 |

Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
Lesson
8
CREATED
PRIVATE MEDIA
Overview
In
this lecture information will be
provided about various
created private media, its
different kinds and
their
importance.
We will also explain about
various types and points
regarding house journals; and
how to plan
them.
We will also deal with
methods of assessing results
and matters pertaining to
market research, its
importance
and how to conduct
it.
In
order to reach certain
publics to achieve particular objectives,
the mass media of press,
radio and
television
may not be appropriate, especially if
these publics comprise small
or specialized groups.
One
public
which comes to mind is the staff
(or the membership) who may
be best reached by house
journal.
The
main forms of such created
private media are given
below.
Private
Media.
1.
House Journal.
2.
Videos
3.
Slides.
4.
Audio Cassettes.
5.
Spoken word.
6.
Private exhibitions.
7.
Seminars etc.
8.
Educational Literature
4
Types of House
Journals.
1.
Magazines - -
A4
size.
2.
Newspapers - -
like
a tabloid.
3.
Newsletter - -
2
to 8 pages.
4.
Wall newspaper - - like a
poster.
Points
To Note When Planning A
House Journal
1.
Determining
Readership .
2.
Quantity.
3.
Frequency
of publication
4.
Policy.
5.
Title.
6.
Printing
process.
7.
Style
& Format.
8.
Priced
or free.
9.
Advertisements.
10.
Distribution.
11.
Budgeting.
12.
Considerations.
13.
Obtaining
material
14.
Designing.
New
Forms of House
Journals.
In
recent years following
4
new
forms of house journals have given new
dimension to management-
employee
relations.
1.
Audio
Tapes.
2.
CD/Video
House journals.
3.
Corporate
video .
4.
Electronic
Newspaper.
Videos.
CD
ROMs, Videos etc.
Slides.
Another
important media for TV's
Cinemas etc.
Transparencies,
35mm slides, OHP
films.
Audio
Cassettes.
Use
of Audio cassettes in cars,
conferences etc.
Educational
Literature.
For
encouraging, explaining use of a
product.
The
spoken word.
Talks
etc.
Seminars
& Conferences.
Receptions
in hotels, basically educational
for the consumers, users,
beneficiaries so that they are
made
aware
about its proper usage and
benefits.
Private
Exhibitions.
Could
be permanent on company premises or at a
special venue/site.
Evaluating
Results
20
Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
Once
all parameters of a public relations
plan are in place, it is imperative to
evaluate the results to
determine
the success and benefits accrued
from such plan. There can be
basically two types of
results;
2
Kinds Of Results.
Qualitative.
These cannot be measured statistically.
Many results of PR activity
will be of this kind, that
is,
these
will be only judged by experience
and self-evident qualities e.g. the
evidence that the job
applicants are
now
better educated, more proficient or in
some other way more
suitable than in the
past.
Quantitative.
These are statistics based
results. These are generally
self evident results which
are seen or
experienced
for instance a percentage
increase in awareness , a reduced number
of complaints, improved
sales
etc..
Methods
of Assessment.
By
Enquiries Received. When
media coverage produces direct
enquiries their numbers can
be totaled, and
if
they are converted into sales
their value can also be
calculated.
By
Statistical Data.
Readership figures and
audience ratings can be a
good measure.
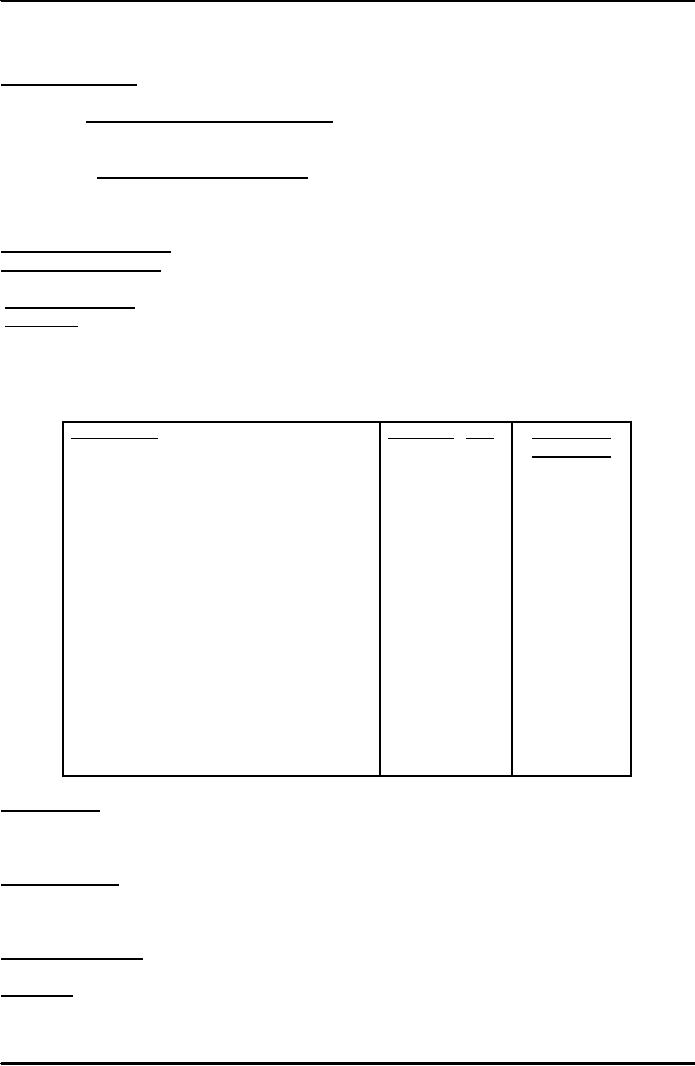
By
Source. Another
good method of evaluating media coverage
is to give values to each newspaper
or
magazine
and so arrive at a source for
each news release issued.
This will vary from product
to product, but
for
understanding purpose let us take the
value of a financial /commercial /stock
market story i.e.
press
release,
following chart will explain the
rating valuations. However it will be
totally different in case
of
house
hold products or consumer
goods.
Financial
Story
Household
Newspapers
Goods,
etc.
Daily
Business Recorder
12
4
Daily
Dawn
10
8
Daily
Jang
9
12
Daily
News
8
7
Daily
Nation
7
6
Daily
Nawa-i-Waqt
6
11
Daily
Khabrain
5
10
Daily
Pakistan
4
9
TOTAL
61
67
Opinion
Polls. The
shift of opinion or the extent of
awareness can be measured by
means of an opinion
poll.
If samples of relevant publics are
interviewed after every six months, it is
possible to measure the
upward
or downward trend of these
shifts.
Media
Feedback. If the
media have shown
misunderstanding, skepticism or hostility
in the past, does the
media
now is well informed and
more sympathetic? This could be direct
result of Public relations
activity
such
as news releases, feature
articles, press information
service, press receptions
and facility visits.
Marketing
Research.
Definition
`A
branch of social science
which uses scientific methods to collect
information about markets for
goods &
services.'
21

Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
Research
Terminology
Marketing
research has its own
special language. Some of the
terms have lay meanings
and the student
ought
to be careful to understand the precise
research meanings of the following
terms.
1.
Population
or universe in marketing
research both words means
the total number of people
relevant
to a particular survey. E.g. all
dentists or university students depending
upon the subject of
study.
2.
Respondent
or interviewee - A
person questioned in a
survey.
3.
Sample
This should not be confused
with a `free sample', in fact it
means a survey of a
proportion
of the population or universe to be
questioned.
4.
Characteristics
- distinctions
which are known to exist in
the population.
5.
Sampling
frame - specification of
the kinds of people.
6.
Random
walk - list
of names & addresses may
not exist. Random method
calling homes like
select
every
10th house.
7.
Structured
interview
conducted with a prepared
questionnaire.
8.
Depth
interview
one with no prepared
questionnaire.
9.
Questionnaire.
A
specially devised format has
to be prepared to meet the demand the
particular
survey
requirement.
10.
Social
grades
classification of people into socio
economic groups based on
incomes. Can be a
very
effective and useful method of survey
for the assessment of
results.
Marketing
Research Methods
Published
Survey Findings. For
various purposes beginning with the
census of population, surveys
may
have
been made by official,
institutional or commercial
organizations. These findings
may have been
published
and made available to
concerned and interested
parties.
Commissioned
Surveys. For
marketing and advertising purposes the PR
practitioner may have
commissioned
surveys and the results could be
helpful when determining the current
image and planning a
PR
program.
Advertising
Media Research.
Advertising media research
could be useful when
measuring press
readership
and television ,radio and poster
audiences.
Original
Or Primary Research. As a
matter of appreciating the situation
(using image studies or
opinion
/attitude
surveys) and of monitoring the
progress and success of PR
campaign, original research
can be
commissioned.
Types
of Research
Desk
Research It is
basically a study of existing statistics
and survey reports.
Field
Research
This normally done by interviewing people
`in the field', as when interviewers
contact
respondents.
Ad
hoc Research
This means one - off
surveys, complete in one
project only.
Continuous
Research
These are the surveys
carried out regularly e.g.
monthly, thus recording
changes
or
trends.
Marketing
Research Techniques.
Opinion,
attitude or shift surveys.
These are usually for
seeking "yes" or "no",
"don't know", answers,
often
continuous or at least repeated at
regular intervals to know what people
know, think or believe and
to
measure
changes or shifts in awareness
opinions or beliefs.
Consumer
Panels. A
panel is a recruited group of respondents
who serve more or less
permanently to
answer
questions or to test
products.
Motivational
Research. This
research seeks by means
techniques similar to those
used in clinical and
intelligence
testing, to reveal hidden
motives, instead of stated
opinions.
Discussion
Group. This
is a much modified and less
expensive form of motivational
research.
Tele(phone)
Questionnaire.
Surveys of distant or scattered
respondents can be conducted by
pre
arranged
telephone interview. This can be
pretty useful in industrial
research.
22
Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
Postal
Questionnaire.
This
is posted to respondents and
return of the completed forms will
depend
upon
the extent to which the respondents are
motivated or will cooperate,
perhaps because they
are
committed
to the subject.
Coupon
Survey. This
is a survey published in the press, but
it has the obvious weakness
that only those
very
interested will bother to submit
answers.
Dealer,
retail or shop audit. This is in
fact a form of continuous research,
whereby the stocks and
invoices
of a recruited panel of dealers are
checked at regular intervals. The
figures are taken of
goods
bought
and remaining in stock thus
revealing how various brands
are moving out of the shops,
making
comparison
between rival brands, and in
the aggregate showing the market share of
each brand.
Qualitative
Research. This
is like depth interviewing,
which overcomes some of the
difficulties which
hamper
research in developing countries
where facilities are different
from those in industrial
countries.
Image
study. The
object of an image study is to compare
the strengths and weaknesses of a number
of
similar
companies, of which the sponsor is
one although not identified
as such to respondents.
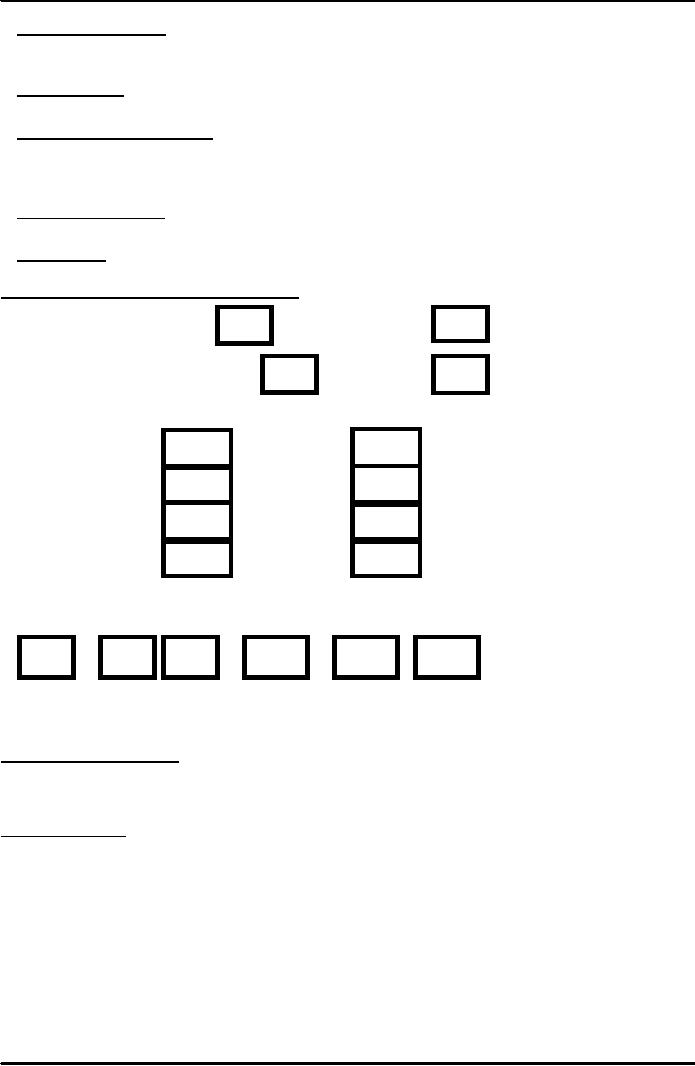
Marketing
Research ( a model
survey form )
Do
you drive a car
YES
NO
If
YES , Do you own a
car
YES
NO
(b)
Which of the following makes of
car do you normally
drive?
Suzuki
Fiat
Honda
Toyota
Santro
Kia
Mercedes
BMW
(c)
How would you rate
the reliability of the car
you normally
drive?
Very
bad
Bad
Poor
Fairly
good
Good
Very
Good
(d)
State briefly why you would,
or would not buy the same
make of car again
---------------------------
---------------------------
Press
Events. --- 3 kinds.
1.
Conference.
2.
The Press Reception.
3.
The Facility visit.
How
to organize?
Plan
the reception well in advance, so that
all pros and cons
are considered ahead of
time.
·
Choose
a convenient venue. Location always
plays a vital role as easy
access will not only
improve
·
image
but will also attract
larger audience.
Send
invitations to selected named
guests in good time. (May vary).
Although the list may vary
but
·
enough
time margin should be given for dignitaries and
celebrities to plan well in
advance to attend them.
State
the time table on the invitation card. This
will let the guests know
about the plan of events.
·
Make
sure catering is good &
adequate. This helps in good
image and leaves a good
taste about the
·
whole
event.
Rehearse
& time speakers. It is important so
that the whole program runs
according to schedule.
·
Make
sure everything required is provided on time.
This will leave good
impression on the
·
audience.
23

Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
Provide
adequate press information,
but do not overload. This
will enable the press to
report
·
appropriately
and your angle will be
more or less projected.
Identify
staff from guests with
different colored badges. It is essential
for ushering and help to
the
·
guests
and also differentiate for
better service.
Get
on with business on time & stick to
timetable. It helps in swift and
quick culmination of the
·
proceedings.
Do
not mix journalists with
other guests like
customers.
·
Have
enough hosts to take care of the
guests. Ensure those guests
are properly taken care of
for
·
better
service resulting in better PR.
24
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION & BRIEF HISTORY:Definitions Of Public Relations
- HOW DOES PR WORK?:OVERVIEW, Formulation of policy
- PUBLIC RELATIONS DISTINGUISHED:Size of a PR Department.
- PUBLICS OF PR:Expanded Publics, Few Examples Of Publics
- PLANNING PUBLIC RELATIONS PROGRAMMES:Print Media, Electronic Media
- MEDIAS OF PR:Media for External Publics, Principles of Good Press Relations
- PRESS RELATIONS IN PR:What is News, Secrets Of Good News Release.
- CREATED PRIVATE MEDIA:Private Media, New Forms of House Journals
- SPECIAL USES OF PUBLIC RELATIONS:Crisis Management, Skills Of PR
- BUDGETING IN PR:Labour, Office Overheads, PR & Photographs
- PUBLIC RELATIONS PROBLEMS:Defining PR problems, C’s of PR explained
- METHODS OF COMMUNICATION:Psychology of Public Relations
- PR IN VARIOUS ORGANIZATIONS:Techniques of Trade Association PR
- PR IN LABOUR UNIONS & RELIGIOUS GROUPS:Community Public Relations
- PR IN EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS & IN MEDIA CHANNALS
- USING ADVERTISING FOR P R COMMUNICATION:Role Of PR
- ROLE OF PUBLIC RELATIONS IN MARKETING:How To Educate The Market
- PUBLIC RELATIONS AND CORPORATE STRUCTURE:Corporate Identity Essentials
- E-PR & ITS TOOLS:Immediate Points To Consider, Using Email As PR Tool
- SPONSORSHIP—AN IMPORTANT PR TOOL:PR & Communication Audit
- HOUSE JOURNALS:Possible Publics Of House Journals, Exhibitions & PR
- CRISIS MANAGEMENT IN PR:Plan Of Action Adopted, Interview at your place
- ADVERTISING IN PR:Broad Objectives Of Advertising, Direct Advertising.
- INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC RELATIONS:Media Used, Within Store Contacts
- PUBLIC RELATIONS CONSULTANCY:Disadvantages, Mass Communication
- PUBLIC RELATION’S ROLE IN MARKET EDUCATION:Kinds Of Markets
- MODERN DAY VALUES OF PR:Ethics Of Public Relations
- CHOICE OF MEDIA FOR PR COMPAIGN:Communication Channels & Media
- PR TECHNIQUES:Tactics & Techniques
- DESIGNING PR COMPAIGNS:Definitive Mission statement, Reputation.
- PUBLIC OPINION:Identifying Priority Publics, If Goal Is Attitude Change
- PUBLIC RELATIONS AND RESEARCH:Planning Phase Of Research
- PR AND RESEARCH:Unobtrusive Measures, Questionnaires For Survey
- PROBLEMS SOLVING STRATEGIES:Communicate results
- PERSUASION & COMMUNICATION THEORIES:Message Orientation
- COMMUNICATION CONCEPTS & THEORIES:Research and Persuasion
- PUBLIC RELATIONS & LAW:How To Stay Out Of Trouble
- PUBLIC RELATIONS & CASE STUDIES:Case Analysis, Images Of Public Relations
- PR AND PRINTING PROCESSES:Fundamentals Of Printing
- PUBLIC SPEAKING -- A PR TOOL:Key Benefits, How To Prepare
- PR -- COPING WITH UNEXPECTED:Some Possible PR Ideas
- DREAMS & REALITIES OF PR:Who Takes Charge Of Identity?
- CHANGING INTO OVERDRIVE:How International Is PR?
- GETTING ON WITH PR:Where does PR fit in the structure?
- FUNDAMENTALS OF A SUCCESSFUL NEWSLETTER:RESEARCH, WRITING