 |

Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
Lesson
34
OTHER
ADVERTISING MEDIUM
OVERVIEW
Magazines
are also an important medium of
advertising amongst the
print media the
students
will
be explained as to who should
use magazines for their
advertisements and cost to be
incurred
thereon. Besides this a
traditional yet effective
electronic media like radio and
its
usage
and its utility will be discussed.
The students will also be explained
the criteria and
essentials
of making a good spot to be released on
radio. Like radio television
has assumed lot
of
importance as a very effective
advertising media and with the
advent of many channels
it
gives
a great opportunity for the advertisers
to use this very
illustrative and effective
medium.
In
this context students will
know about producing TV spots, a
typical TV script and
the
process
of choosing a production company to
prepare outstanding TV
advertisements.
HOW
TO USE MAGAZINES:
Who
should use
magazines?
Magazines
are primarily directed at a broad
market like newspapers but
our directed at
specific
audiences
therefore there are an
excellent medium for
advertisers who's potential
market is
highly
targeted and / or scattered over a vide
geographical area with their
long slow publication
schedules
magazines are for those advertisers who
are more interested in
building long term
business
than generating rapid sales.
To elaborate further following is the
classification of
advertisers
who should use
magazines.
·
Whose
potential market is highly targeted and /
or scattered over a wide
geographical
area.
·
For
advertisers with a broader target and a
more narrow geographic
range.
·
For
advertisers who have patience &
generally for those more interested in
building long
term
business than in generating
rapid sales
Cost
of magazine advertising:
Generally
the cost of magazines advertising vary
based on following
criteria.
1.
Types of magazines.
2.
Circulation.
3.
Positioning.
4.
Strength.
HOW
TO USE RADIO:
Who
should use Radio?
Following
are different components of
consumers who can effectively
use this medium
for
immediate
response for their sales or
promotion.
·
Almost
any business serving a
consumer market can use
Radio.
·
Radio
can bring immediate response
for your sale &
promotion.
·
It is
equally good at increasing awareness of
your business.
Costs:
The
costs vary based on
following factors.
·
An
excellent radio spot can be produced
from nothing to several
thousand Rupees.
·
Air
time depends upon coverage and Size of
the market.
·
Radio
station rates are based on 3
Factors.
i.
Length of spot.
100

Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
ii.
No of spots bought in a given
time.
iii.
Time of day the
daypart.
Daypart
buying options:
The
chunks and spots costs vary
based on the part of the
day and the position of the
ad with
regard
to the timing and program
results in variation of costs
thereby resulting in different
day
part
buying options. Following
are three different day
part buying options.
1.
Buying
by specific daypart: Specific
dayparts that are at the
precise time in which
they
want
their ads to be heard.
2.
Buying
package: Buying a
package of spots at a flat rate &
the station decides
when
the
spots will run.
3.
Buying
sponsorships or adjacencies: Associating
your company name with a
specific
program.
Adjacency is next to sponsorship
just before or just after
the program.
Producing
a Radio Spot:
In
order to produce a good and effective
ratio spot following three
basic elements should
be
kept
in mind.
1.
Good
Voice
·
Using local radio
talent.
·
Using amateur
voice
·
Hiring professional voice
talent.
2.
Good
Music
·
Can produce original
music
·
Use free music from
station's library.
·
Buy canned music by popular
music composers etc.
3.
Good
background Effects.
·
Many available on line, and on
radio etc.
Radio
Copy Tips:
There
are three things a radio
spot (or any advertising
needs to do.
1.
Grab
the attention of listeners in
less than 7 SECONDS.
2.
Make
an offer.
3.
Give
the listener all the
Information he or she needs to act on
the offer.
AUDIO
LOGOS:
If
you cannot afford a jingle
then there is inexpensive
alternative. If you have a
slogan than the
announcer
can read it at the end of every
single spot you ever produce
this is called an
audio
logo.
HOW
TO USE TELEVISION:
Television
is ideal for advertisers who
need to demonstrate their product. As
they say "Look
the
customer in the eye" and
creates sense of excitement.
Many advertisers consider
television
to
the most powerful of all
advertising media because it can give
the viewer a sense of what
it
is
likely to actually own, use
and experience what is being
advertised. It is a complex,
often
expensive
medium that can demand more of
your time, thought and
budget than any
other.
101

Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
HOW
TV STATIONS DIVIDE DAYS &
RATES:
As
with radio the TV stations
also divide their day in to
dayparts although these time
divisions
may
differ from place to place area to
area yet a typical day
looks something like given
below:
Morning
6 AM to 9 AM
·
Programs
like news, weather,
interviews etc.
·
Typical
Audience --- people getting
ready for work
MID
day. -------- 9 AM to 4 PM
·
Programs
like Dramas, game shows
,movies, some talk
shows.
·
Typical
Audience ------ housewives
etc.
Early
Fringe. ------- 4 PM to 7 PM
·
After
school kid's shows, local
national news etc.
·
Typical
Audience ---- Children, people
coming back from
work.
Prime
Access. ----- 7 PM to 8 PM
·
Game
shows and entertainment
etc.
·
Typical
Audience ----
General.
Prime.
------ 8 PM to 11 PM
·
News ,
comedies, dramas and movies
·
Typical
Audience ---- General
Late
Fringe.---- 11 PM to 1 AM
·
News,
Talk shows, Dramas, music
shows, movies.
·
Typical
Audience ---- Adults, Teens
etc.
Late
Night. ----- 1 AM till 6 AM or
sign off.
·
Movies,
Dramas.
·
Typical
Audience --- Adults,
Teens
PRODUCING
TV SPOTS
·
FORMING
CONCEPT: A good TV concept should be
simple and the advertiser
should
not
try to say too much and show
too much as such ads
are confusing and
cluttered.
·
WHAT
MAKES A GOOD CONCEPT: The
adds should be very simple,
very
memorable,
very effective and should be able to
deliver the message about
your business,
basically
look for effectively
communicative messages that will
appeal to your
target.
·
THE
SCRIPT: The usage of the
script while producing your
commercial TV spot is
essential.
A good strip at the end helps in
preparing an effective television
commercial.
Following
is a typical TV script
102
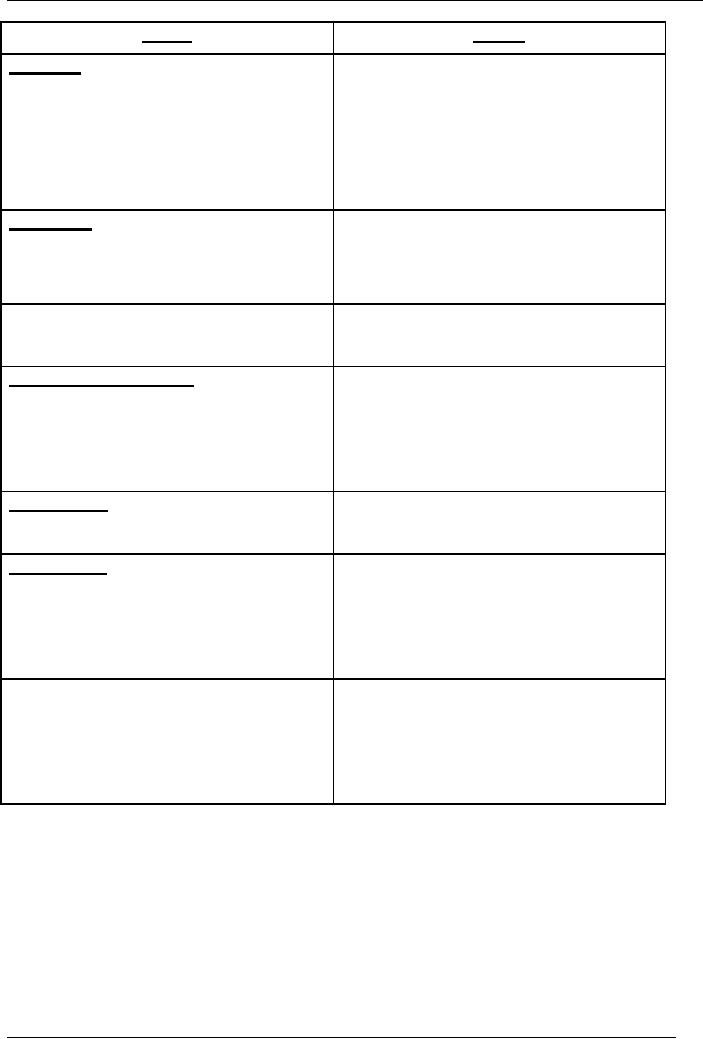
Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
TYPICAL
TV SCRIPT
Video
Audio
FADE
IN
Establishing
shot of typical
Office;
young mother at
Computer
looks at watch.
Tight
Shot
Announcer
Voice Over
Face
of young mother, Looking off
to
camera
left & Preoccupied.
She
turns to look directly Into
camera; Woman At home.
Aren't they?
concerned
CUT
to Medium shot of 8 Year girl
Announcer: Sure, that's
where you told
idling
along street cars go by, one
them to be, but kids
Are kids, wouldn't
slows.
you
rather be certain?
Tight
shot:
Woman's
hands
at
Woman (ironically) Sure. I
will just quit
keyboard,
she gestures
Helplessly.
my
Job and stay
home.
TWO
SHOT
(no
audio)
Child
talks to shadowy
Male
driver inside car.
Announcer:
But now there's a way
even
struggling single moms can
afford
good,
safe, after school child
care....
·
LIVE
VIDEO or SLIDES: Another way
to save money for producing
TV spots is to use
slides
or art work instead of "live"
film or video action. If
used creatively slides or
art
work
can create an attractive, captivating
spot.
·
·
CHOOSING
PRODUCTION COMPANY: You can have
two major options for
getting
your
TV spots produce:
·
Either
let the TV station produce
it
·
Or
Hire an independent production
co.
103

Advertising
and Promotion (MKT621)
VU
Appraise
Production Company as
under
When
choosing a production company,
keep following important
points in mind:
1.See
what they have done so
far.
2.Check
their experience for your
type.
3.Ensure
co. has broadcast quality
equipment.
4.Beware
of a co. bragging about
equipment.
5.Know
about co. charges before
hand.
Tape
or Film:
Hiring
Talent:
104
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:Its growing importance, Explanation of Personal and non-personal selling
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:ADVANTAGES, Communication, Information, Various Media
- INTRODUCTION TO ADVERTISING:FUNCTIONS OF ADVERTISING, IMPACT OF ADVERTISING
- ADVERTISING AND SOCIETY:PRACTICAL BENEFITS, ETHICS IN ADVERTISING, Marketplace & Market space
- MARKETING TOOLS:COMPONENTS OF MARKETING MIX, PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE (PLC) CURVE
- MARKETING TOOLS:SWOT Analysis, Contents & Structure, ROLE & FUNCTION OF ADVERTISING
- ROLE AND FUNCTIONS OF ADVERTISING:Structure of an Advertising Agency, How to Select an Advertising Agency
- ADVERTISING PLANNING:ADVERTISING OBJECTIVES, Types of Advertising, Positioning Strategies
- POSITIONING:BRANDING, 7 Steps of Creative Process, UNIVERSAL ADVERTISING STANDARDS
- ADVERTISING MESSAGE:Message Content, BASIC TERMS & CONCEPTS
- ADVERTISING BUDGET:4 Methods to determine, ADVERTISING RESEARCH, ADVERTISING RESEARCH
- ADVERTISING REACH:BROAD COMMUNICATION OBJECTIVES, ADVERTISING COPY METHODS, MEDIA RESEARCH
- PRE – PLACEMENT EVALUATION:ACCOUNT PLANNING, MARKET, COMPETITION
- WORKING OF ADVERTISING:12 Steps to develop effective campaign, SOURCE or THE ADVERTISER
- ADVERTISING RESPONSE HIERARCHY MODELS:AIDA MODEL, PROCESS REQUIRED TO GET BIG IDEA
- PROBLEM SOLVING STRATEGIES:Procedure to Handle Problems, In brief, Eight principles apply to consumer behavior
- CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR:ADVERTISING APEALS, MEDIA MIX DECISIONS, Target Rating Point (TRP)
- CREATIVITY IN ADVERTISING:Three aspects are most accepted, Four Rules of Creativity
- COPY WRITER:CHARACTERISTICS OF COPYWRITER, IMPORTANCE OF LANGUAGE
- WHY ADVERTISING:Advertising & Market Education, ADVERTISEMENT CAMPAIGNS
- METHODS TO APPRECIATE A PROBLEM:SPONSORSHIP—an important tool, Special Characteristics
- IMPORTANT TOOL OF ADVERTISING:TELEVISION ADVERTISING, TRANSIT ADVERTISING
- ONLINE ADVERTISING:Banners, Logos, Email Ads, Keywords on Search Engines, New Developments
- ONLINE ADVERTISING:Structural Challenges, Adobe Photoshop, JAVA, HTML, DHTML, ASP & JSP
- SALES PROMOTION:Consumer Oriented Promotion, HOW TO USE TRADE PROMOTION, Dealing with the Trade
- PUBLICITY:PERSONAL SELLING, ROLE OF SALES PERSON, FUTURE OF GLOBAL ADVERTISING
- MARKETING ENVIRONMENT:Competitors, The Target Buyer, Segmenting your Market, FUTURE OF MARKET GROWTH
- MARKETING PLAN:Situational Analysis, Macro – Environment Situation, Marketing Objectives, Financial Objectives
- MARKETING PLAN:PROMOTING BUSINESS IN LOW COST, SUPPLY CHAIN, BUYER IDENTIFICATION
- HOW TO BE GOOD CLIENTS:CHANNEL BUYERS, HOW TO BE GOOD CLIENTS 14 RULES
- CLIENT – AGENCY RELATIONSHIP:HOW TO KEEP CLIENTS (10 Ways), Three Points for Consideration
- CLIENT – AGENCY RELATIONSHIP:ADVERTISING WITHOUT AN AGENCY, LOGO AND CORPORATE IDENTITY
- NEWSPAPER ADVERTISING:AD PRODUCTION,TYPES OF NEWSPAPER ADS, CIRCULATION
- OTHER ADVERTISING MEDIUM:HOW TO USE MAGAZINES, HOW TO USE RADIO, Daypart buying options
- UTILITY OF VARIOUS MEDIA:TAPE OR FILM, UTILITY OF TV, DIRECT MAIL PACKAGE
- OTHER ADVERTISING MEDIA:POINT OF PURCHASE (POP), TRANSIT ADVERTISING, LIMITS OF ADVERTISING
- CONTINUOUS TRACKING:PLANNING CAMPAIGN, HOW TO UNDERSTAND ADS, ASK BASIC QUESTIONS
- SEASONAL ADVERTISING:MAXIMIZING IMPACT, THE WEB ADVERTISING, MEASURING ADVERTISING
- COMPONENTS OF ADVERTISING:BUY - OLOGY OF MIND, BUY - OLOGY OF MIND
- CRITICISM ON ADVERTISING:SHOULD ADVERTISING BE ABOLISHED,
- EFFECT OF ADVERTISING:HOW TO PROMPT AWARENESS, CREATING DESIGN THAT SELLS
- CREATING EFFECTIVE DESIGN:LANGUAGE OF TYPOGRAPHY, HEADLINES THAT COMMUNICATE
- WORKSHEETS:DEMOGRAPHICS OF YOUR TARGET, YOUR COMPETITOR
- GLOSSARY OF ADVERTISING:ACCOUNT EXECUTIVE, PROOF, VOICE OVER
- CONCEPT OF AN AD:HOW TO DEVELOP A CONCEPT OF AN AD