 |
PR AND PRINTING PROCESSES:Fundamentals Of Printing |
| << PUBLIC RELATIONS & CASE STUDIES:Case Analysis, Images Of Public Relations |
| PUBLIC SPEAKING -- A PR TOOL:Key Benefits, How To Prepare >> |
Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
Lesson
39
PR
AND PRINTING PROCESSES
Overview
Printing
is and has been an important
tool of public relations. It is
important that a PR professional
should
know
about the printing processes,
its fundamentals and its
various important segments required
for
outstanding
results etc. besides
explaining about different
processes and printing
methods.
Why
is printing important in
PR?
---A
principle medium for
disseminating information, a
primary function of PR.
Fundamentals
Of Printing
·Types
& uses of printed material in
public relations.
·Methods
of distributing public relations printed
matter.
·Printing
processes & techniques.
·Preparing
copy for printing.
·Typography.
·Engraving.
Why
Important?
PR
professional should know about
print, printers, printing methods &
printing Requirements.
Generally
Important
to distinguish between 5 main processes
of printing.
1.
Letterpress
2.
Lithography
3.
Photogravure
4.
Flexography
5.
Silk Screen
PR
and Printing Processes
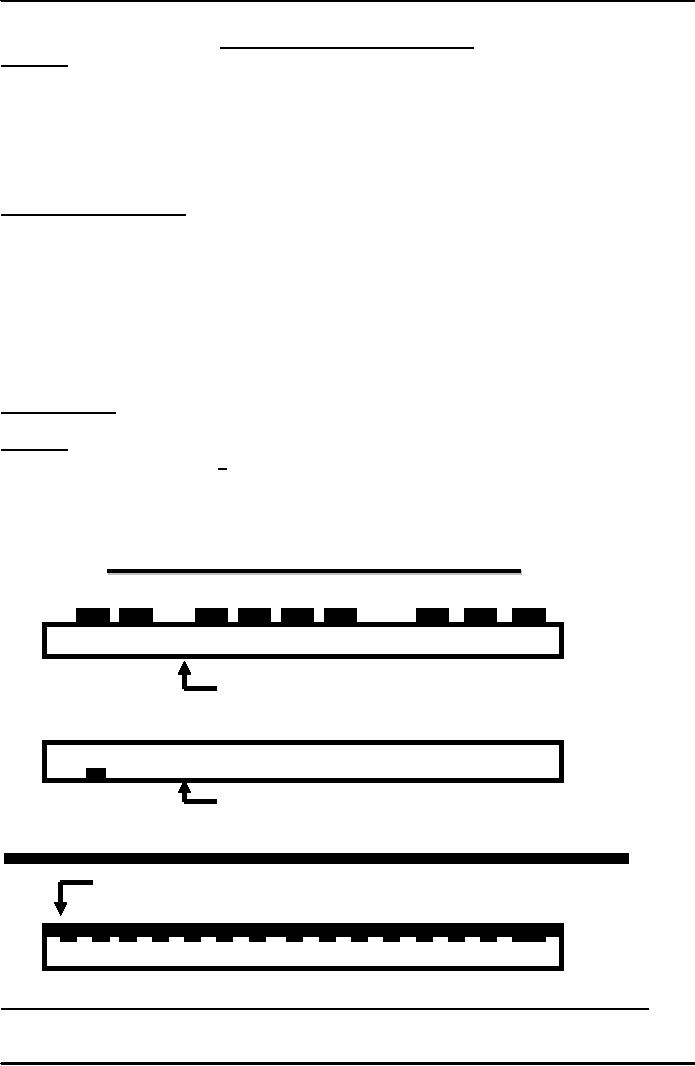
Printing
Plate (Type, blocks, electro
etc)
Letterpress
(Relief
process Printing surface
raised)
Printing
Plate (Photographic)
Lithography
(
Planographic process Printing
surface level )
Photogravure
: Recessed surface
Printing
Plate ( Photographic )
Grid
or resist formed by edges of
cells etched into
surface
93

Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
Typography: The
point System
Letterpress
words in metal, while wooden
words used for printing
large posters.
Typefaces
(individual type designs) are
measured by point system
originating to USA.
Typical
typestyles were 6, 12 & so on
e.g.
See
below:
Fonts:
A in 12
points A in 20 points A in 24 points
& so on
Style: A in
ARIAL style A in Calligrapher
style
& so on
Different
Names Of Fonts In Use
ARIAL,
BROADWAY, CALLIGRAPHER, ALGERIAN,
BAZOOKA, HEATHER,
CASTELLAR,
FORTE,
LUCIDA,
SCRIBBLE, GEORGIA & TIMES
NEW ROMAN
Letterpress
It
is a printing process that
works by taking hard type (lead,
magnesium, and polymer) applying
ink to it and
the
having it striking paper under great
pressure. It works in much the same
way a rubber stamp
works
except
the hard type actually penetrates the
paper leaving a product that
has depth and feel.
Both can be
adjusted
by varying the amount of pressure.
Offset
Printing
In
the early part of 20th century, it
was discovered that ink
could be transferred from the
lithographic
surface
to an intermediate rubber surface &
then to paper. The rubber
intermediate, called a blanket,
can
transfer
ink to paper and to a wide variety of
materials that cannot be printed
directly, including plastics
&
metals.
As the soft blanket conforms to the texture of the
surface to be printed, lithographic
image quality is
unrivaled.
Photogravure
Printing
Photogravure
prints an image from an
etched copper engraving plate
that is created from a
transparency of
a
photographic image. The
photogravure printing process
produces a photographic image
composed of fine
lines
rather than dots.
Silk
Screen Printing
This
is based on the Stencil principle.
The printing area being
cutout to allow the ink or
paint to be pressed
through
the space which is covered
with a screen of silk, nylon or
organdie mesh. This is an
old Chinese
invention.
Types
Of Paper Used For
Printing
1.
Newsprint
A
cheap, absorbent paper
suitable for
newspapers.
2.
Offset
paper
A
super calendared & polished paper
suitable for magazines,
letterheads, prestigious
stationery.
3.
Imitation
Art
A
polished paper with china
clay content.
4.
Art
Paper
A
high class paper with a
coating of china clay or
similar substance on one or
both sides which is
highly
polished.
5.
Antique
Paper
A
very rough, bulky, absorbent
paper.
Some
important tips for
printing.
Copy
Tips
·Copy should be
typewritten in double spaced
lines.
·At
least 1 inch should be allowed for
margins on left & right
side of paper.
·Don't
carry a paragraph to another
page.
94

Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
·Type
only on one side of paper.
PR
And Printing
Processes
·Place
the word "continued or more" at the
bottom of page if copy
continues to next page.
·Number
pages.
·Clearly
indicate end of copy.
Artwork
Tips
Photos,
drawings, tint blocks &
other decorative matter should be
marked for size &
position in the
finished
job.
Layout
Tips
·In
selecting type variations for a layout
select type that will reflect the
message you wish to convey.
·Select
type variations which will harmonize
& avoid too many type
variations.
·Best
to confine to family of one type
family.
Fundamentals
Of Printing
·Types
& uses of printed material in
public relations.
·Methods
of distributing public relations printed
matter.
·Printing
processes & techniques.
·Preparing
copy for printing.
·Typography.
·Engraving.
95
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION & BRIEF HISTORY:Definitions Of Public Relations
- HOW DOES PR WORK?:OVERVIEW, Formulation of policy
- PUBLIC RELATIONS DISTINGUISHED:Size of a PR Department.
- PUBLICS OF PR:Expanded Publics, Few Examples Of Publics
- PLANNING PUBLIC RELATIONS PROGRAMMES:Print Media, Electronic Media
- MEDIAS OF PR:Media for External Publics, Principles of Good Press Relations
- PRESS RELATIONS IN PR:What is News, Secrets Of Good News Release.
- CREATED PRIVATE MEDIA:Private Media, New Forms of House Journals
- SPECIAL USES OF PUBLIC RELATIONS:Crisis Management, Skills Of PR
- BUDGETING IN PR:Labour, Office Overheads, PR & Photographs
- PUBLIC RELATIONS PROBLEMS:Defining PR problems, C’s of PR explained
- METHODS OF COMMUNICATION:Psychology of Public Relations
- PR IN VARIOUS ORGANIZATIONS:Techniques of Trade Association PR
- PR IN LABOUR UNIONS & RELIGIOUS GROUPS:Community Public Relations
- PR IN EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS & IN MEDIA CHANNALS
- USING ADVERTISING FOR P R COMMUNICATION:Role Of PR
- ROLE OF PUBLIC RELATIONS IN MARKETING:How To Educate The Market
- PUBLIC RELATIONS AND CORPORATE STRUCTURE:Corporate Identity Essentials
- E-PR & ITS TOOLS:Immediate Points To Consider, Using Email As PR Tool
- SPONSORSHIP—AN IMPORTANT PR TOOL:PR & Communication Audit
- HOUSE JOURNALS:Possible Publics Of House Journals, Exhibitions & PR
- CRISIS MANAGEMENT IN PR:Plan Of Action Adopted, Interview at your place
- ADVERTISING IN PR:Broad Objectives Of Advertising, Direct Advertising.
- INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC RELATIONS:Media Used, Within Store Contacts
- PUBLIC RELATIONS CONSULTANCY:Disadvantages, Mass Communication
- PUBLIC RELATION’S ROLE IN MARKET EDUCATION:Kinds Of Markets
- MODERN DAY VALUES OF PR:Ethics Of Public Relations
- CHOICE OF MEDIA FOR PR COMPAIGN:Communication Channels & Media
- PR TECHNIQUES:Tactics & Techniques
- DESIGNING PR COMPAIGNS:Definitive Mission statement, Reputation.
- PUBLIC OPINION:Identifying Priority Publics, If Goal Is Attitude Change
- PUBLIC RELATIONS AND RESEARCH:Planning Phase Of Research
- PR AND RESEARCH:Unobtrusive Measures, Questionnaires For Survey
- PROBLEMS SOLVING STRATEGIES:Communicate results
- PERSUASION & COMMUNICATION THEORIES:Message Orientation
- COMMUNICATION CONCEPTS & THEORIES:Research and Persuasion
- PUBLIC RELATIONS & LAW:How To Stay Out Of Trouble
- PUBLIC RELATIONS & CASE STUDIES:Case Analysis, Images Of Public Relations
- PR AND PRINTING PROCESSES:Fundamentals Of Printing
- PUBLIC SPEAKING -- A PR TOOL:Key Benefits, How To Prepare
- PR -- COPING WITH UNEXPECTED:Some Possible PR Ideas
- DREAMS & REALITIES OF PR:Who Takes Charge Of Identity?
- CHANGING INTO OVERDRIVE:How International Is PR?
- GETTING ON WITH PR:Where does PR fit in the structure?
- FUNDAMENTALS OF A SUCCESSFUL NEWSLETTER:RESEARCH, WRITING