 |
Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
Lesson
21
Lesson
overview and learning objectives:
In
last Lesson we discussed the
concept regarding some individual
decisions about the product
like
product
attributes, labeling and packaging.
Today we will continue the
same topic and will
discuss
the
process of new product
development again as
well.
o
PRODUCT
o
NEW
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS
A.
Product Line Strategies
We
have looked at product strategy
decisions such as branding, packaging,
labeling, and support
services
for individual products and
services. But product
strategy also calls for
building a product
line.
A product line is a group of
products that are closely
related because they
function in a similar
manner,
are sold to the same
customer groups, are marketed
through the same types of
outlets, or
fall
within given price ranges.
For example, Nike produces
several lines of athletic
shoes and
Motorola
produces several lines of
telecommunications products. In developing
product line
strategies,
marketers face a
number
of tough decisions.
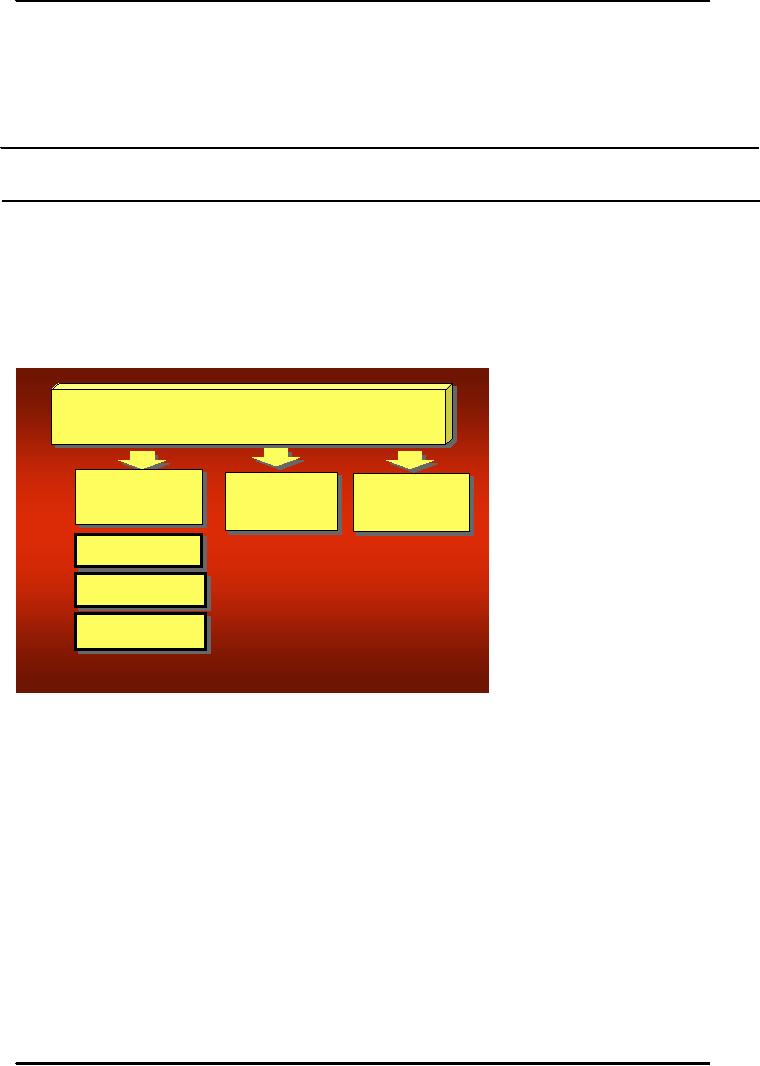
The
major product
line
P
ro d u c tt
L
iin e E x tte n s iio n s
P
ro d u c L n e E x e n s o n s
decision
involves product
line
length--the number of
items
in the product line.
Stretching
Filling
Conttractng
a
ractiing
a
The
line is too short if
the
Con
PrroductLine
P
oduct Line
Adding
new
Adding
sizes or
manager
can increase profits
items
to line
styles
Drroppng
ittems
D
oppiing iems
by
adding items; the line
is
too
long if the manager
can
Dow
nw ard
increase
profits by dropping
items.
Company objectives
Upw
ard
and
resources influence
product
line length. Product
Tw
o-w ay
lines
tend to lengthen over
time.
The sales force
and
distributors
may pressure the
product
manager for a more complete
line to satisfy their customers.
Or, the manager may
want to
add
items to the product line to
create growth in sales and
profits. However, as the
manager adds
items,
several costs rise: design
and engineering costs,
inventory costs, manufacturing
changeover
costs,
transportation costs, and
promotional costs to introduce
new items. Eventually
top
management
calls a halt to the
mushrooming product line.
Unnecessary or unprofitable items
will
be
pruned from the line in a
major effort to increase
overall profitability. This
pattern of
uncontrolled
product line growth followed
by heavy pruning is typical and
may repeat itself
many
times.
The
company must manage its
product lines carefully. It
can systematically increase
the length of
its
product line in two ways: by
stretching its line and by
filling its line. Product
line stretching
stretches
its line downward, upward, or
both ways.
Many
companies initially locate at
the upper end of the market
and later stretch their
lines
downward.
A company may stretch
downward to plug a market hole
that otherwise would attract
a
new
competitor or to respond to a competitor's
attack on the upper end. Or
it may add low-end
products
because it finds faster
growth taking place in the
low-end segments.
100

Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
B.
New-product development
Given
the rapid changes in consumer
tastes, technology, and
competition, companies
must
develop
a steady stream of new
products and services. A
firm can obtain new
products in two
ways.
One is through acquisition--by
buying a whole company, a patent, or a
license to produce
someone
else's product. The other is
through new-product development in
the company's own
research
and development department. By new
products we mean original
products, product
improvements,
product modifications, and
new brands that the
firm develops through its
own
research
and development efforts. In
this chapter, we concentrate on
new-product development.
New
products continue to fail at a
disturbing rate. One source
estimates that new
consumer
packaged
goods (consisting mostly of line
extensions) fail at a rate of 80 percent.
Moreover, failure
rates
for new industrial
products
may
be as high as 30 percent.3Why
Marketing
Business
do
so many new products
fail?
Strategy
Analysis
There
are several
reasons.
Although
an idea may be good,
the
Concept
market
size may have
been
Product
Development
Development
overestimated.
Perhaps the actual
and
Testing
product
was not designed as
well
as
it should have been. Or
maybe
it
was incorrectly positioned in
the
Test
Idea
market,
priced too high,
or
Marketing
Screening
advertised
poorly. A high-level
executive
might push a favorite
idea
despite poor
marketing
Idea
research
findings. Sometimes
the
Commercialization
Generation
costs
of product development
are
higher
than expected,
and
sometimes
competitors fight back harder
than expected.
Because
so many new products fail,
companies are anxious to learn how to
improve their odds of
new-product
success. One way is to identify
successful new products and
find out what they
have
in
common. Another is to study
new-product failures to see what lessons
can be learned.
Various
studies
suggest that new-product
success depends on developing a unique
superior product, one
with
higher quality, new
features, and higher value in
use. Another key success
factor is a well-
defined
product concept prior to development, in
which the company carefully
defines and
assesses
the target market, the
product requirements, and the benefits
before proceeding. Other
success
factors have also been
suggested--senior management commitment,
relentless innovation,
and
a smoothly functioning new-product
development process. In all, to
create successful new
products,
a company must understand its consumers,
markets, and competitors and
develop
products
that deliver superior value to
customers.
So
companies face a problem--they
must develop new products,
but the odds weigh
heavily
against
success. The solution lies
in strong new-product planning
and in setting up a systematic
new-product
development process for
finding and growing new
products. Figure shows the
eight
major
steps in this
process.
a)
Idea generation
New-product
development starts with idea
generation--the systematic search
for new-product
ideas.
A company typically has to
generate many ideas in order
to find a few good ones.
Major
sources
of new-product ideas include
internal sources, customers, competitors,
distributors and
suppliers,
and others. Using internal
sources, the company can
find new ideas through
formal
research
and development. It can pick
the brains of its executives,
scientists, engineers,
101

Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
manufacturing,
and salespeople. Some
companies have developed
successful "entrepreneurial"
programs
that encourage employees to
think up and develop new-product
ideas. Good new-
product
ideas also come from
watching and listening to customers.
The company can
analyze
customer
questions and complaints to
find new products that
better solve consumer problems.
The
company can conduct surveys
or focus groups to learn about consumer
needs and wants. Or
company
engineers or salespeople can
meet with and work
alongside customers to get
suggestions
and
ideas. Finally, consumers
often create new products
and uses on their own,
and companies can
benefit
by finding these products
and putting them on the
market. Customers can also be a
good
source
of ideas for new product
uses that can expand
the market for and extend
the life of current
products.
Competitors are another good
source of new-product ideas.
Companies watch
competitors'
ads and other communications
to get clues about their
new products. They
buy
competing
new products, take them
apart to see how they work,
analyze their sales, and
decide
whether
they should bring out a
new product of their own.
Finally, distributors and
suppliers
contribute
many good new-product ideas.
Resellers are close to the
market and can pass
along
information
about consumer problems and new-product
possibilities. Suppliers can
tell the
company
about new concepts, techniques,
and materials that can be
used to develop new
products.
Other
idea sources include trade
magazines, shows, and
seminars; government agencies;
new-
product
consultants; advertising agencies; marketing
research firms; university
and commercial
laboratories;
and inventors.
The
search for new-product ideas
should be systematic rather
than haphazard. Otherwise, few
new
ideas
will surface and many
good ideas will sputter in
and die. Top management can
avoid these
problems
by installing an idea
management system that
directs the flow of new
ideas to a central
point
where
they can be collected, reviewed,
and evaluated. In setting up such a
system, the company
can
do
any or all of the
following:
∑
Appoint
a respected senior person to be the company's
idea manager.
∑
Create
a multidisciplinary idea management
committee consisting of people from
R&D,
engineering,
purchasing, operations, finance, and sales
and marketing to meet regularly
and
evaluate
proposed new-product and
service ideas.
∑
Set
up a toll-free number for anyone
who wants to send a new idea
to the idea manager.
∑
Encourage
all company stakeholders--employees,
suppliers, distributors, dealers-- to
send
their
ideas to the idea
manager.
∑
Set
up formal recognition programs to reward
those who contribute the
best new ideas.
The
idea manager approach yields
two favorable outcomes. First, it
helps create an
innovation-
oriented
company culture. It shows
that top management supports,
encourages, and
rewards
innovation.
Second, it will yield a larger
number of ideas among which
will be found some
especially
good ones. As the system
matures, ideas will flow
more freely. No longer will
good ideas
wither
for the lack of a sounding
board or a senior product advocate
b)
Idea Screening
The
purpose of idea generation is to create a
large number of ideas. The
purpose of the
succeeding
stages
is to reduce
that
number. The first
idea-reducing stage is idea
screening, which helps
spot
good
ideas and drop poor
ones as soon as possible. Product
development costs rise greatly in
later
stages,
so the company wants to go ahead
only with the product
ideas that will turn
into profitable
products.
As one marketing executive suggests, "Three
executives sitting in a room
can get 40
good
ideas ricocheting off the
wall in minutes. The
challenge is getting a steady stream of
good
ideas
out of the labs and
creativity campfires, through marketing
and manufacturing, and all
the
way
to consumers."
Many
companies require their executives to
write up new-product ideas on a
standard form that
can
be reviewed by a new-product committee.
The write-up describes the
product, the target
market,
and the competition. It
makes some rough estimates
of market size, product
price,
development
time and costs,
manufacturing costs, and
rate of return. The
committee then
102

Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
evaluates
the idea against a set of
general criteria such as these: Is the
product truly useful
to
consumers
and society? Is it good for
our particular company? Does
it mesh well with
the
company's
objectives and strategies? Do we have
the people, skills, and
resources to make it
succeed?
Does it deliver more value to customers
than do competing products? Is it
easy to
advertise
and distribute? Many companies
have well-designed systems
for rating and
screening
new-product
ideas.
c)
Concept Development and
Testing
An
attractive idea must be
developed into a product concept. It is
important to distinguish
between
a product idea, a product concept,
and a product image. A
product
idea is an
idea for a
possible
product that the company
can see itself offering to
the market. A product
concept is
a
detailed
version of the idea stated
in meaningful consumer terms. A product
image is the
way
consumers
perceive an actual or potential
product.
Concept
testing calls for testing new-product
concepts with groups of target consumers.
The
concepts
may be presented to consumers
symbolically or physically For
some concept tests, a
word
or picture description might be
sufficient. However, a more concrete
and physical
presentation
of the concept will increase
the reliability of the concept
test. Today, some
marketers
are
finding innovative ways to
make product concepts more
real to consumer subjects.
For
example,
some are using virtual
reality to test product
concepts. Virtual reality
programs use
computers
and sensory devices (such as
gloves or goggles) to simulate
reality.
d)
Marketing strategy
Development
The
next step is marketing
strategy development, designing an
initial marketing strategy
for
introducing
this car to the
market.
The
marketing
strategy statement consists
of three parts. The first
part describes the target
market; the
planned
product positioning; and the
sales, market share, and
profit goals for the
first few years.
The
second part of the marketing
strategy statement outlines the
product's planned price,
distribution,
and marketing budget for the
first year. The third
part of the marketing
strategy
statement
describes the planned long-run
sales, profit goals, and
marketing mix strategy:
e)
Business
Analysis
Once
management has decided on its
product concept and marketing strategy,
it can evaluate the
business
attractiveness of the proposal. Business
analysis involves a review of
the sales, costs,
and
profit
projections for a new
product to find out whether
they satisfy the company's objectives.
If
they
do, the product can move to
the product development
stage.
To
estimate sales, the company
might look at the sales
history of similar products and
conduct
surveys
of market opinion. It can then
estimate minimum and maximum
sales to assess the
range
of
risk. After preparing the sales
forecast, management can
estimate the expected costs
and profits
for
the product, including marketing,
R&D, operations, accounting, and
finance costs. The
company
then uses the sales
and costs figures to analyze
the new product's financial
attractiveness.
f)
Product
Development
So
far, for many new-product
concepts, the product may
have existed only as a word
description, a
drawing,
or perhaps a crude mock-up. If the
product concept passes the
business test, it
moves
into
product development. Here, R&D or
engineering develops the
product concept into a
physical
product. The product
development step, however,
now calls for a large
jump in
investment.
It will show whether the
product idea can be turned
into a workable
product.
The
R&D department will develop and
test one or more physical versions of the
product concept.
R&D
hopes to design a prototype
that will satisfy and
excite consumers and that
can be produced
quickly
and at budgeted costs.
Developing a successful prototype
can take days, weeks,
months, or
even
years. Often, products
undergo rigorous functional
tests to make sure that
they perform
103

Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
safely
and effectively. The
prototype must have the
required functional features and
also convey
the
intended psychological
characteristics.
g)
Test
Marketing
If
the product passes
functional and consumer tests,
the next step is test
marketing, the stages at
which
the product and marketing program
are introduced into more
realistic market settings.
Test
marketing
gives the marketer experience
with marketing the product before going
to the great
expense
of full introduction. It lets
the company test the
product and its entire
marketing
program--positioning
strategy, advertising, distribution, pricing,
branding and packaging,
and
budget
levels.
The
amount of test marketing
needed varies with each
new product. Test marketing
costs can be
enormous,
and it takes time that
may allow competitors to
gain advantages. When the
costs of
developing
and introducing the product
are low, or when management
is already confident
about
the
new product, the company
may do little or no test marketing.
Companies often do not
test-
market
simple line extensions or copies of
successful competitor
products.
h)
Commercialization
Test
marketing gives management
the information needed to
make a final decision about
whether
to
launch the new product. If
the company goes ahead
with commercialization--introducing
the
new
product into the market--it
will face high costs.
The company will have to
build or rent a
manufacturing
facility. The company
launching a new product must
first decide on
introduction
timing
Next,
the company must decide
where
to
launch the new product--in a
single location, a
region,
the national market, or the
international market. Few companies
have the confidence,
capital,
and capacity to launch new
products into full national
or international distribution.
They
will
develop a planned market
rollout over
time. In particular, small companies
may enter attractive
cities
or regions one at a time. Larger
companies, however, may
quickly introduce new models
into
several
regions or into the full
national market.
Speeding
Up New-Product Development
Many
companies organize their
new-product development process
into the orderly sequence
of
steps
starting with idea generation
and ending with commercialization.
Under this sequential
product
development approach, one company
department works individually to complete
its stage
of
the process before passing
the new product along to the
next department and stage.
This
orderly,
step-by-step process can help
bring control to complex and
risky projects. But it also
can
be
dangerously slow. In fast-changing, highly
competitive markets, such slow-but-sure
product
development
can result in product failures,
lost sales and profits,
and crumbling market positions.
"Speed
to market" and reducing new-product
development cycle time have
become pressing
concerns
to companies in all industries.
In
order to get their new
products to market more quickly,
many companies are adopting a
faster,
team-oriented
approach called simultaneous (or
team-based) product development.
Under this
approach,
company departments work closely
together, overlapping the
steps in the product
development
process to save time and
increase effectiveness. Instead of
passing the new
product
from
department to department, the company
assembles a team of people
from various
departments
that stay with the
new product from start to
finish. Such teams usually
include people
from
the marketing, finance, design,
manufacturing, and legal departments,
and even supplier and
customer
companies.
Top
management gives the product
development team general
strategic direction but no
clear-cut
product
idea or work plan. It
challenges the team with
stiff and seemingly
contradictory goals--
"turn
out carefully planned and superior
new products, but do it
quickly"--and then gives the
team
whatever
freedom and resources it
needs to meet the challenge.
In the sequential process,
a
104
Principles
of Marketing MGT301
VU
bottleneck
at one phase can seriously slow
the entire project. In the
simultaneous approach, if one
functional
area hits snags, it works to
resolve them while the
team moves on.
KEY
TERMS
New-product
development: The
development of original products,
product improvements,
product
modifications, and new
brands through the firm's
own R&D efforts.
Idea
generation: The
systematic search for
new-product ideas.
Idea
screening: screening
new-product ideas in order to spot
good ideas and drop
poor ones as
soon
as possible.
Product
concept: A
detailed version of the
new-product idea stated in
meaningful consumer
terms.
Concept
testing: Testing
new-product concepts with a
group of target consumers to find
out if
the
concepts have strong consumer
appeal.
Business
analysis: A
review of the sales, costs,
and profit projections for a
new product to find
out
whether these factors satisfy
the company's objectives.
Product
development: A
strategy for company growth
by offering modified or new
products to
current
market segments. Developing
the product concept into a physical
product in order to
ensure
that the product idea
can be turned into a workable
product.
Commercialization:
Introducing
a new product into the
market.
Test
marketing: The
stage of new-product development in
which the product and
marketing
program
are tested in more realistic
market settings.
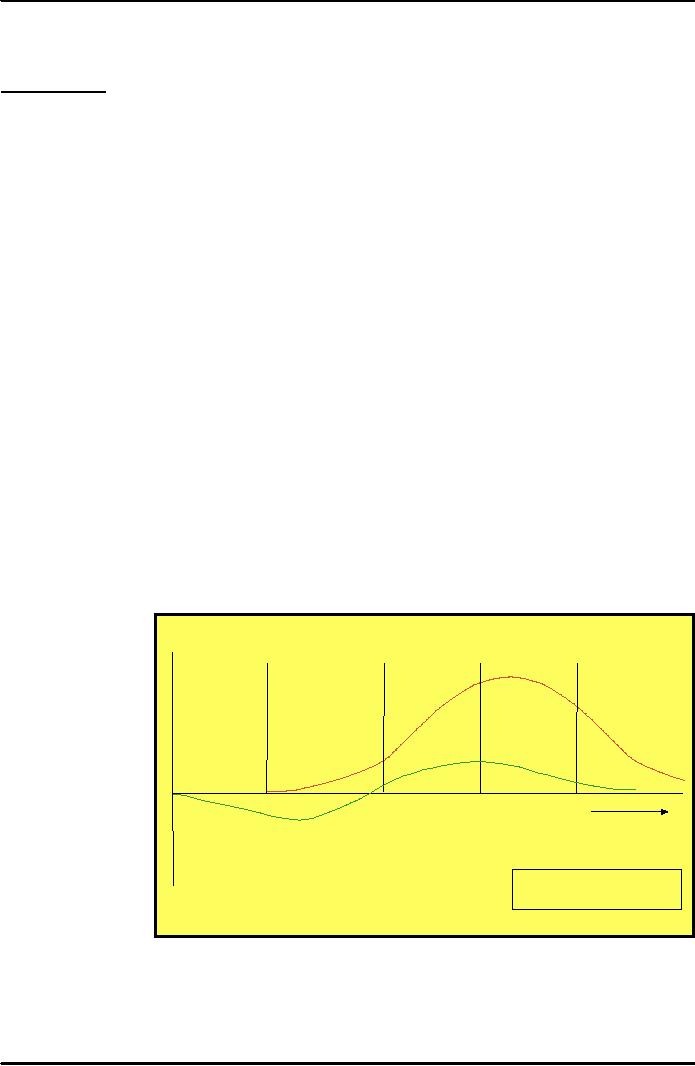
Sequential
S
a le s a n d
P
r o fits ($ )
product
development
A
S
a le s
new-product
development
approach
in which
P
r o fits
one
company
department
works
to
complete its
T
im e
stage
of the process
In
tr o d u c tio n
P
ro d u c t
G
ro w th
M
a tu r ity
D
e c lin e
before
passing the
D
e v e lo p m e n t
S
ta g e
new
product along
to
the
next
S
a le s a n d P r o fits O v e r
th
e P r o d u c t's L ife F r o
m
department
and
In
c e p tio n to D e m is e
stage.
105
Table of Contents:
- PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING:Introduction of Marketing, How is Marketing Done?
- ROAD MAP:UNDERSTANDING MARKETING AND MARKETING PROCESS
- MARKETING FUNCTIONS:CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT
- MARKETING IN HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE AND EVOLUTION OF MARKETING:End of the Mass Market
- MARKETING CHALLENGES IN THE 21st CENTURY:Connections with Customers
- STRATEGIC PLANNING AND MARKETING PROCESS:Setting Company Objectives and Goals
- PORTFOLIO ANALYSIS:MARKETING PROCESS,Marketing Strategy Planning Process
- MARKETING PROCESS:Analyzing marketing opportunities, Contents of Marketing Plan
- MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:The Companyís Microenvironment, Customers
- MARKETING MACRO ENVIRONMENT:Demographic Environment, Cultural Environment
- ANALYZING MARKETING OPPORTUNITIES AND DEVELOPING STRATEGIES:MIS, Marketing Research
- THE MARKETING RESEARCH PROCESS:Developing the Research Plan, Research Approaches
- THE MARKETING RESEARCH PROCESS (Continued):CONSUMER MARKET
- CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIOR:Model of consumer behavior, Cultural Factors
- CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIOR (CONTINUED):Personal Factors, Psychological Factors
- BUSINESS MARKETS AND BUYING BEHAVIOR:Market structure and demand
- MARKET SEGMENTATION:Steps in Target Marketing, Mass Marketing
- MARKET SEGMENTATION (CONTINUED):Market Targeting, How Many Differences to Promote
- Product:Marketing Mix, Levels of Product and Services, Consumer Products
- PRODUCT:Individual product decisions, Product Attributes, Branding
- PRODUCT:NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS, Idea generation, Test Marketing
- NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT:PRODUCT LIFE- CYCLE STAGES AND STRATEGIES
- KEY TERMS:New-product development, Idea generation, Product development
- Price the 2nd P of Marketing Mix:Marketing Objectives, Costs, The Market and Demand
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:General Pricing Approaches, Fixed Cost
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:Discount and Allowance Pricing, Segmented Pricing
- PRICE THE 2ND P OF MARKETING MIX:Price Changes, Initiating Price Increases
- PLACE- THE 3RD P OF MARKETING MIX:Marketing Channel, Channel Behavior
- LOGISTIC MANAGEMENT:Push Versus Pull Strategy, Goals of the Logistics System
- RETAILING AND WHOLESALING:Customer Service, Product Line, Discount Stores
- KEY TERMS:Distribution channel, Franchise organization, Distribution center
- PROMOTION THE 4TH P OF MARKETING MIX:Integrated Marketing Communications
- ADVERTISING:The Five Mís of Advertising, Advertising decisions
- ADVERTISING:SALES PROMOTION, Evaluating Advertising, Sales Promotion
- PERSONAL SELLING:The Role of the Sales Force, Builds Relationships
- SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT:Managing the Sales Force, Compensating Salespeople
- SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT:DIRECT MARKETING, Forms of Direct Marketing
- DIRECT MARKETING:PUBLIC RELATIONS, Major Public Relations Decisions
- KEY TERMS:Public relations, Advertising, Catalog Marketing
- CREATING COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE:Competitor Analysis, Competitive Strategies
- GLOBAL MARKETING:International Trade System, Economic Environment
- E-MARKETING:Internet Marketing, Electronic Commerce, Basic-Forms
- MARKETING AND SOCIETY:Social Criticisms of Marketing, Marketing Ethics
- MARKETING:BCG MATRIX, CONSUMER BEHAVIOR, PRODUCT AND SERVICES
- A NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT:PRICING STRATEGIES, GLOBAL MARKET PLACE