 |
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
LESSON
13
APPLICATION
SOFTWARE
The
focus of the last Lesson was
on Operating Systems
Learning
Goals for Today
To
learn about application
software
To
become familiar with various
software used in the following
application areas:
e.g.
Scientific/engineering/graphics
Business
Productivity
Entertainment
Educational
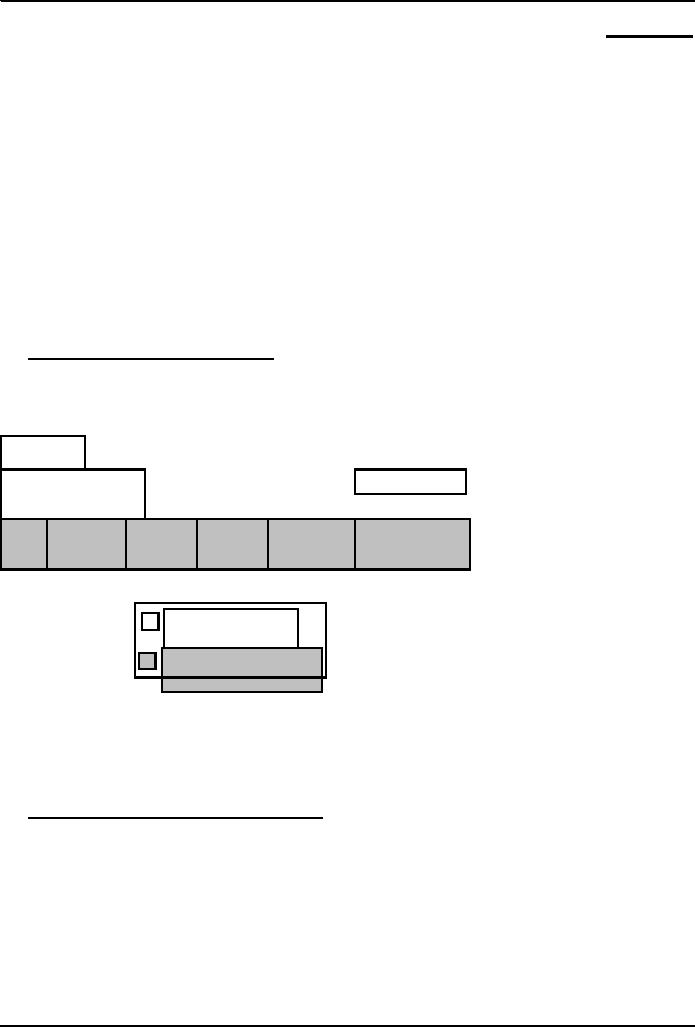
13.1
Two Major Types of
Software
System
Software
Application
Software
Hardware
Operating
System
Device
Driver
Utility
Language Scientific Business
Productivity Entertainment
Translator
Apps.
Apps.
Apps.
Apps.
System
software
Application
software
13.2
Application Software
Application
software are programs that
interact directly with the
user
They
generally do not talk
directly to the hardware
13.3
Classification According to the
Mode
Interactive-mode
The
user runs the program on the computer and
keeps on interacting with the computer
while the
program
runs
Example:
Word processor
Batch-mode
The
user starts the program and the computer
processes the provided data
and produces results
without
any
further intervention of from the
user
Example:
Payroll
74
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
13.4
Classification According to Application
Area
Scientific/engineering/graphics
Business
Productivity
Entertainment
Educational
13.5
Scientific/Engineering/Graphics Apps
Key
feature: Intense floating-point
calculations
Scientific/engineering/mathematical
apps
Computers
initially were designed just to run
them
Generally
designed for specialists
Rudimentary
UI's
Many
run in batch mode
13.6
Scientific SW
Simulation
of natural systems
Deforestation
and effect on green-house
gases
Simulation
of artificial systems
NeuralWare
(Simulator for artificial
neural networks)
Thermo-nuclear
explosions
Mathematical
computation packages
Mathematica
(can do hundreds, if not thousands of
functions, e.g. solving a differential
eq,
symbolically)
MathCAD
13.7
Engineering SW
Computer-aided
design (CAD)
AutoCAD
SPICE
Virtual
wind tunnels
Computer-aided
manufacturing (CAM)
Telecommunication
system SW
Centrex
Industrial
control SW
13.8
Graphics & Animation SW
(1)
Two
types:
Moving
graphics
1.
Vector graphics
e.g.
cartoons
Treats
everything that is drawn as an
object
Objects
retain their identity after
they are drawn
These
objects can later be easily
moved, stretched, duplicated,
deleted, etc
Are
resolution independent
Relatively
small file size
Example:
MS Visio, Corel Draw,
Flash
75

Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Graphics
& Animation SW (2)
2.
Bit-mapped or raster graphics
Treats
everything that is drawn as a
bit-map
If an
object is drawn on top of another, it is
difficult to move just 1 of them
while leaving the
other
untouched
Changing
the resolution often requires considerable
touch-up work
Relatively
large file size
Example:
MS Paint, Adobe Photoshop
13.9
Business Applications
Most
of the SW being developed today belongs
to this category
SW
that is required to run most
any sort of biz:
Payroll
General
ledger
Order
entry
Accounts
receivable & accounts
payable
Inventory
control
Let's
now discuss a few business
SW categories which are not
that common, but are
becoming more
and more
popular with time
13.10
E-Commerce Software
Key
requirements:
Reliability
Security
Ability
to handle 1000's of transactions,
simultaneously
13.11
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
SW
Very
large scale, complex &
expensive SW
Ties
together all key activities
& major systems of an organization
into a single SW
system
Key
benefit: Optimization of the business
processes of an organization as a single
system instead of
many
loosely-related stand-alone
systems
Example:
SAP, Oracle, PeopleSoft, Baan
13.12
DSS (Decision Support
Systems) SW
Sometimes
also called "expert
systems"
Many
times are based on a branch of computer
science called "artificial
intelligence"
This
category of SW is designed to help
business managers in making
effective decisions in complex
situations
based on the analysis of the relevant
data
13.13
Productivity SW
Most
popular category in terms of
licenses sold
Common
features
Ability
to simplify, automate everyday business
tasks
Highly
interactive and user-friendly
design
Designed to
run on PC's
Most
users do not use 90% of the
SW features
Popular
productivity SW
Word
Processing
--
Spreadsheets
Presentations
--
Databases
13.14
Word Processors
Probably
the most popular productivity
app
Initially
designed as a replacement for the
typewriter
76
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Automation
Automatic
end-of-line soft carriage
return
Style
sheets
Table
of contents & index
Spelling
& grammar checking
Two
approaches: WYSIWYG (e.g. Word,
WordPerfect, Star) or traditional markup
(LaTeX)?
Desktop
publishing
13.15
Web Page Development
SW
Web
pages can be developed using
a simple plain-text editor
like the "notepad", but more
efficient,
easy-to-use
HTML editors can make the
process quicker
Some
of them are WYSIWYG (i.e.
you don't really need to
know any HTML to use them),
others are
not,
while some provide both
types of interfaces (DreamWeaver)
Most
popular word processors now
come with a built-in Web
page development
facility
13.16
Spreadsheet SW (1)
Electronic
replacement for ledgers
Is
used for automating
engineering, scientific, but in
majority of cases, business
calculations
A
spreadsheet - VisiCalc - was the
first popular application on
PC's.
It
helped in popularizing PC's by making the
task of financial-forecasting much
simpler, allowing
individuals
to do forecasts which previously were
performed by a whole team of
financial wizard
13.17
Spreadsheet SW (2)
Consist of cells
arranged in rows and columns
Each
cell may contain numeric
values, text or formulas
Automation
Recalculations
Charts
13.18
Presentation Development SW
Used to prepare
multimedia material for lectures &
presentations to display key points,
graphics,
animation,
or video with the help of
multimedia projectors
Have
replaced acetate films (slides) that were
used with over-head
projectors
Key
advantage over acetate slides:
Easy
to modify
Can
be sent electronically
Its
multimedia nature makes it more
interesting for the audience
13.19
Small-Scale Databases SW (1)
Easy
to use applications designed for
efficient storage and fast
and easy retrieval of
data
That
data may be in the form of
numbers, text, or even multimedia,
i.e. sounds, graphics,
animation,
video
13.20
Small-Scale Databases SW (2)
Before
the advent of the currently popular
"relational" database model, the
databasing function was
performed
using what is called the
"flat-file" model
That
model is not very efficient
for storing and searching in large
databases
A
database consists of a file or a
set of files. Information in
these is stored in the form of
records, and
the
records are further
subdivided into
fields
13.21
Productivity SW Suites
A set
of stand-alone productivity applications designed to
work easily with each
other
Share
a common UI
77
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Are
available as a bundle along
with additional useful
utilities
Examples: MS
Office, Corel WordPerfect
Office, Lotus SmartSuite, Star
Office
SW
Suites for other app
areas are available as well,
e.g. the Adobe suite of graphics
apps
13.22
Document-Centered Computing (DCC) -
1
The
increasing cooperation among the apps
included in productivity suites
has given rise to a
new
computing
paradigm called DCC
DCC
implies that instead of developing
parts of a doc in a number of apps, and
then cutting-&-pasting
them to
form the final doc, you stay
in a single doc and call-up
appropriate apps to insert the
required
objects
13.23
Document-Centered Computing (DCC) -
2
Let's
say that we want to write a
letter containing a map, a
table and a graph
We
can:
Launch
the WP and type the text in
Insert
a drawing by calling up the drawing
toolbar app (without leaving the
WP) & draw the
map
Insert
a table by calling up the spreadsheet app
(without leaving the WP) &
build the table
Insert
a graph based on that table
using the same spreadsheet app
without leaving the WP
13.24
Entertainment SW
Key
feature: Simple, intuitive,
many times social UI's
The
user is generally assumed to
know nothing about
computers
Both
Microsoft & Apple are
pursuing a PC-as-a-personal-entertainment-hub strategy. Probable
result:
Already
popular entertainment SW will
become even more popular
13.25
Music & Video Players
Music
players (WinAmp)
Video/Music
players (Real player,
Windows Media player,
QuickTime player)
The
Web Browsers can also
display video, animation, and
play music with the help of
helper
applications
like Flash
13.26
Music Generation & Movie Editing
SW
A PC
can be made the hub of a
music making studio with
help of appropriate HW & SW
Inexpensive,
easy-to-use video editing SW
has recently become
available for the
iMac
13.27
Games
Many
types
Educational
(especially for
toddlers)
Strategy/Simulation
Sports
Shoot'em
ups
The
saddest aspect: You do not
need any opponents or partners to
play computer games
The
application SW category that
provides the toughest challenge for
computer HW
13.28
Educational SW
Category
with probably the highest
growth rate
Current
focus on augmenting traditional training
and education methods, but it is
shifting towards
replacing
traditional methods
13.29
Electronic Encyclopedias
Great
resource of useful information
presented in a very interesting
format
Superior
to the paper-based version
because:
Access
speed is dramatically
higher
78

Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Can
contain animation and
sound
Much
lower cost as thousand's of pages in
dozens of volumes have been replaced by a
couple of CD's
13.30
On-Line Learning
With
time, the VU Web site will become more
and more focused on interactive
online learning
The
Website of our textbook "Understanding
Computers" is an example of an on-line
learning Website
Key
features of good online
learning SW:
The
student can learns at his or her
own pace
The
student can select his or her
own hours
13.31
Interactive CD's
Same
as on-line learning, but
through a CD instead of a Web site
Key
advantage:
Ideal
for students with slow
Internet access
13.32
Attributes of Good Application
Software
Easy
to install, un-install
User
Interface
Consistent
Intuitive
Configurable
Adapts
to the users need
Has a
tutorial and a complete help
manual
Does
not have any critical
bugs
13.33
Most Popular Application Software
Categories
Web
browsers
Email
clients
Word
processors
What
have we learnt
today?
Application
software are programs that
interact directly with the
user for the performance of a
certain
type
of work
That
work generally falls into
one of the following usage
areas
Scientific/engineering/graphics
Business
Productivity
Entertainment
Educational
Focus
of the Next Lecture
Next
Lesson will be the first among the
four lectures that we plan
to have on productivity SW
That
first Lesson will be on word
processing
We'll
learn about what we mean by
word processing
We'll
discuss the usage of various
functions provided by common word
processors
79
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION
- EVOLUTION OF COMPUTING
- World Wide Web, Web’s structure, genesis, its evolution
- Types of Computers, Components, Parts of Computers
- List of Parts of Computers
- Develop your Personal Web Page: HTML
- Microprocessor, Bus interface unit, Data & instruction cache memory, ALU
- Number systems, binary numbers, NOT, AND, OR and XOR logic operations
- structure of HTML tags, types of lists in web development
- COMPUTER SOFTWARE: Operating Systems, Device Drivers, Trialware
- Operating System: functions, components, types of operating systems
- Forms on Web pages, Components of Forms, building interactive Forms
- APPLICATION SOFTWARE: Scientific, engineering, graphics, Business, Productivity, Entertainment, Educational Software
- WORD PROCESSING: Common functions of word processors, desktop publishing
- Interactivity to Forms, JavaScript, server-side scripts
- ALGORITHMS
- ALGORITHMS: Pseudo code, Flowcharts
- JavaScript and client-side scripting, objects in JavaScript
- Low, High-Level, interpreted, compiled, structured & object-oriented programming languages
- Software Design and Development Methodologies
- DATA TYPES & OPERATORS
- SPREADSHEETS
- FLOW CONTROL & LOOPS
- DESIGN HEURISTICS. Rule of thumb learned through trial & error
- WEB DESIGN FOR USABILITY
- ARRAYS
- COMPUTER NETWORKS: types of networks, networking topologies and protocols
- THE INTERNET
- Variables: Local and Global Variables
- Internet Services: FTP, Telnet, Web, eMail, Instant messaging, VoIP
- DEVELOPING PRESENTATIONS: Effective Multimedia Presentations
- Event Handlers
- GRAPHICS & ANIMATION
- INTELLIGENT SYSTEMS: techniques for designing Artificial Intelligent Systems
- Mathematical Functions in JavaScript
- DATA MANAGEMENT
- DATABASE SOFTWARE: Data Security, Data Integrity, Integrity, Accessibility, DBMS
- String Manipulations:
- CYBER CRIME
- Social Implications of Computing
- IMAGES & ANIMATION
- THE COMPUTING PROFESSION
- THE FUTURE OF COMPUTING
- PROGRAMMING METHODOLOGY
- REVIEW & WRAP-UP of Introduction to Computing