 |
NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS |
| << ACCOUNTING SYSTEM IN NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS |
| PREPARATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS FROM INCOMPLETE RECORDS >> |

Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
LESSON
# 7
NON-PROFIT
ORGANIZATIONS
Preparing
financial statements with
incomplete records
Most of
the non-profit organizations
operate in medium scale and do not
prepare
proper
books of accounts. The only
accounting record that is
maintained in such
sized
organizations
is cash book along with year
end adjustments. The
management also
keeps
Statement of Affairs as on opening
date to maintain during the
year movements
in
the balance sheet
items.
o Cash
Book (Receipt and Payment
Account)
o Statement
of Affairs (as on opening
date)
o Year
end Adjustments
Accrued
incomes and expenses
Advance
receipts and payments
Depreciation
rate
Like
business entities, these few
accounting records are used
to convert the
information
into double entry system and to produce
Income & Expenditure
Account
and
Balance Sheet.
The
technique of preparing financial
statements of a non-profit organization
is similar
to
that used for preparing
financial statements of a business
entity.
While
preparing Income
& Expenditure Account following
shall be assumed to
calculate
expenses
and incomes
Calculation
of incomes
For
non-profit organizations the
incomes are picked up from
the cash books and
amended
with the year end
adjustment:
Cash
based incomes
Cash
based incomes are the
revenue receipts that are
picked up from its origin
cash
book
and are processed into the
filter of accruals, like
this:
Rs.
Cash
received during the
year
***
Less
Opening balance of accrued
income
***
Add
Closing balance of accrued
income
***
Add
Opening balance of advance
receipts
***
Less
Closing balance of advance
receipts
***
***
Fixed
Assets based
incomes
Profit/gain
on disposal of Assets are
calculated with the help of
sales proceeds
appearing
in receipts side of Cash
Book and some relevant
information appearing in
the
year-end adjustments like
cost and accumulated depreciation of
the asset disposed
off.
Calculation
of expenses
For
non-profit organizations the
expenses are picked up from
the cash books and
amended
with the year end
adjustment:
Cash
based expenses
Cash
based expenses are the
revenue payments that are
picked up from its origin
cash
book
and are processed into the
filter of accruals, like
this:
31

Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
Rs.
Expenses
paid in cash during the
year
***
Less
Opening balance of accrued
expenses
***
Add
Closing balance of accrued
expenses
***
Add
Opening balance of prepaid
expenses
***
Less
Closing balance of prepaid
expenses
***
Expense
for the year to be shown in the
Income Statement
***
Fixed
Assets based expenses
1.
Depreciation is calculated based on
the depreciation rate
mentioned in the
Year-end
Adjustments
2.
Loss on disposal of an asset
are calculated with the help
of sales proceeds
appearing
in receipts side of Cash
Book and some relevant
information
appearing
in the year-end adjustments
like cost and accumulated
depreciation
of
the asset disposed
off.
Balance
Sheet of a
non-profit organization is prepared in
the usual way and
contains
particulars
of all assets and liabilities of the
organization on the date on which it
is
prepared.
Net assets of non-profit organization are
represented by Capital Fund in
the
balance
sheet. This Capital Fund
replaces the owner's
equity.
The
opening balance of Capital Fund is
calculated through the Statement of
Affairs as
on
the opening date. Such
opening Capital Fund is then adjusted
with the surplus or
deficit
in the Balance Sheet.
Capital
receipt like; specific
donations, funds, grants
etc. for purchase/acquisition or
construction
of assets are also included in
the Capital Fund of the
organization.
Calculating
Subscription Income
Although
calculating subscription income is not a
separate issue apart from
the
calculation
of incomes for the year
originating from the cash
book, but even then
its
calculations
are being shown over here
just to give confidence through
practice.
Subscription
is cash based income and
like other revenue receipts
it appears in receipts
side
of the cash book summary. It
is picked up from there and then amended
with the
opening
and closing balances of subscriptions
accrued and received in
advance.
Solved
Problem # 1
Rupees
Subscription
received during the year
2007
7,000
Subscription
outstanding at the beginning of
2007
1,400
Subscription
outstanding at the closing of
2007
1,600
Calculate
the amount of subscription
income for the year
2007.
Working:
Subscription
received during the
year
7,000
Less
Opening due
1,400
Add
Closing due
1,600
Income
for the year
7,200
32
Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
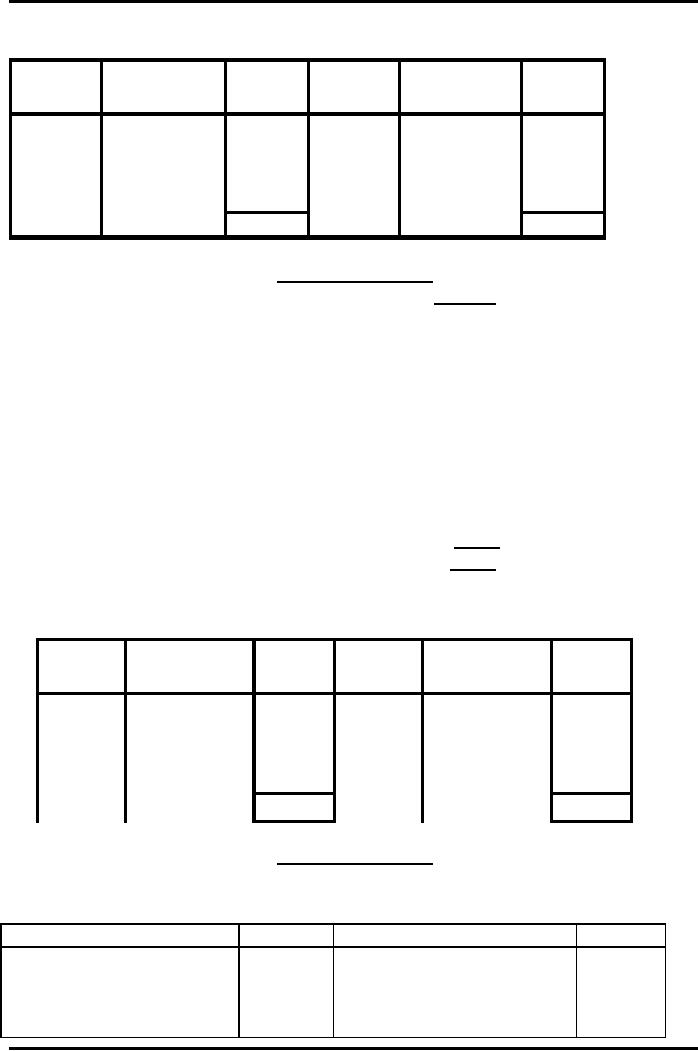
Subscription
Income Account
Date
Particulars
Amount
Date
Particulars
Amount
Rs.
Rs.
1/1/07
Subscription
DTY
Cash
7,000
opening
due
1,400
31/12/07 Subscription
7,200
31/12/07
Subscription
closing
due
1,600
income
8,800
8,800
Solved
Problem # 2
Rupees
Subscription
received during the year
2007
12,000
Subscription
received in advance for 2008
1,400
Subscription
outstanding at the beginning of
2007
1,600
Subscription
outstanding at the closing
2007
700
Calculate
the amount of subscription at
the closing of
2007.
Working:
Subscription
Received during the year
2007
12,000
Less
Opening due
2,000
Less
Closing advance
1,600
Add
Closing due
700
Income
for the year
9,100
Subscription
Income Account
Date
Particulars
Amount
Date
Particulars
Amount
Rs.
Rs.
1/1/07
Opening
due
2,000
DTY
Subscription
12,000
31/12/07
Closing
1,600
31/12/07 received
31/12/07
advance
9,100
Subscription
700
Income
for the
closing
due
year
12,700
12,700
Solved
Problem # 3
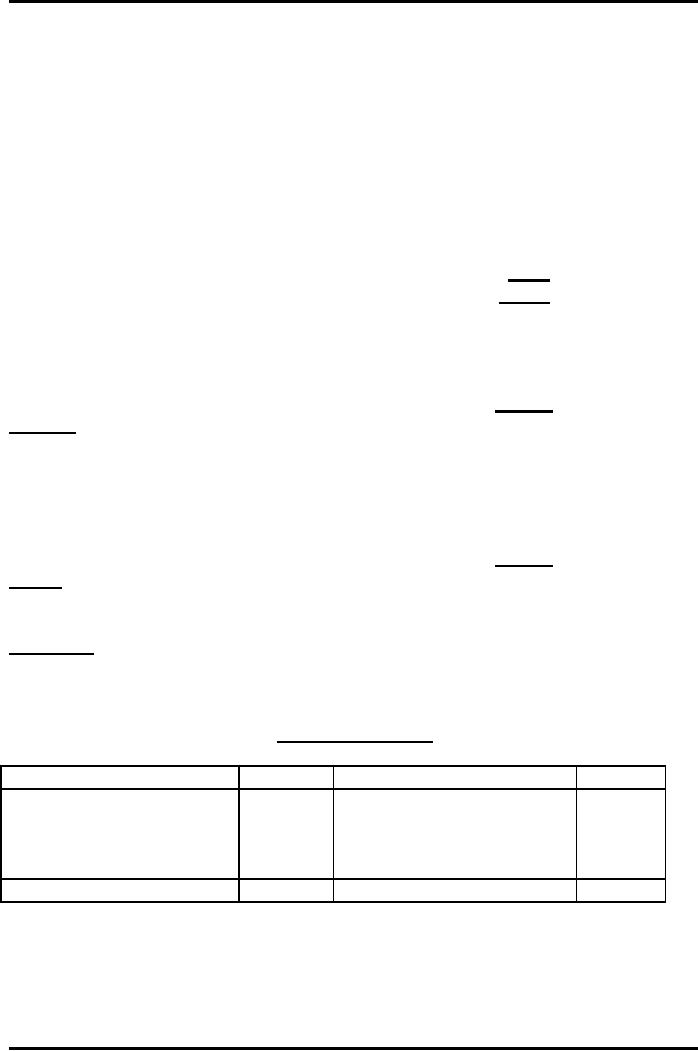
Receipts
and Payment Account
For
the year ended December
31, 2008
Receipts
Rs.
Payments
Rs.
Subscription
2007
Rs.2,000
2008
6,000
2009
2,000
10,000
33
Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
Additional
information:
1.
Subscription due on 31-12-2007
Rs.
2,000
2.
Subscription due on 31-12-2008
Rs.
4,000
3.
Subscription received in advance as on
31-12-2007
Rs.
3,000
4.
Subscription received in advance as on
31-12-2008
Rs.
2,000
Working:
Rupees
Cash
received during the
year
10,000
Less
Opening balance of accrued
income
2,000
Add
Closing balance of accrued
income
4,000
Add
Opening balance of advance
receipts
3,000
Less
Closing balance of advance
receipts
2,000
Income
for the year
13,000
Income
and Expenditure
Account
For
the year ended December
31, 2008
(Extract)
Rupees
Incomes
Subscription
income
13,000
Balance
Sheet
As at
December 31, 2008
(Extract)
Rupees
Assets
Subscription
receivable
4,000
Liabilities
Subscription
received in advance
2,000
Solved
Problem # 4
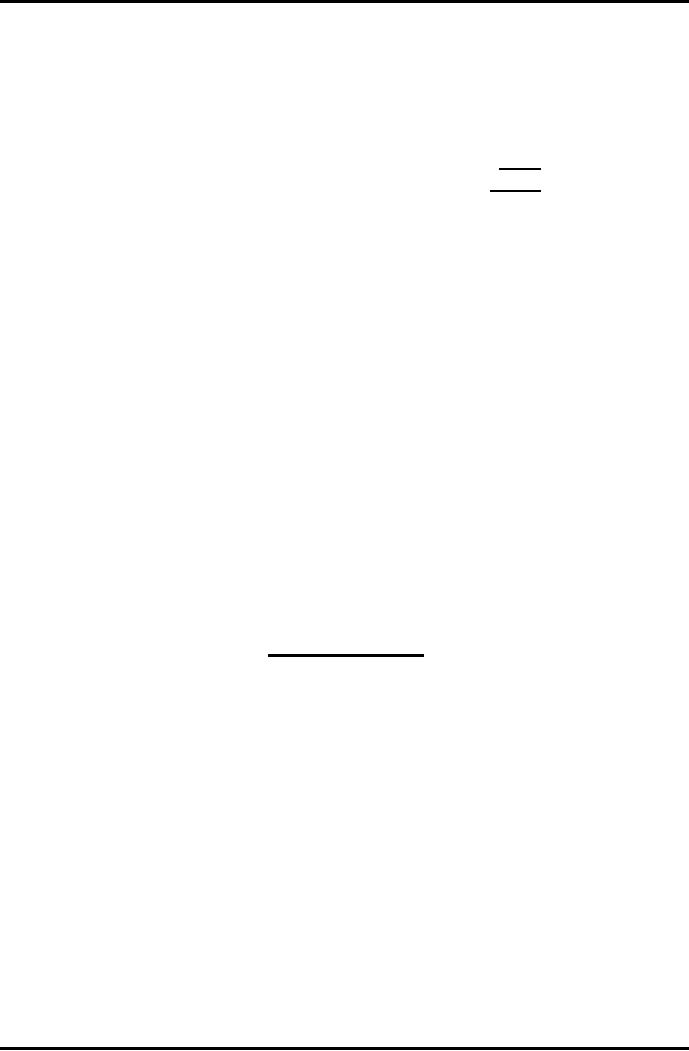
Receipts
Rs.
Payments
Rs.
Subscription
2007
Rs.
1,800
2008
10,000
2009
4,000
15,800
Additional
information:
1.
Subscription due on 31-12-2007
Rs.
2,000
2.
Subscription due on 31-12-2008
Rs.
3,000
3.
Subscription received in advance as on
31-12-2007
Rs.
2,000
4.
Subscription received in advance as on
31-12-2008
Rs.
4,000
34
Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
Working:
Rupees
Cash
received during the
year
15,800
Less
Opening balance of accrued
income
2,000
Add
Closing balance of accrued
income
3,000
Add
Opening balance of advance
receipts
2,000
Less
Closing balance of advance
receipts
4,000
Income
for the year
14,800
Income
and Expenditure
Account
For
the year ended December
31, 2008
(Extract)
Rupees
Incomes
Subscription
income
14,800
Balance
Sheet
As at
December 31, 2008
(Extract)
Rupees
Assets
Subscription
receivable
3,000
Liabilities
Subscription
received in advance
4,000
Solved
Problem # 5
Following
is the data relating to
membership fee of HF Club for the
accounting year
April 2007 to
March 2008.
1.
Cash/Cheque received during the
year totaled Rs.
100,000.
2. As on April
1, 2007 Rs. 2,000 was in
arrears for March 31, 2007 and Rs. 800
was
received
in the previous year as
advance membership
fee.
3.
Received Rs. 1,500 towards
the next year's membership
fee, but could not yet
recovered
Rs. 1,700 from current year
members.
Calculate
"Membership Fee" for the
year 2007-08
Working:
Membership
fee received during the
year
Rs.
100,000
Opening
advance
Rs.
800
Closing
advance
Rs.
1,500
Opening
due
Rs.
2,000
Closing
due
Rs.
1,700
35
Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
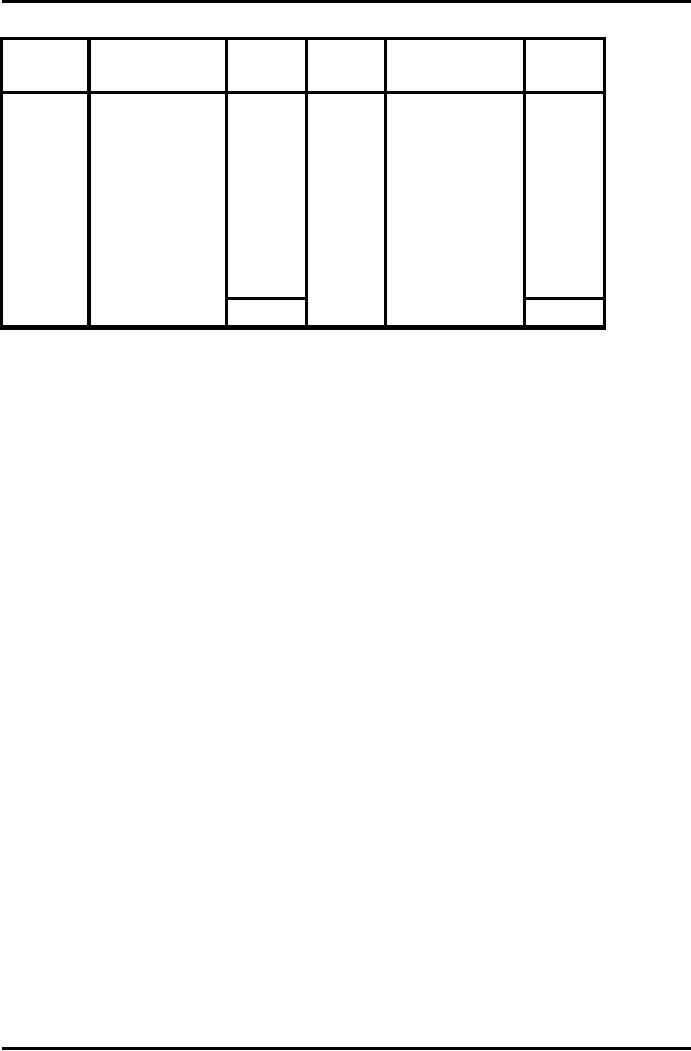
Membership
fee Account
Date
Particulars
Amount
Date
Particulars
Amount
(Rs.)
(Rs.)
1/4/07
Opening
due
2,000
1/4/07 Opening
800
1,500
DTY
31/3/07
Closing
advance
100,000
9,100
31/3/08 Cash
31/12/07
advance
700
Income
for the
Closing
due
year
12,700
12,700
36
Table of Contents:
- ACCOUNTING FOR INCOMPLETE RECORDS
- PRACTICING ACCOUNTING FOR INCOMPLETE RECORDS
- CONVERSION OF SINGLE ENTRY IN DOUBLE ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
- SINGLE ENTRY CALCULATION OF MISSING INFORMATION
- SINGLE ENTRY CALCULATION OF MARKUP AND MARGIN
- ACCOUNTING SYSTEM IN NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS
- NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS
- PREPARATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS FROM INCOMPLETE RECORDS
- DEPARTMENTAL ACCOUNTS 1
- DEPARTMENTAL ACCOUNTS 2
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING SYSTEMS
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING - STOCK AND DEBTOR SYSTEM
- STOCK AND DEBTORS SYSTEM
- INDEPENDENT BRANCH
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING 1
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING 2
- ESSENTIALS OF PARTNERSHIP
- Partnership Accounts Changes in partnership firm
- COMPANY ACCOUNTS 1
- COMPANY ACCOUNTS 2
- Problems Solving
- COMPANY ACCOUNTS
- RETURNS ON FINANCIAL SOURCES
- IASBíS FRAMEWORK
- ELEMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- EVENTS AFTER THE BALANCE SHEET DATE
- PROVISIONS, CONTINGENT LIABILITIES AND CONTINGENT ASSETS
- ACCOUNTING POLICIES, CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES AND ERRORS 1
- ACCOUNTING POLICIES, CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES AND ERRORS 2
- BORROWING COST
- EXCESS OF THE CARRYING AMOUNT OF THE QUALIFYING ASSET OVER RECOVERABLE AMOUNT
- EARNINGS PER SHARE
- Earnings per Share
- DILUTED EARNINGS PER SHARE
- GROUP ACCOUNTS
- Pre-acquisition Reserves
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Minority Interest
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Inter Company Trading (P to S)
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Fair Value Adjustments
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Pre-acquistion Profits, Dividends
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Profit & Loss
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Minority Interest, Inter Co.
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Inter Co. Trading (when there is unrealized profit)
- Comprehensive Workings in Group Accounts Consolidated Balance Sheet