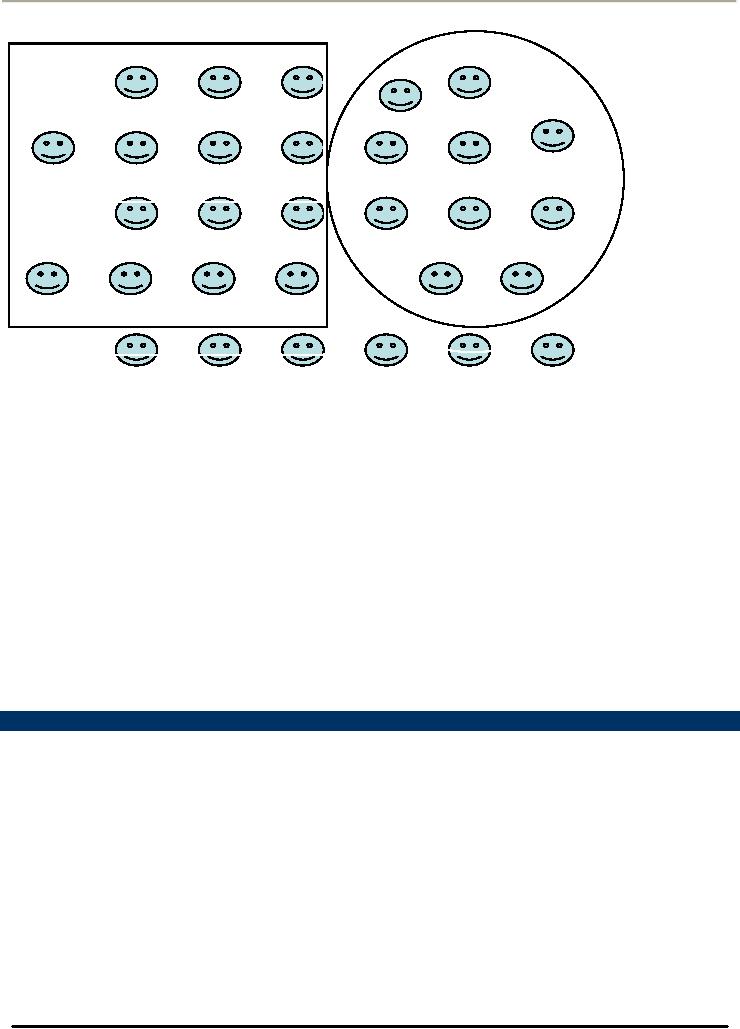
How
Market Looks After
Segmentation
Quantitative
Research Designs & Data Collection
Instruments
Segmentation
benefits both marketers and the
consumers. Marketers in all
organizations/institutions and
industries
practice segmentation strategies.
This may include consumer
goods industries, hotels,
development
sector,
etc.
How
Market Segments
Operates
1.
Fill the gaps in the
marketplace
Many
new products have been
registered to fill the gaps in the
marketplace revealed by the segmentation
studies
2.
To identify the most Appropriate
Media
Segmentation
studies are used to identify
the most appropriate media in which to
place the advertisements.
All
media
vehicles from TV and Radio
Stations to Newspapers and
magazines use segmentation
research to determine
the
characteristics of their audience
and to publicize their findings in
order to attract advertisers. In
cases if the
segments
of customers are large enough
and can attract enough advertising the
media spins off separate
programs
or
publications targeted to the specific
segments
Bases
for Segmentation
The
first step in developing the segmentation
strategy is select most appropriate
base(s) on which to segment
the
market
42
Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
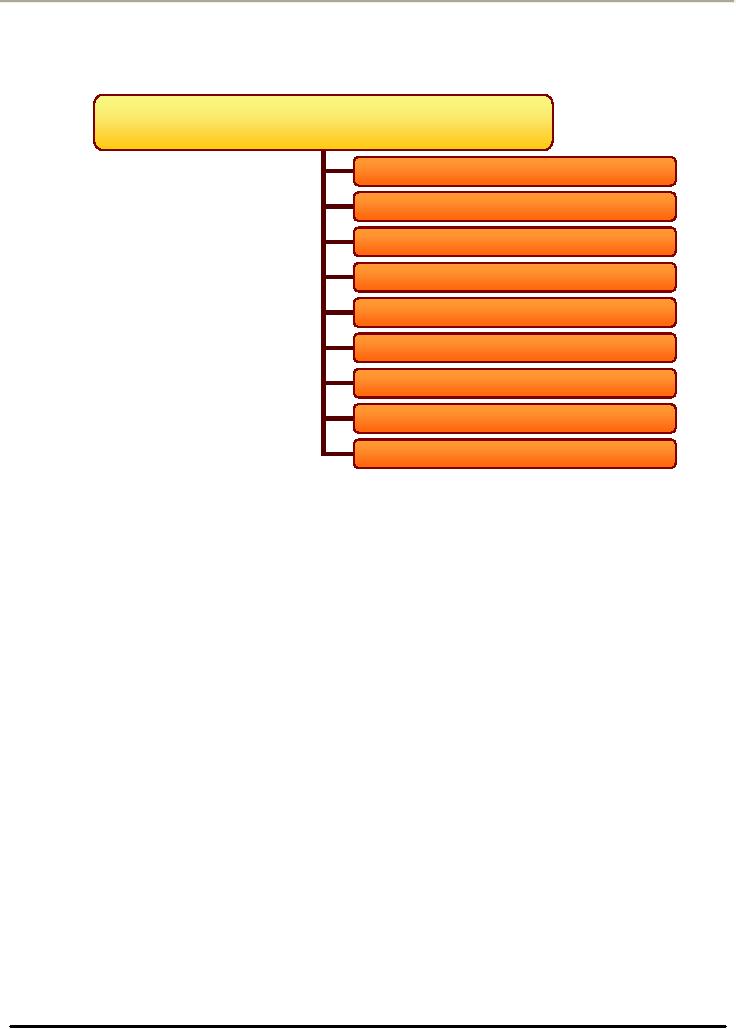
Nine
Bases for
Segmentation
Segmentation
Bases
Geographic
Segmentation
Demographic
Segmentation
Psychological
Segmentation
Psychographic
Segmentation
Sociocultural
Segmentation
Use-Related
Segmentation
Use-Situation
Segmentation
Benefit
Segmentation
Hybrid
Segmentation
1.
Geographical Segmentation
In
Geographical Segmentation, the market is
divided by location. The theory
behind the strategy is that
people
who
live in the same area share
similar needs and wants
which differ from needs
and wants of people living
in
other
areas. Variables included in the geographical
segmentation are:
Region
City
Size
Density
of Area
Climate
Global
Marketing Strategy
Some
marketers believe that the
internet has erased all
regional boundaries and clearly,
any company that
decides
to
put its catalog on the
internet makes it easy for
the individuals all over the
world to browse and
become
customers.
Divergent
Consumer Patterns
Marketers
have observed divergent consumer
patterns among urban, suburban
and rural areas
Urban
Areas
o
Population in Pakistan is focused
in the urban areas
o
Every year there is a
greater influx of population
that permanently migrates to bigger
cities or the
nearby
urban areas
Small
Towns and Villages
o
People in small towns when they
have to purchase their electronic
items, electrical
appliances,
furniture
and other technical equipment they do it
from the urban areas
o
The markets in the rural
areas merely include raw
food items and local
cultural products, local
fruits
and crops, etc.
Benefits
of Geographical Segmentation
It
is relatively easy to find geographically
based differences for many
products. Geographic Segments can be
easily
reached
through local media
43
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Consumer Behavior
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Consumer research
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Marketing Mix, Product, Price
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Customer Value, Perceived Value
- VALUE AND RETENTION FOCUSED MARKETING AND CONSUMER DECISION MAKING PROCESS
- CONSUMER RESEARCH:Quantitative Research, Qualitative Research
- MAJOR STEPS IN CONSUMER RESEARCH PROCESS:Design of Primary research
- QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH DESIGNS & DATA COLLECTION METHODS
- QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH DATA COLLECTION TECHNIQUES:ATTITUDE SCALES
- QUALITATIVE RESEARCH DESIGNS & DATA COLLECTION METHODS
- CUSTOMER SATISFACTION MEASUREMENT, SAMPLING, AND DATA ANALYSIS AND REPORTING
- MARKET SEGMENTATION AND ITS BASES:Geographical Segmentation
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: DEMOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION PSYCHOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: SOCIOCULTURAL SEGMENTATION USE RELATED SEGMENTATION USAGE SITUATION SEGMENTATION
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: BENEFIT SEGMENTATION:Intrinsic Cues
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: HYBRID SEGMENTATION STRATEGIES
- MARKET SEGMENTATION IMPLEMENTING SEGMENTATION STRATEGIES ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES CULTURE
- HOW CULTURE IS LEARNT ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Formal Learning
- CULTURE AND ITS MEASUREMENT ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- MEASUREMENT OF CULTURE ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Consumer Fieldwork
- SUBCULTURE CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- AGE AND GENDER SUBCULTURE CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: BENEFIT SEGMENTATION:Market Segmentation
- SOCIAL CLASS CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Occupation
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Affluent Consumer
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Membership Group
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Shopping Groups
- UNDERSTANDING PERSONALITY CHAPTER 5: INDIVIDUAL DETERMINANTS OF CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
- CONSUMER PERSONALITY, TRAIT THEORY AND SELF IMAGES
- CONSUMER MOTIVATION:Needs, Goals, Generic Goals
- UNDERSTANDING LEARNING:Intentional and Incidental Learning, Implications for Marketers
- INSTRUMENTAL CONDITIONING, INFORMATION PROCESSING AND MEMORY
- ATTITUDES:Characteristics of Attitudes, Attitudes have consistency
- ATTITUDE FORMATION AND CHANGE:How attitudes are learned?
- ATTITUDE CHANGE STRATEGIES:Resolving two conflicting attitudes
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER DECISION MAKING:Decision Complexity
- Problem Recognition, Search and Evaluation and Decision and Purchase
- Decision and Purchase:Consumer Decision Rules, Output, Relationship Marketing
- Decisions Related to Post Purchase:Product Set up and Use
- Marketing Implications of Decisions Related to Post Purchase:Understanding
- Post Purchase Evaluation:Determinants of Satisfaction, Consumer Complaint Behavior
- Post Purchase Dissonance:Dissonance Reduction, Marketing Implications
- Consumerism:Roots of Consumerism, The Nature of Consumerism
- Consumerism – Issues and Responses:Environmental Concerns, Consumer Privacy
- Review – Consumer Psychology Course:Consumer Research, Consumerism