 |

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
LESSON
05
HUMAN
RELATIONS SCHOOLS
Text
Books
Khan,
Sultan, Public
Administration with Special Reference to
Pakistan,
Urdu
Bazar, Lahore (latest
edition)
Nigro
and Nigro, Modern
Public Administration, Harper
& Row, NY (latest edition)
At
the end of the lecture the students
will be able to understand the
following:-
1.
Main
features of Human Relations
Schools
2.
The
concept of behaviour and the common
features of behavioural School and
Human Relations
3.
Theory
X and Theory Y
4.
Maslow
hierarchy of need i.e. the
concepts in need
theory
5.
Concepts
and main features of System
school
We
will now conclude Hebert
Simons work. But before we do
that we attempt to see how
Simon
classified
administrative behaviour.
He
has classified the administrative
behaviour as follows:-
1.
The study of bureaucracy: In
order to understand decision
making, it is better to understand
the
structure
of organization, because the structure
determines behaviour.
2.
Human relations pertaining to
motivation and increasing
job satisfaction: The study
of human
relations
and motivation determines the
performance in organization.
3.
Decision-making studies emphasizing
cognitive processes and the
rational components of
administrative
behaviour: The decision making behaviour
in organization is based on
cognitive
process
as well as rational
In
his view, all behaviour
involves conscious or unconscious
selection of particular actions.
For
example:
If
a manager has to decide to
fire Mr. X., the conscious
considerations would be like the
employee
was
undisciplined, and continuously performed
unsatisfactorily. His unconscious consideration
might be
that
the manager did not like
his him personally.
Main
Features of Human of Relation
Approach
This
is a brief snapshot of the human
relations theories. The
Human Relations School
focused on
the:-
Individuals
behaviour, cognitive decision-making
process and nature of
authority in organization
Informal,
interpersonal relationship, group dynamics
and communication pattern
Behavioural
School
The
Behavioural School looked at human
motivation and social
environment in which the
organizations
work. They studied the behaviour of
individuals in the organization and the affect
of
behaviour
on organizational performance. The main
contributors to Behavioural School were
Psychologists
and
Sociologists.
What
is behaviour?
Behaviour
is defined in general sense as
actions of people that are
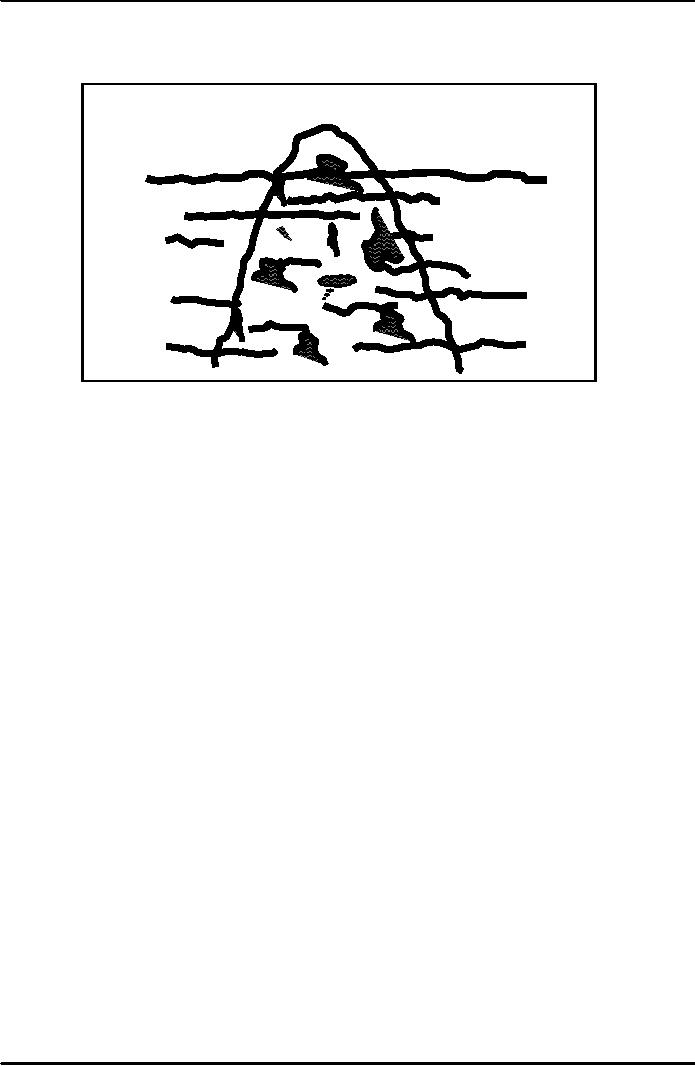
seen. As you can see in the
figure
the
behaviour that can be seen
is really the tip of the ice
being. Below this tip is the unseen
attitudes,
thoughts,
feelings, perception, motive etc.
The unseen attitudes etc.
drive certain behaviour which is
seen.
17
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
For
example we can see the
behaviour of a person who
violates traffic signal or
who litters around. From
this
behaviour we can infer his
perceptions and attitudes
towards rules and
cleanliness respectively.
Figure
Behaviour
Seen
Behaviour
Attitudes
Thoughts
Motives
Feelings
Not
Seen
The
Human Relation School and Behavioural
School have many things in
common. These are:
1.
Both
focus on motivation of people
2.
Both
emphases Clarity of communication
3.
They
emphasize interpersonal relationship: How people
relate with each
other
4.
Both
look at individual and group
behaviour: Behaviour of people in the group and
individual
behaviour
Main
Contributors of Behavioural
The
main contributors whose work
is analyzed are:-
1.
Douglas McGregor
2.
Abraham Maslow
Douglas
McGregor:
Douglas
McGregor presented a theory
called Theory X and Theory
Y. His Theory X and Y are
the
negative
and positive assumption about
human behaviour.
Theory
X
Theory
X has negative assumptions,
which are as
follows:-
1.
Dislike work: It is assumed
that human beings are
lazy and docile, therefore, they avoid
work.
2.
Avoid responsibility: Because human
beings are lazy, they do not
want to take any
responsibility.
3.
They need to be supervised: From the
above two assumption it
follow that they need to
be
supervised.
As human beings are lazy,
therefore, in order to get work
out of them they need to be
closely
supervised.
Theory
Y
Theory
Y is a positive assumption about
human behaviour, and its
assumptions are just
the
opposite
of Theory X. These assumptions
are:
1.
People accept responsibility: Because
they are willing to work and
agile and active. They want
to
achieve
goals for the organization and
accept responsibility.
2.
Can exercise control:
Because they are responsible, therefore,
they want to have control over
things
3.
Have capacity to be creative:
People want to be creative and
look for challenge.
18
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
4.
Can work as natural as rest or
play: For people work and
rest are equal, i.e. people
want to work
and
rest which is natural they cannot rest
all the time because it becomes
boring and they cannot
work
all the time because it becomes
dull as well
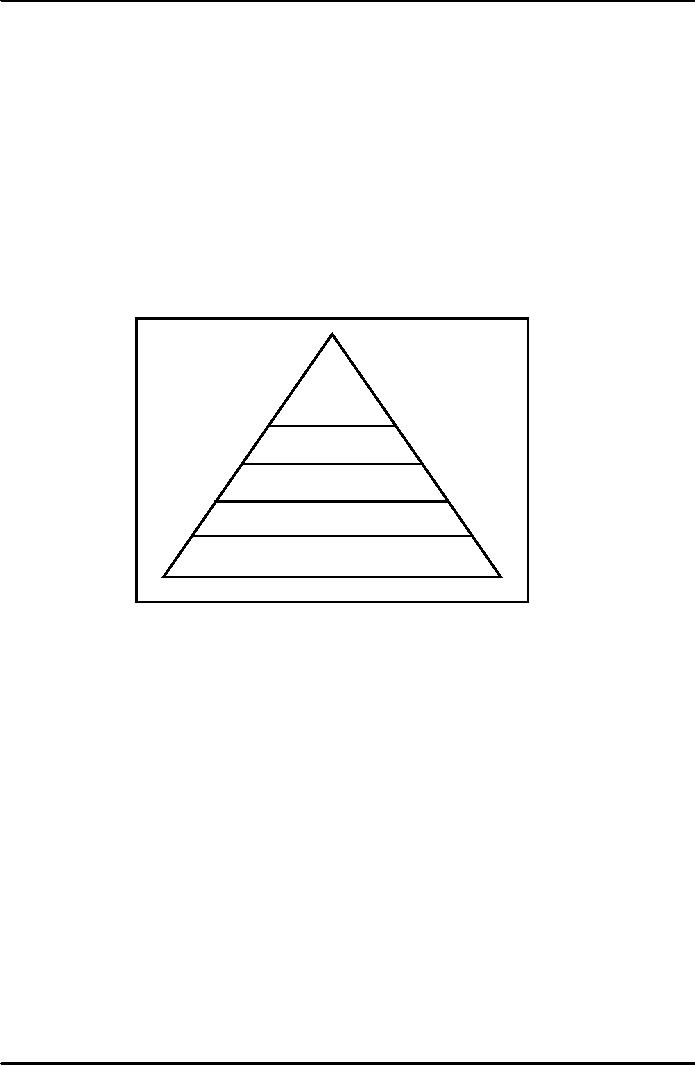
Maslow's
Need Hierarchy
This
theory was developed by Abraham Maslow.
This theory has received
more attention from
managers.
Maslow viewed human
motivation as a hierarchy of five
needs (see figure) ranging
from the most
basic
physiological or basic needs to the
highest level of need for
"self actualization". According to
Maslow,
individuals
will be motivated to fulfill the
most pressing need at a time.
The importance of need depends
on
the
deprivation of the need and current
situation. If the individual is deprived of basic
need he will be at
that
level of need. For example the
basic needs are food,
clothing and shelter. If one
is hungry and is
starving
one will not be able to
think of higher level of need i.e.
safety. The needs at the
lower level must be
satisfied
before one moves to higher level of
needs.
Figure
Self
Actualization
Ego-Status
Belongingness
Safety
Basic
Needs
System
Schools
The
main contributors of system
schools are:-
1.
Fermont E. Kast
2.
James E. Rosenzweig
3.
William Scott
The
word `system' is borrowed
from biological sciences to
social science. It attempts to
see
organizations
as other systems, like
irrigation system, Ecosystem, circulatory
system, digestive system,
solar
system,
etc.
Some
of these are mechanistic
system, some are organic
system. The mechanistic
system is static
e.g.
these do not change with
changes outside the system. Organic
systems are not static.
Organic System
responds
to external environment.
There
are two basic components of
system Theory. These
are:-
System
School views organization as "unified,
purposeful system composed of
interrelated
parts"
This
theory provides opportunity to look at
organization as a whole and as
part of larger external
environment
19
Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Parts
of Organization
An
organization comprise of many parts or
sub-system. The figure shows
an organization structure
of
a university. Three sub-system i.e.
Examination, Registration and
Human Resource management
are
shown.
These sub-systems or parts of
organization constitute one big organization.
Since organizations
are
compared
to organic system, these are
changeable. The organization as a whole
responds to external system.
Figure
Rector
Human
Resource
Examination
Registration
Management
Key
Concepts in System
School
Following
are some key concepts in
System Theory:-
Subsystem:
The part that make up the
whole
Synergy:
whole is greater than the
sum of its part The
combine effect of system
System
boundary: Boundary separates system from
the external environment
Open
& closed system: system
that interacts with its
environment is open system
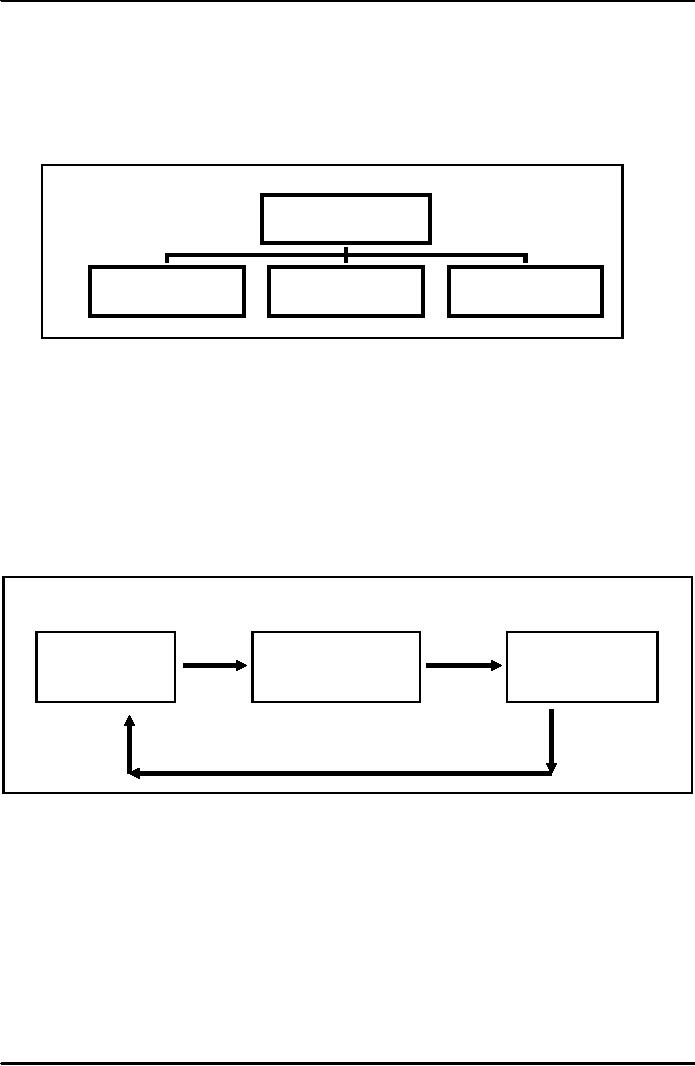
Feedback:
return of information to the organization.
The figure below shows the
feed back
mechanism.
Figure
Inputs
Transformation
Products
Human
Use
of processes to
Good
and Services
Financial
change
resources into
Physical
goods
and services
Feedback
The
theories or schools of thoughts that we
have tried to understand explain us
one aspect of
organization.
Therefore, we cannot say that one
theory is better than other. In fact
all theories if studied
are
helpful
in explaining organizational behaviour,
and explain us different aspects of
organization.
The
classical theories help us
understand the mechanical aspects
like line of command, unity
of
direction
hierarchy etc. While Human
and Behavioural Schools help us
understand the human side
of
organizations.
Concepts
Theory
X:
The
negative assumptions about human
behaviour
Theory
Y:
The
positive assumptions about
human behaviour
Behaviour:
Actions
of Individual that can be
observed
20

Introduction
To Public
AdministrationMGT111
VU
Need
Hierarchy:
Human
needs are placed in
different levels, from the
basic level
to
the highest level.
Sub-System:
The
part that make up the
whole
Feed
back:
Return
of information to the organization
21
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Institutions of State, Individualism
- EVOLUTION OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:Classical School, The Shovelling Experiment
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – I:Theory of Bureaucracy, Human Relation Approach
- CLASSICAL SCHOOL OF THOUGHTS – II:Contributors of This Approach
- HUMAN RELATIONS SCHOOLS:Behavioural School, System Schools
- POWER AND POLITICS:Conflict- as Positive and Negative, Reactions of Managers, Three Dimensional Typology
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – I:Moghul Period, British Period
- HISTORY OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION – II
- CIVIL SERVICE:What are the Functions Performed by the Government?
- CIVIL SERVICE REFORMS:Implementation of the Reforms, Categories of the Civil Service
- 1973 CONSTITUTION OF PAKISTAN:The Republic of Pakistan, Definition of the State
- STRUCTURE OF GOVERNMENT:Rules of Business, Conclusion
- PUBLIC AND PRIVATE ADMINISTRATION:The Public Interest, Ambiguity, Less Efficient
- ORGANIZATION:Formal Organizations, Departmentalization
- DEPARTMENTALIZATION:Departmentalization by Enterprise Function, Departments by Product
- POWER AND AUTHORITY:Nature of Relationship, Delegation of Functional Authority
- DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY:The Art of Delegation, Coordination
- PLANNING – I:Four Major Aspects of Planning, Types of Plans
- PLANNING – II:Planning ProcessThree principles of plans
- PLANNING COMMISSION AND PLANNING DEVELOPMENT:Functions, Approval Authority
- DECISION MAKING:Theories on Decision Making, Steps in Rational Decision Making
- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM):Importance of Human Resource, Recruitment
- SELECTION PROCESS AND TRAINING:Levels at Which Selection takes Place, Training and Development
- PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL:Formal Appraisals, Informal Appraisals
- SELECTION AND TRAINING AND PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS:Performance Evaluation,
- PUBLIC FINANCE:Background, Components of Public Finance, Dissimilarities
- BUDGET:Components of Public Income, Use of Taxes, Types of Taxation
- PUBLIC BUDGET:Incremental Budget, Annual Budget Statement, Budget Preparation
- NATIONAL FINANCE COMMISSION:Fiscal Federalism Defined, Multiple Criteria
- ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROL:Types of Accountability, Internal Control, External Control
- AUDIT:Economy, Effectiveness, Objectives of Performance Audit, Concepts
- MOTIVATION:Assumptions about Motivation, Early ViewsThree Needs
- MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:Reinforcement Theory, Leadership, The Trait Approach
- LEADERSHIP:Contingency Approaches, Personal Characteristics of Employees
- TEAM – I:Formal & Informal teams, Functions of Informal Groups, Characteristics of Teams
- TEAM – II:Team Cohesiveness, Four ways to Cohesiveness, Communication
- COMMUNICATION – I:Types of Communication, How to Improve Communication
- COMMUNICATION – II:Factors in Organizational Communication, Negotiating To Manage Conflicts
- DISTRICT ADMINISTRATION:The British Period, After Independence, The Issues
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – I:Country Information, Tiers or Level of Government
- DEVOLUTION PLAN – II:Aim of Devolution Plan, Administrative Reforms, Separation of powers
- POLITICAL REFORMS:District, Tehsil, Functions of Union Council, Fiscal Reforms
- NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM):Strategy, Beginning of Management Approach
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – I
- MANAGERIAL PROGRAMME AGENDA – II:Theoretical Bases of Management, Critique on Management